- Sugarcane belongs to the family Gramineae and its scientific name is Saccharum officinarum.
- Highest sugar-producing the state of India.
- Sugarcane is the main source of sugar in India and holds prominent position as a cash crop.
- India has the largest area under sugarcane in the world and also ranks first in sugar production.
TEMPRATURE : 20-26 DEGREE
SOIL : LOAMY SOIL
pH : 6.5 - 7.5
RAINFALL : 150 cm
DURATION ; 12-14 months
SOIL TREATMENT:
Use Bhoomi power, Powerplant Premium, and a precautionary Root guard to treat your soil by giving it complete nutrition.
|
BHOOMI POWER 4KG/ACRE |
 |
|
POWER PLANT PREMIUM 1 LITRE/ ACRE |
 |
|
ROOT GUARD 2 KG/ACRE |
 |
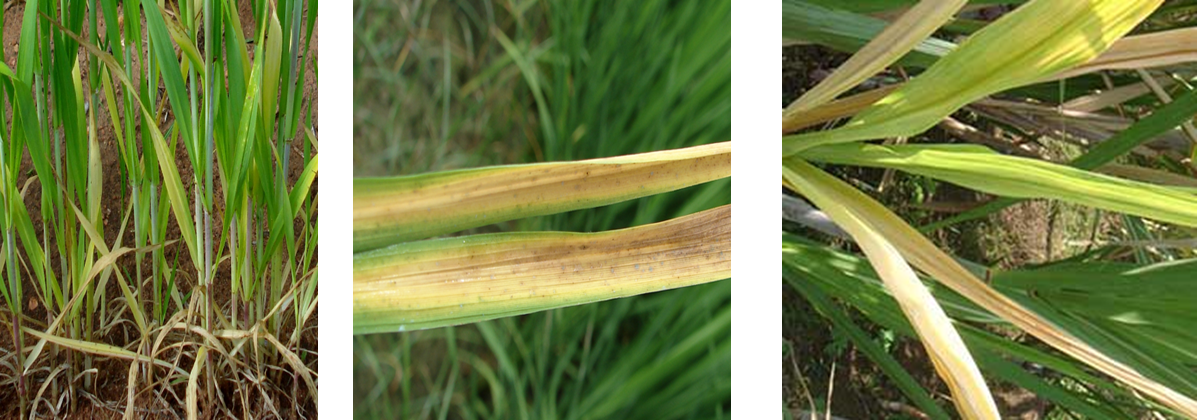
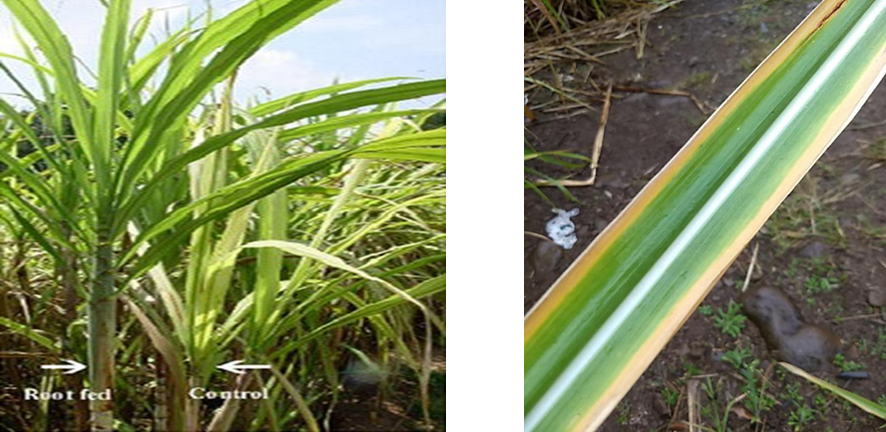
1. DEFICIENCY OF NITROGEN
´Leaves are small , uniformly light green or yellowish.
TREATMENT
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
2. DEFICIENCY OF PHOSPHOROUS
´Narrow and somewhat reduce in length.
TREATMENT
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
3. DEFICIENCY OF SULFUR.
TREATMENT
|
Use Ferric EDTA 0.5-01 gm per litre of water |
.png) |
|
Use Grow 2 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
1. FUNGAL DISEASE:
A. CONTACT-BASED FUNGAL DISEASE
1. ANTHRACANOSE ( Discula destructive)
TREATMENT
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
2. LEAF SCALE DISEASE (Melanaspis glomerata)
TREATMENT
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
3. SMUT (Sporisorium scitamineum)
TREATMENT
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
B. SYSTEMIC BASED
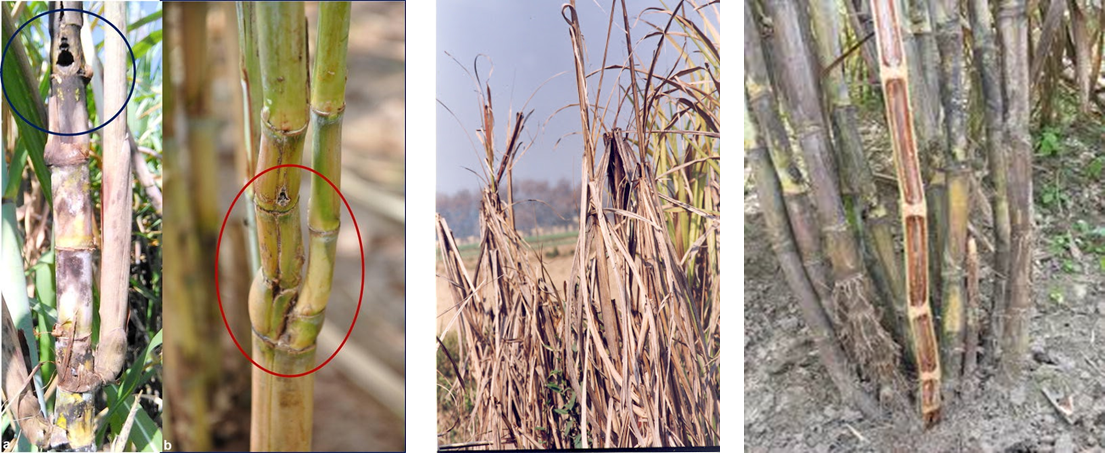
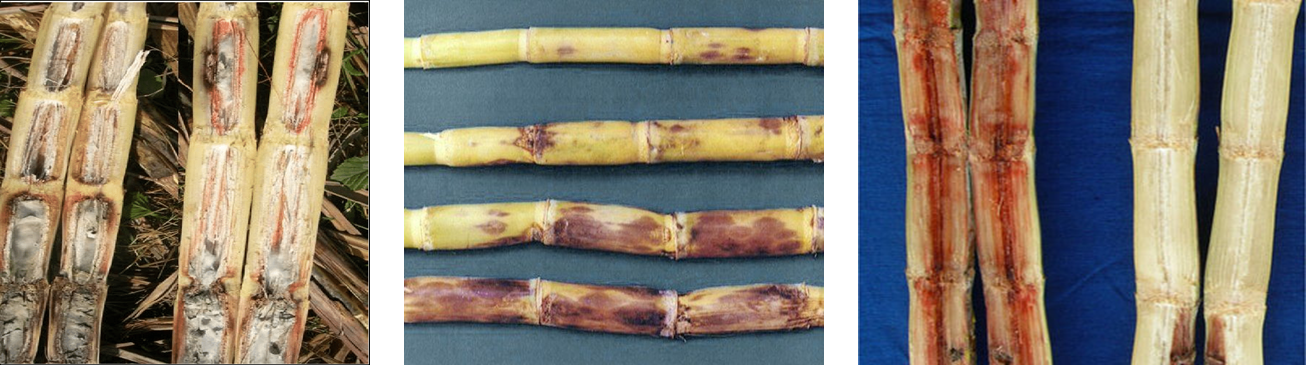
1. RED ROT (Colletotrichum falcatum)
TREATMENT
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
2.FUSARIUM WILT (Fusarium sacchari)
TREATMENT
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
3. DAMPING OFF (Botrytis cinerea)
TREATMENT
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
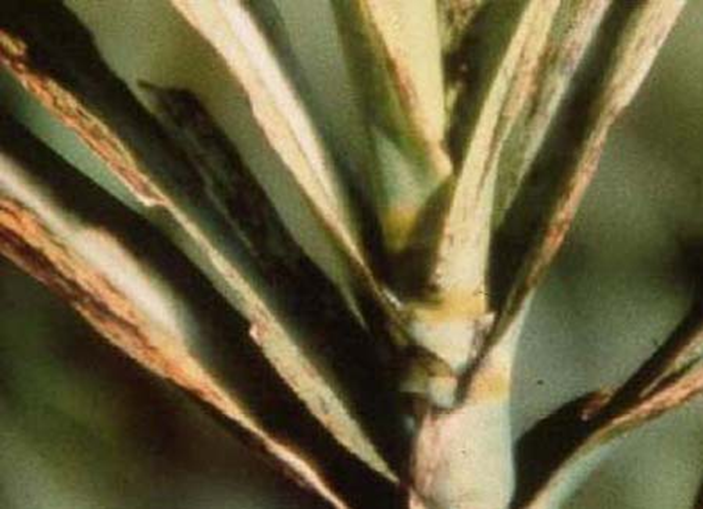
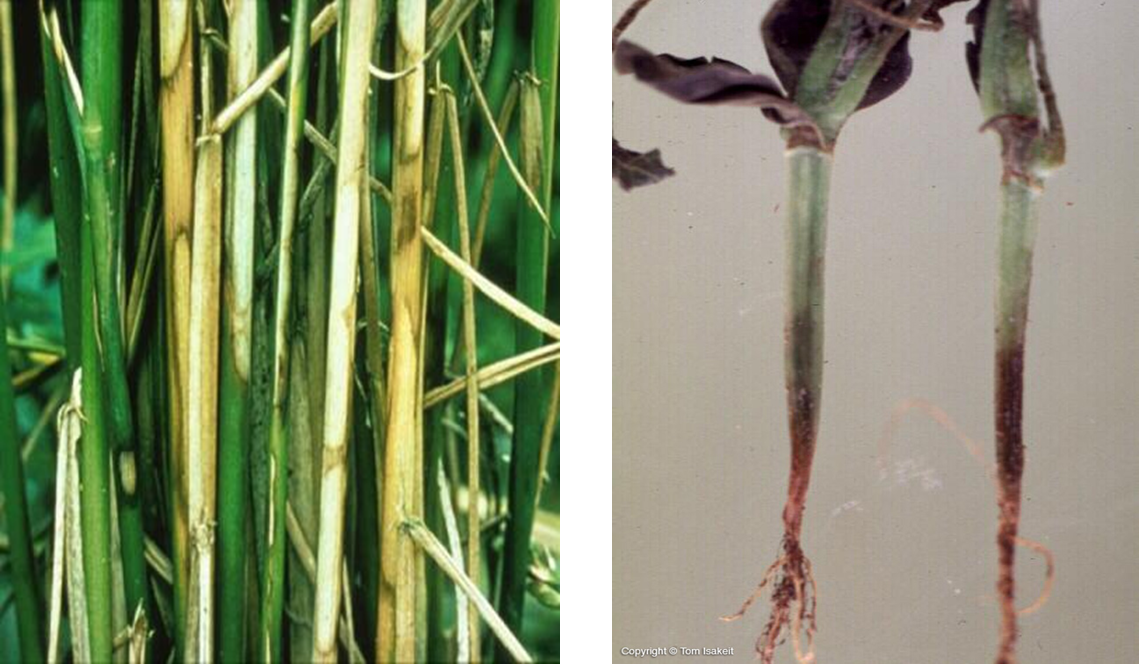
2. VIRUS ATTACK
1. SUGERCANE MOSAIC VIRUS
2. SUGERCANE YELLOW LEAF VIRUS
3. GRASSY SHOOT (Phytoplasma)
TREATMENT
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
3. PEST MANAGEMENT
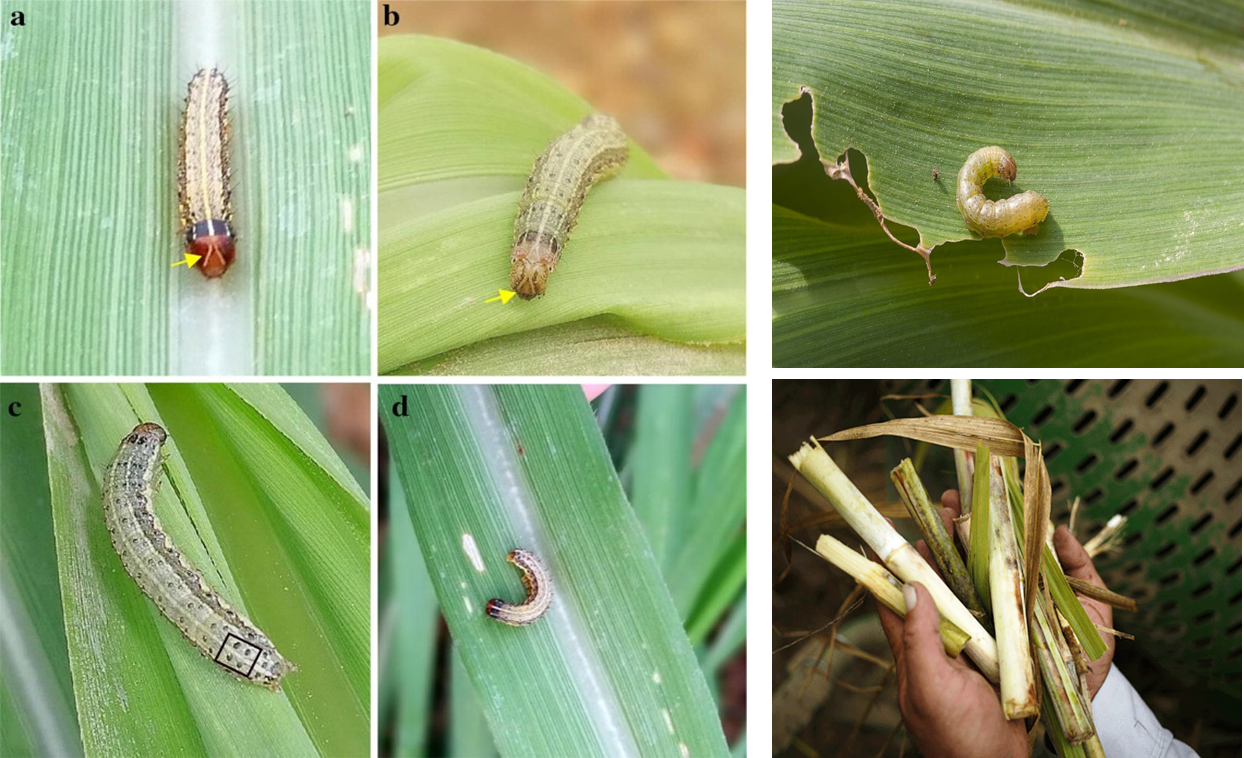
A. CHEWING PEST
1. EARLY SHOOT BORER (Crambus pascuella)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
2. WHITEGRUB (Holotrichia serrata)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
3. ARMYWORM (Spodoptera frugiperda)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
4. BILLBUG (Sphenophorus venatus vestitus)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
B. SUCKING PEST
1. WHITEFLY (Aleyrodidae)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
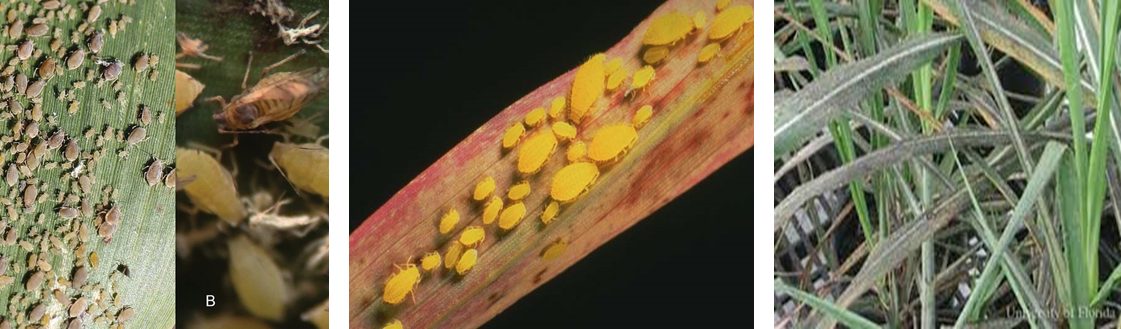
2. THRIP (Thysanoptera)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
3. APHID (Aphidoidea)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
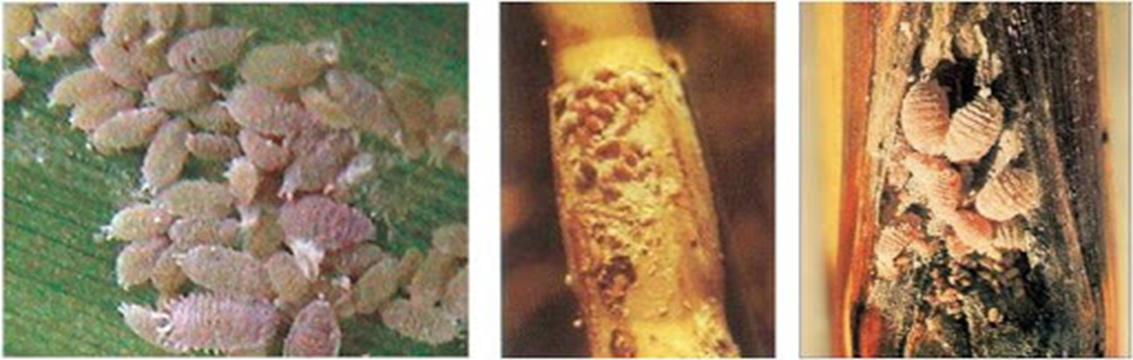
4. MEALYBUG (Pseudococcidae)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |