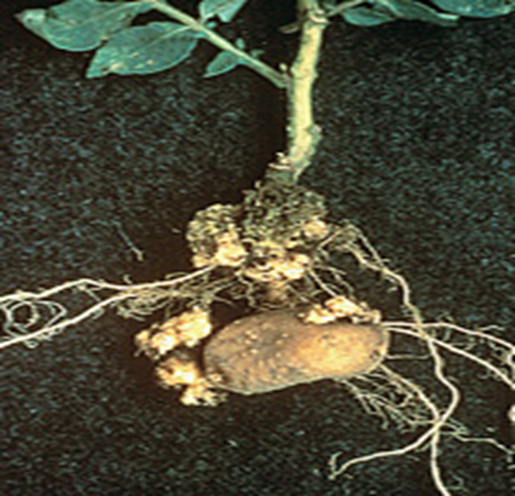
• Soil - Potato can be grown on all types of soil except saline and alkaline soil.
• Temperature - 24?
• pH - 4.8 to 5.8
• Rainfall - Potato is mostly grown as a rainfed crop in regions receiving a rainfall of 1200 – 2000 mm per annum.
Soil
FOR IRRIGATION :
Irrigate your field with Power Plant Bhoomi power, Premium, and Root guard.
|
BHOOMI POWER 4KG/ACRE |
 |
|
POWER PLANT PREMIUM 1 LITRE/ ACRE |
 |
|
ROOT GUARD 2 KG/ACRE |
 |
HOW TO USE IT?
Use Bhoomi power by following methods.
1. By broadcasting over the field.
2. Use in slurry.
3. Give it in cow dung.
4. you can also give it in dry soil.
Note: Repeat Bhoomi power and Root guard every 3 months.
In Plains:
In Hills:
PRODUCT RECOMMENDED:
Treat the bulbs of the banana plants with Power Plant Seed Treatment.
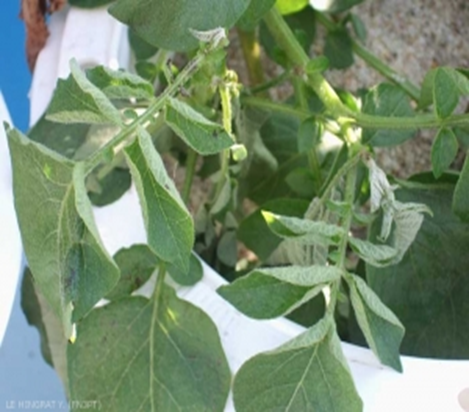
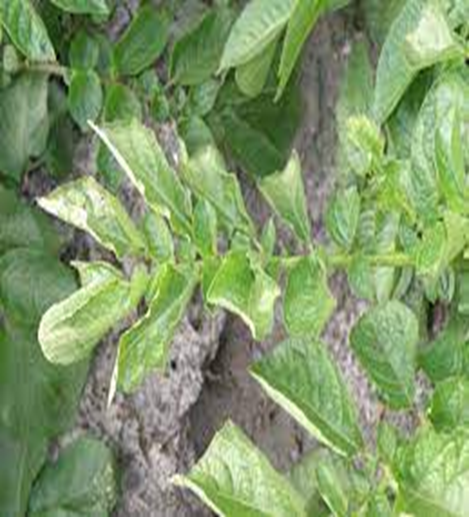
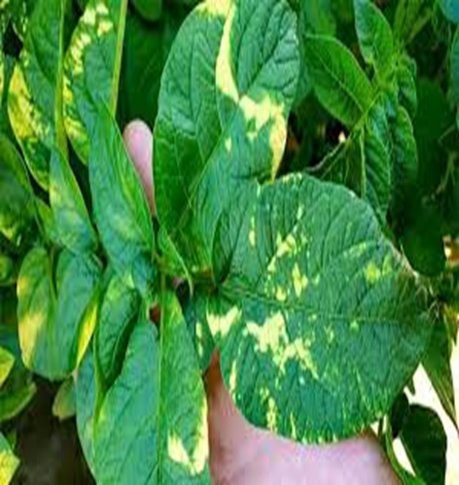
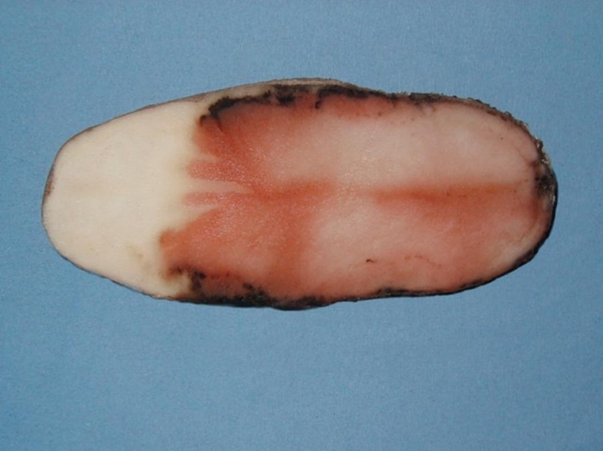
DEFICIENCY OF NITROGEN
´The yellowing in nitrogen deficiency is uniform over the entire leaf including the veins.
TREATMENT :
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use Grow 2 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5ml per litre of water |
 |
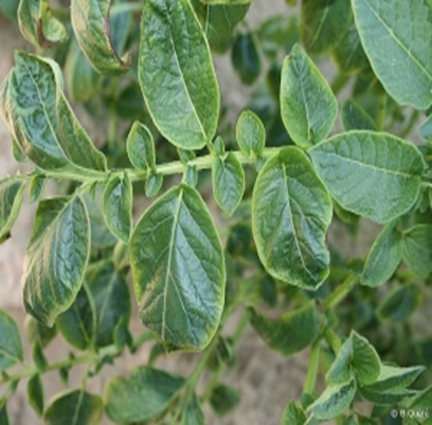
TREATMENT :
|
Use Manganese EDTA 0.5 gm per litre of water |
.png) |
|
Use Grow 2 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
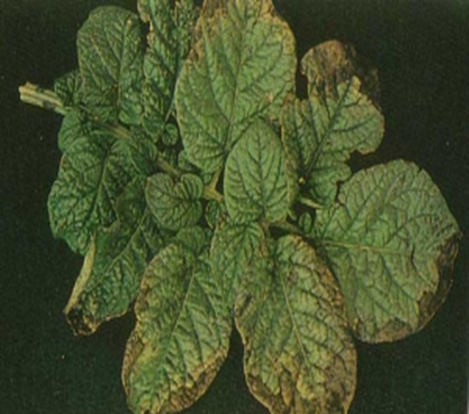
TREATMENT :
Use Ferric EDTA
0.5-01 gm per litre
of water
Use NITROKING
2-3 ml per litre
of water
Use SPALL90
0.5 ml per litre
of water
TREATMENT :
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use BLOOM 2 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5ml per litre of water |
 |
TREATMENT :
|
Use Zinc EDTA 0.5-01 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
TREATMENT :
|
Use Calcium EDTA 0.5-01 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
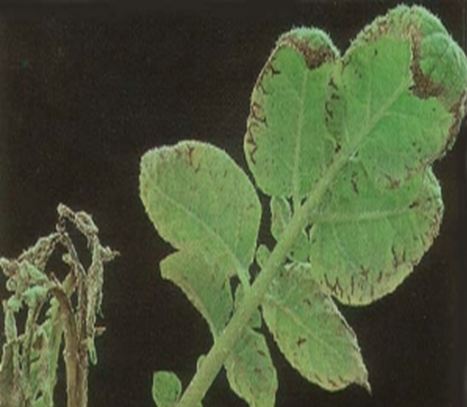
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (i) CONTACT BASED
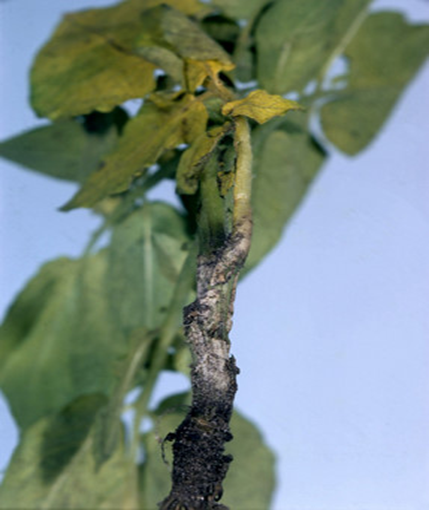
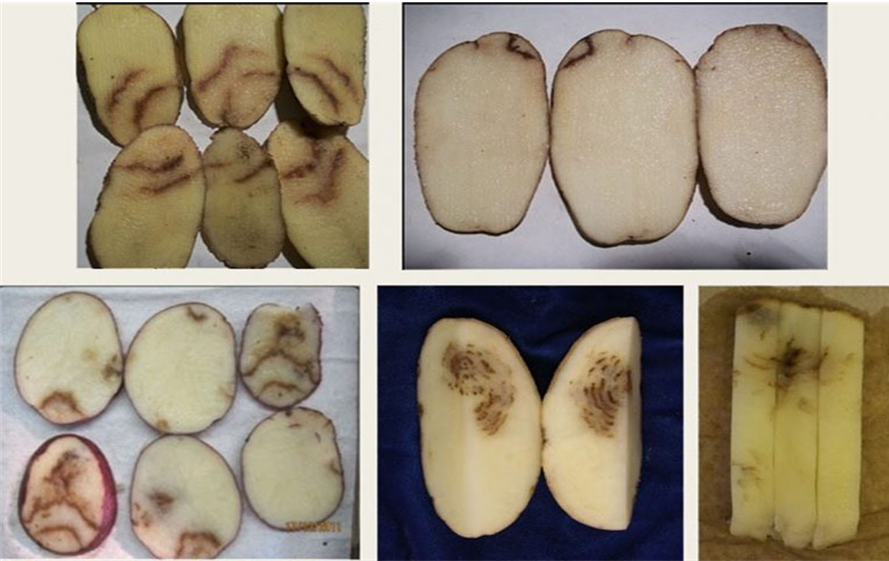
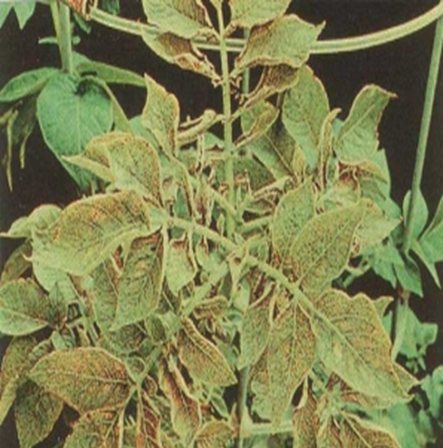
1. LATE BLIGHT (Phytophthora infestans)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (i) CONTACT BASED
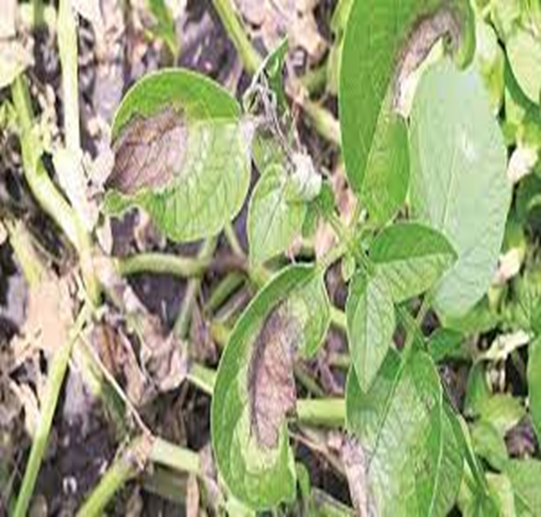
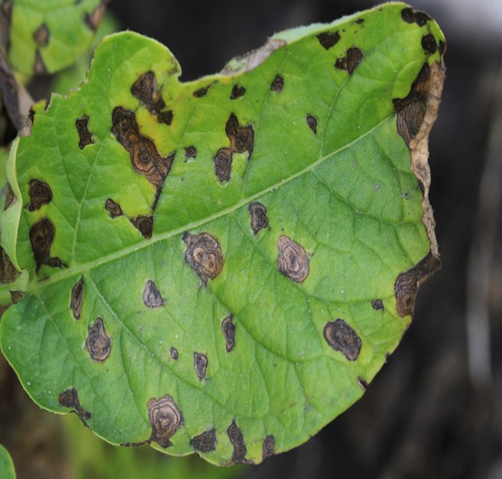
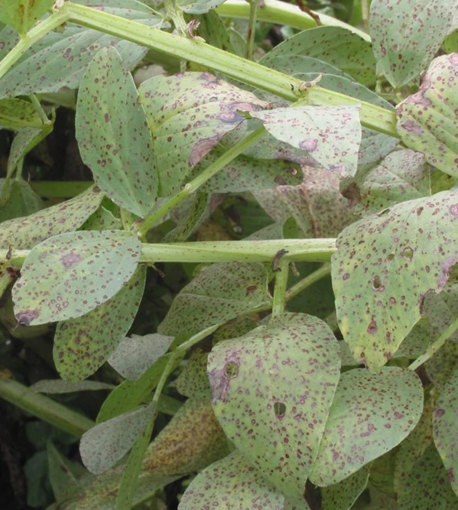
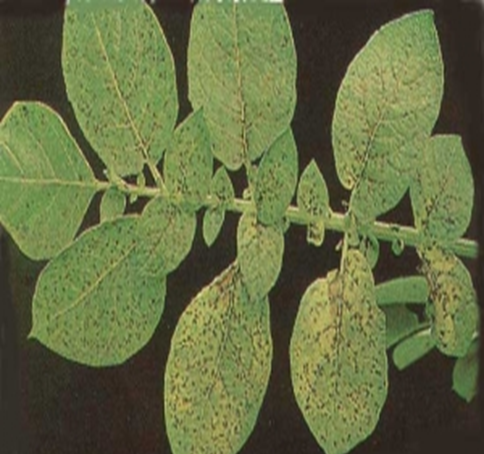
2. EARLY BLIGHT OR ALTERNARIA (Alternaria solani)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (i) CONTACT BASED
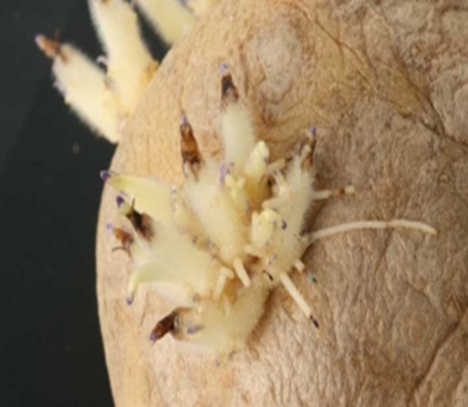
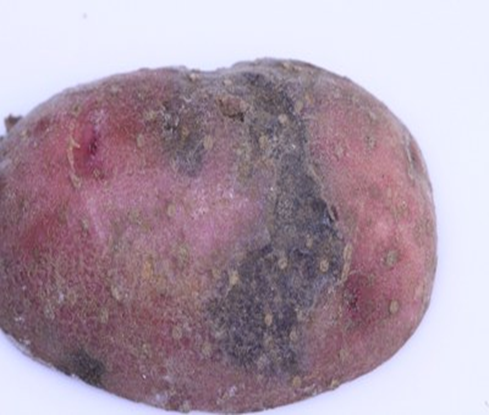
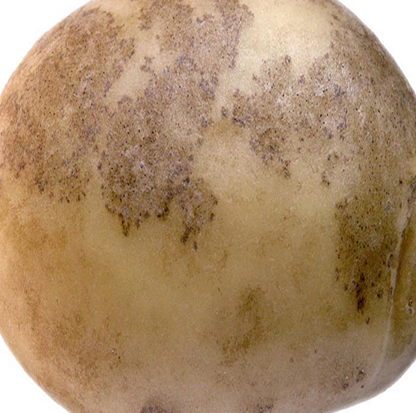
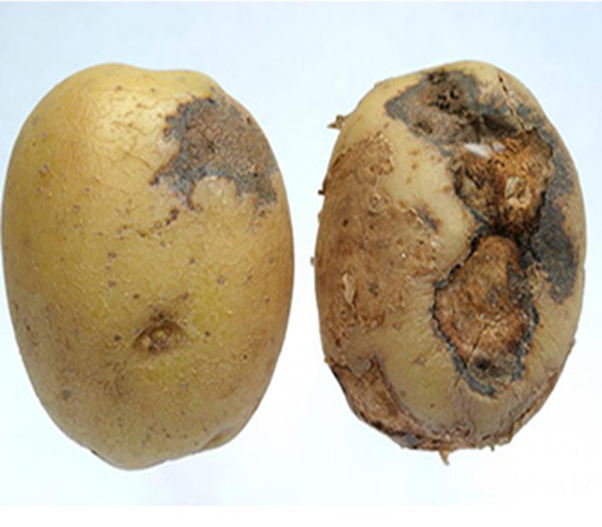
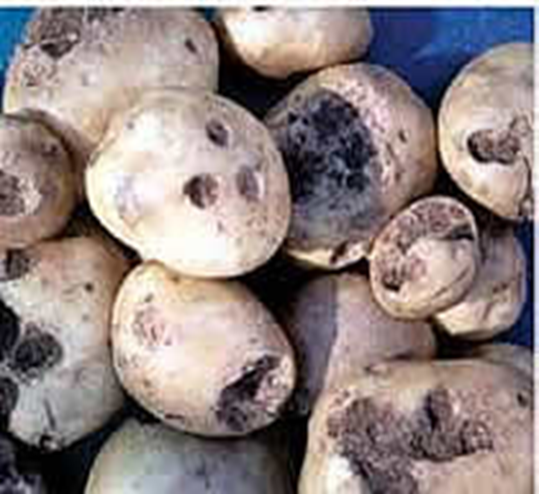
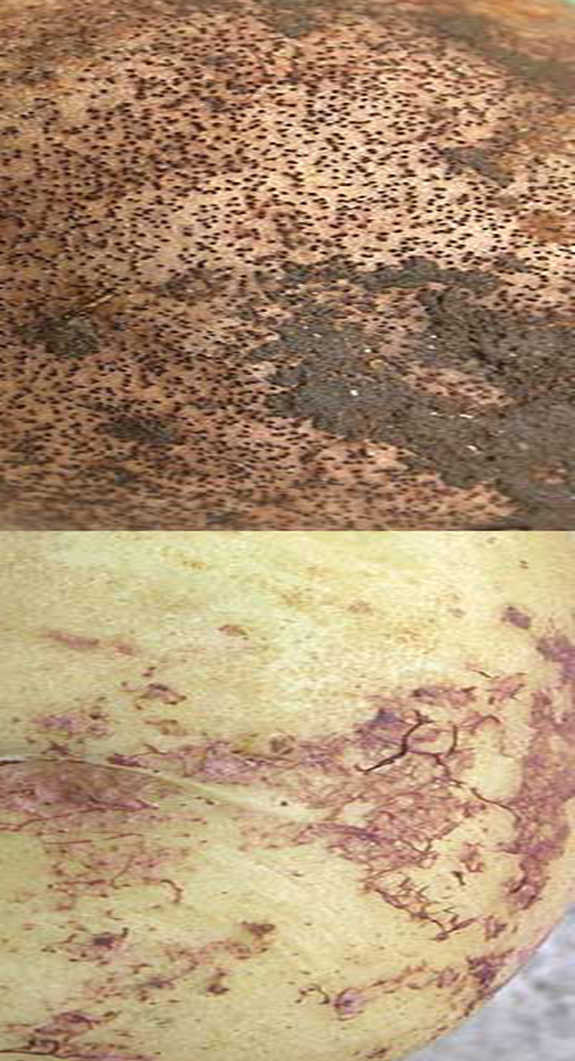
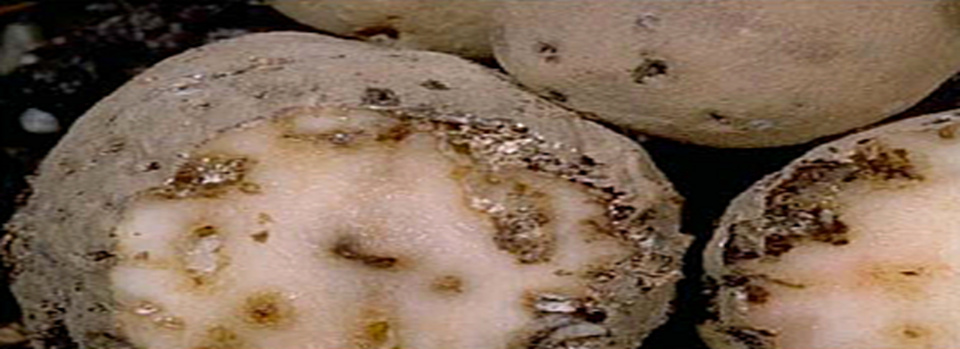
3. BLACK SCARF & RHIZACTONIA CANKER
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (i) CONTACT BASED
4. BLACK DOT(Colletotrichum coccodes)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (ii) CONTACT BASED
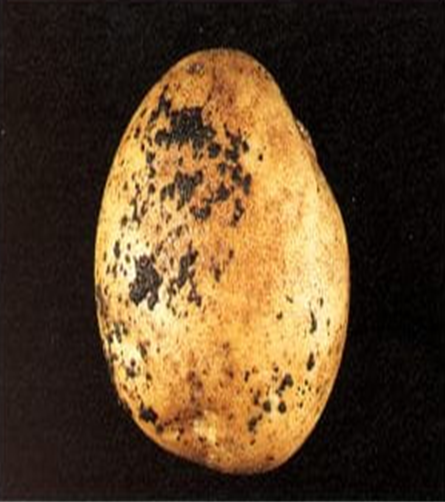
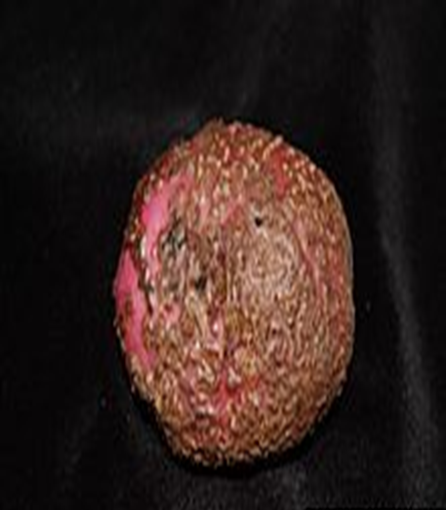
5. POWDERY SCAB(Spongospora subterranean)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (ii) CONTACT BASED
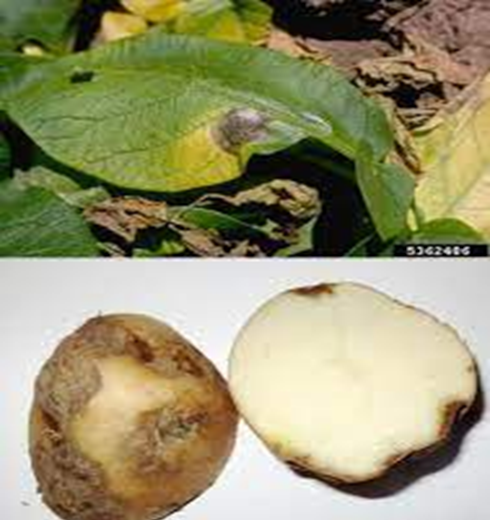
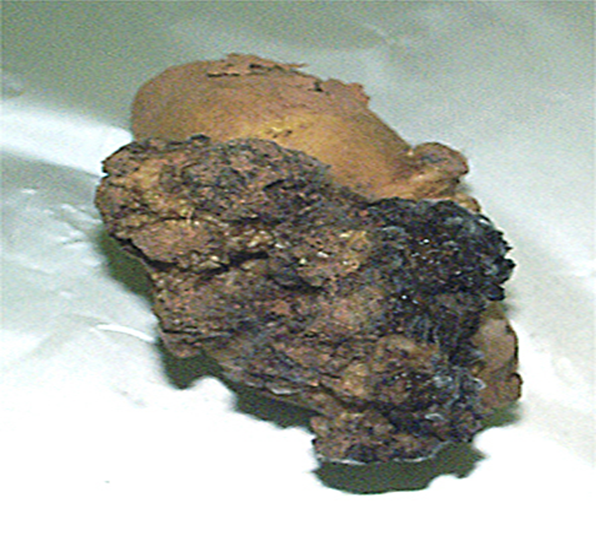
6. DRY ROT ( Fusarium spp.)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (ii) SYSTEMIC BASED
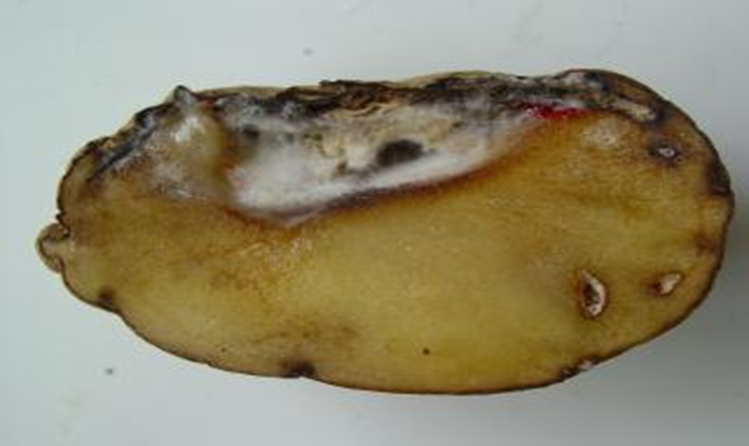
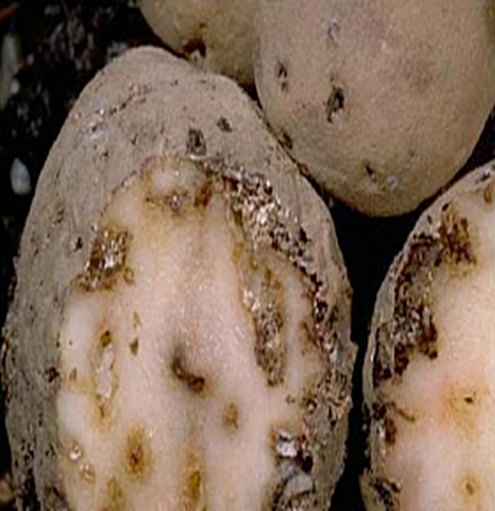
1. PINK ROT (Phytopthora erythroseptica)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (ii) SYSTEMIC BASED
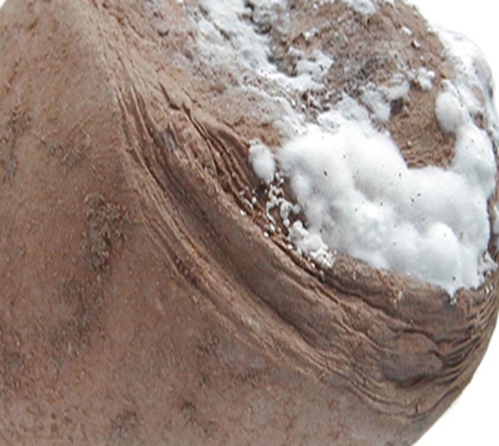
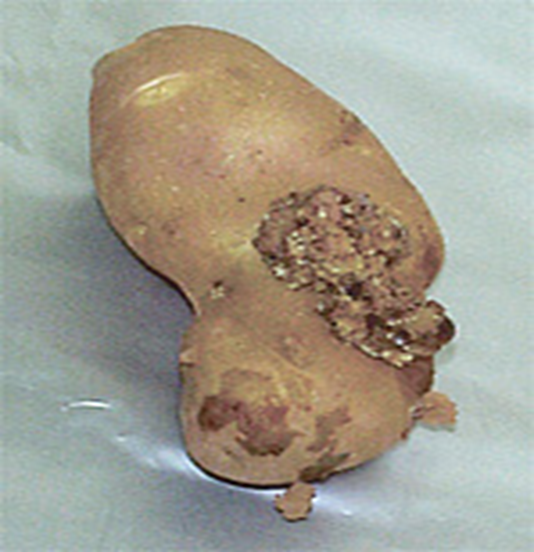
2. POTATO WART(Synchytrium endobioticum)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (ii) SYSTEMIC BASED
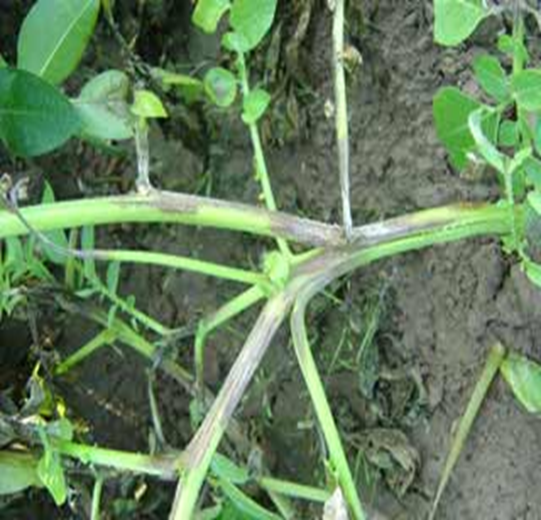
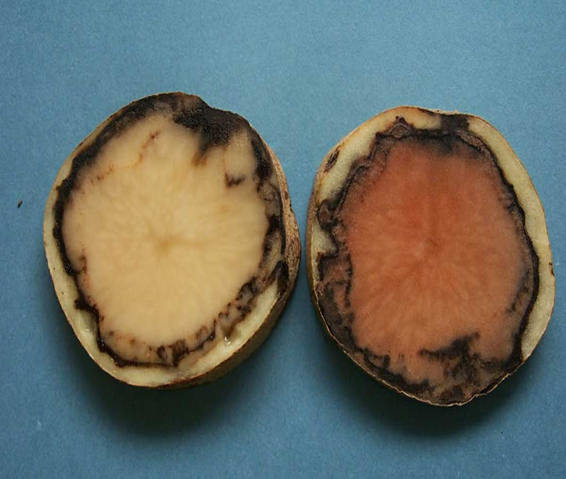
3. VIOLET ROOT ROT(Rhizoctonia crocorum)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
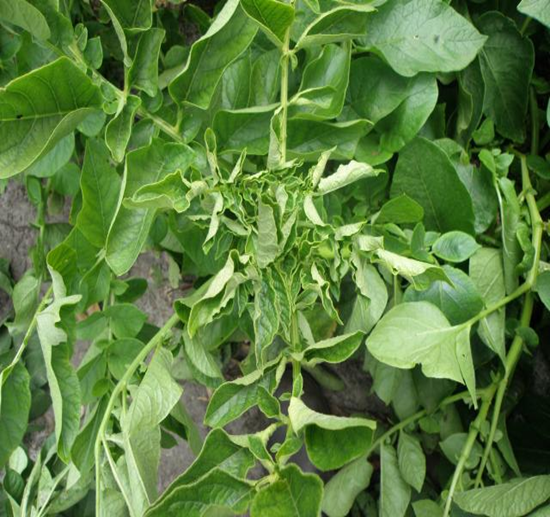
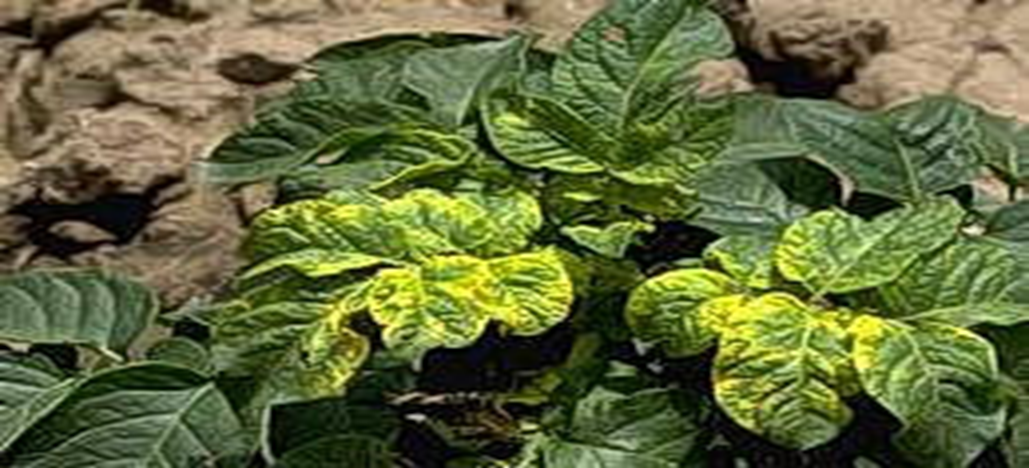
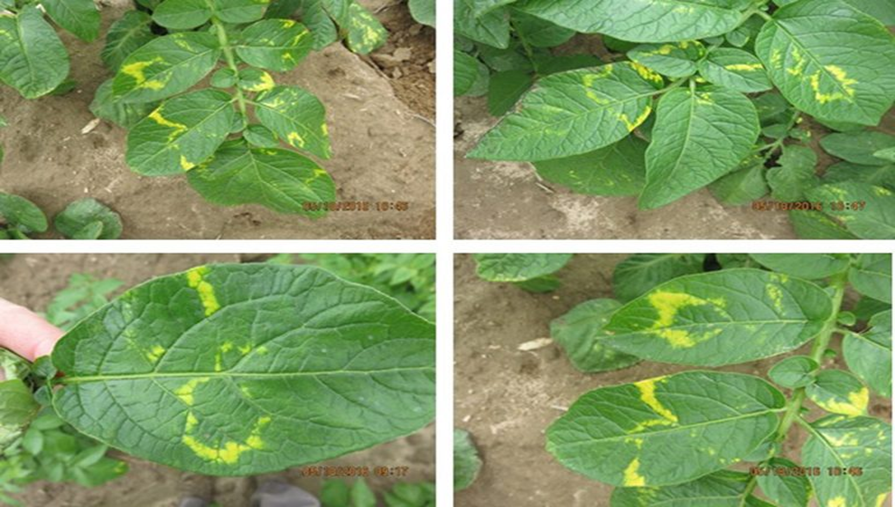
B. VIRUS ATTACK
1. POTATO LEAF ROLL(Potato leafroll virus (PLRV)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
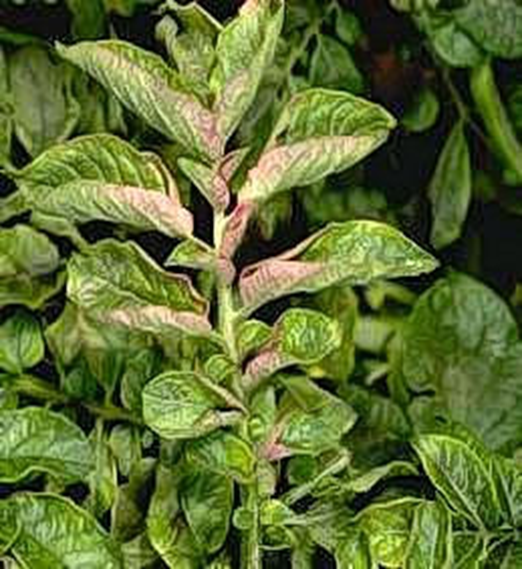
B. VIRUS ATTACK
2. POTATO VIRUS A
TREATMENT :
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
B. VIRUS ATTACK
3. POTATO VIRUS X
TREATMENT :
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
B. VIRUS ATTACK
4. POTATO MOSAIC VIRUS
TREATMENT :
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
B. VIRUS ATTACK
5. POTATO MOP TOP VIRUS
TREATMENT :
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PEST:(i) CHEWING PESTS
1. BLACK CUTWORM (Agrotis ipsilon)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PEST:(i) CHEWING PESTS
2. POTATO TUBER MOTH(Phthorimaea operculella)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PEST:(i) CHEWING PESTS
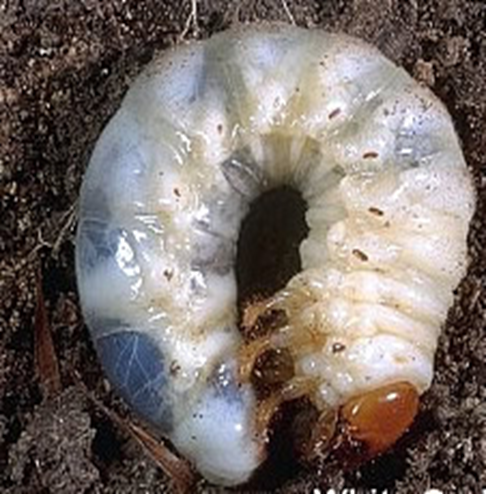
3. WHITE GRUB (Holotrichia sp.)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
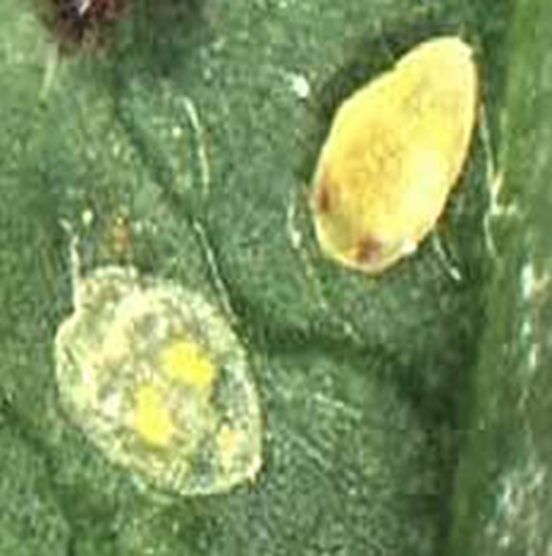
C. PEST:(ii) SUCKING PESTS
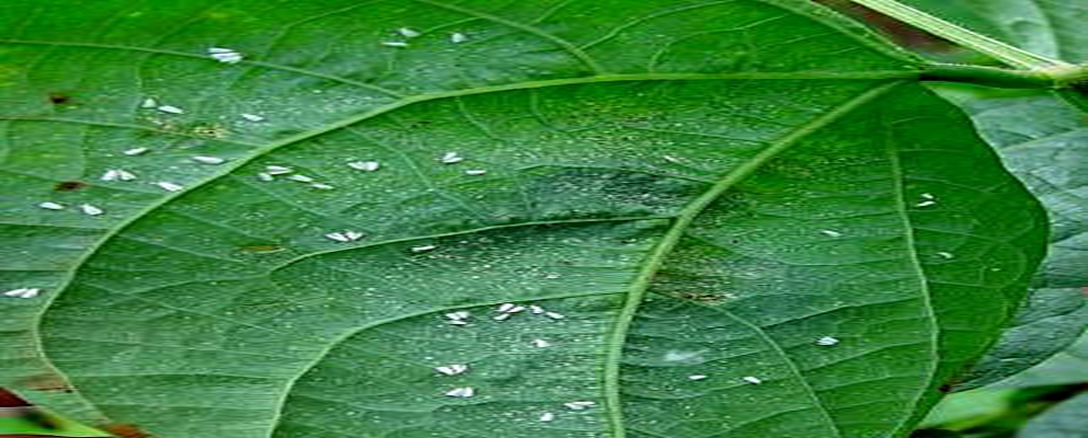
1. WHITEFLY (Bemisia sp.)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
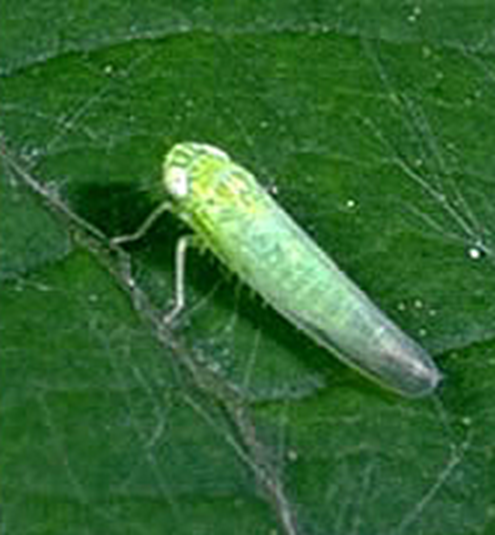
C. PEST:(ii) SUCKING PESTS
GREEN LEAF HOPPER (Empoasca kerri)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
















.png)