- Soil- Sandy loam to clayey loam.
- Temperature- 25°C–30°C
- pH- 6.5 – 7.0
- Rainfall- 750mm
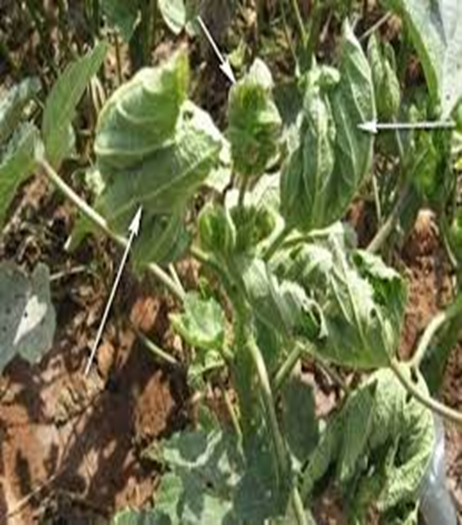
- Susceptibility- Plant Viruses
- A pre-soaking irrigation 3-4 days before sowing is beneficial.
- Irrigation is done at weekly intervals.
- Keep the plants well watered throughout the summer months; 1 inch of water per week is ideal, but use more if you are in a hot,arid region.
FOR IRRIGATION :
Irrigate your field with Power Plant Bhoomi power, Premium, and Root guard.
|
BHOOMI POWER 4KG/ACRE |
 |
|
POWER PLANT PREMIUM 1 LITRE/ ACRE |
 |
|
ROOT GUARD 2 KG/ACRE |
 |
HOW TO USE IT?
Use Bhoomi power by following methods.
1. By broadcasting over the field.
2. Use in slurry.
3. Give it in cow dung.
4. you can also give it in dry soil.
Note: Repeat Bhoomi power and Root guard every 3 months.
- Sow three seeds per hill at 30 cm apart and then thin to 2 plants per hill after 10 days.
- Seeds are sown at a spacing of 45 x 30 cm.
- Hybrid varieties should be planted at a spacing of 60 x 45 cm.
- The seeds germinate in about 4-5 days.
PRODUCT RECOMMENDED:
Treat the bulbs of the banana plants with Power Plant Seed Treatment.
TREATMENT :
|
Use Ferric EDTA 0.5-1 gm per litre of water. |
.png) |
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water. |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water. |
 |
TREATMENT :
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use Grow 2 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
TREATMENT :
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use BLOOM 2 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
TREATMENT :
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use BLOOM 2 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES:(i) CONTACT BASED
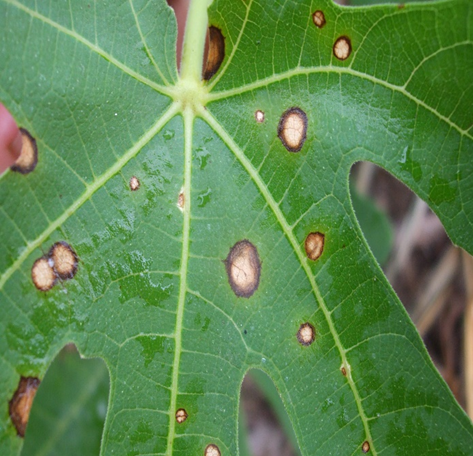
1. ANTHRACNOSE (Colletotrichum spp.)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
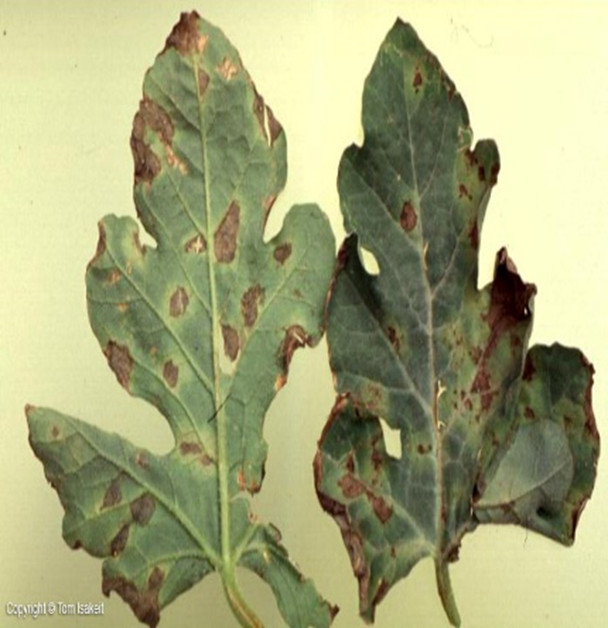
A. FUNGAL DISEASES:(i) CONTACT BASED
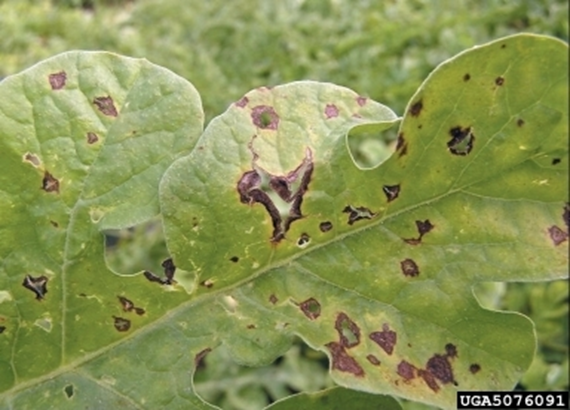
3.CERCOSPORA LEAF SPOT(Cercospora malayensis and Cercospora abelmoschi)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
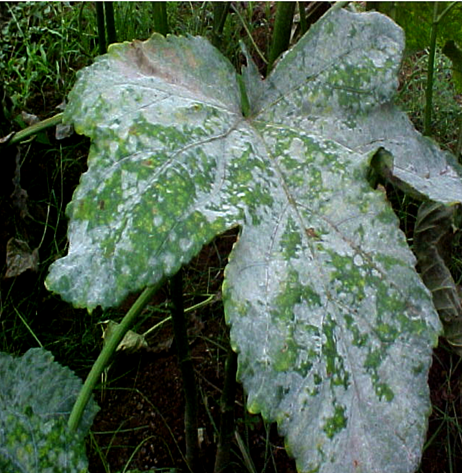
A. FUNGAL DISEASES:(i) CONTACT BASED
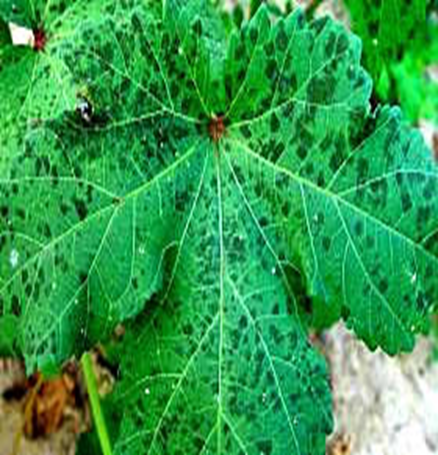
4. POWDERY MILDEW (Erysiphe cichoracearum)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES:(i) CONTACT BASED
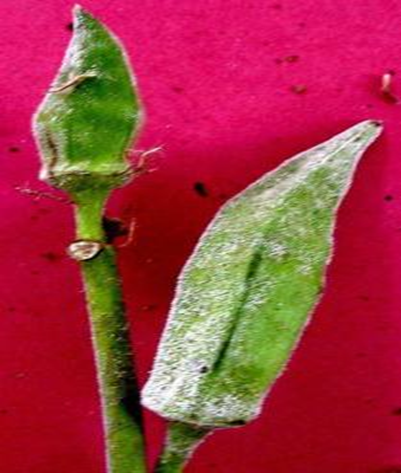
5. DOWNY MILDEW
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES:(ii) SYSTEMIC BASED
1. CHARCOAL ROT (Macrophomina phaseolina)
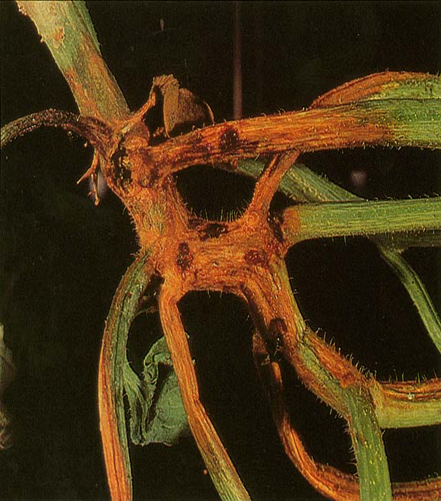
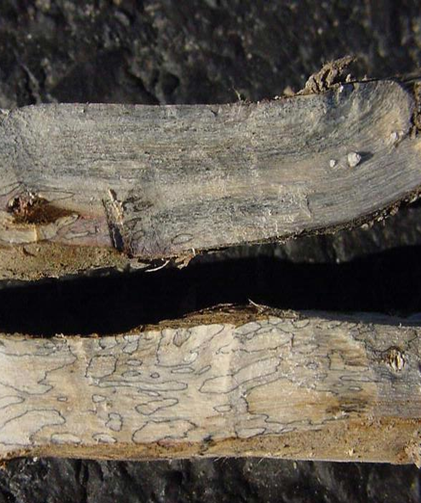


TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES:(ii) SYSTEMIC BASED
2.FUSARIUM WILT (Fusarium oxysporum)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
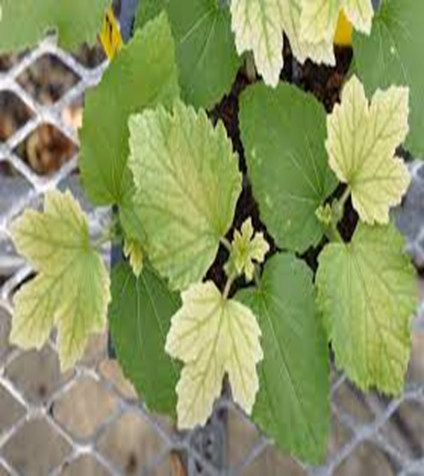
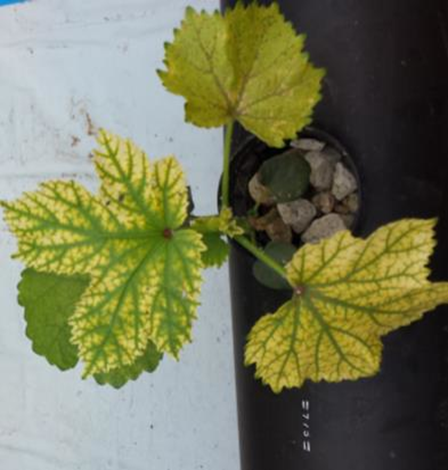
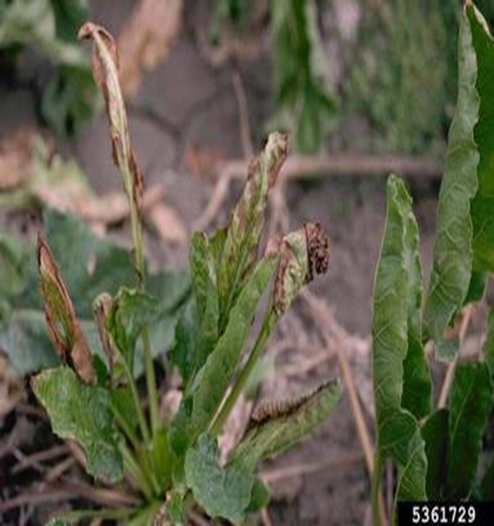
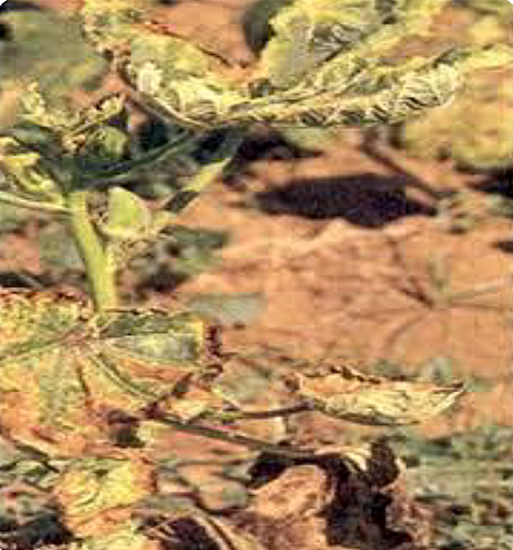
B. VIRAL DISEASES
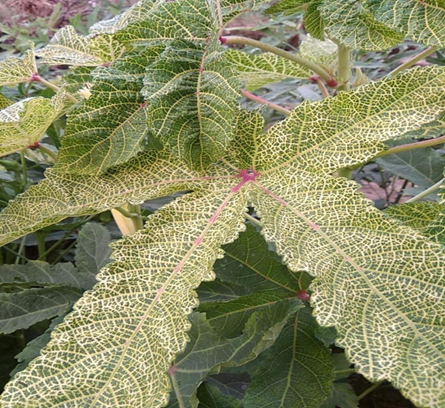
1. YELLOW VEIN MOSAIC VIRUS
TREATMENT :
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
B. VIRAL DISEASES
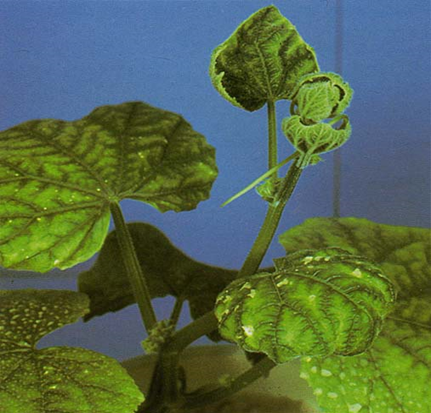
2. LEAF CURL VIRUS
TREATMENT :
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
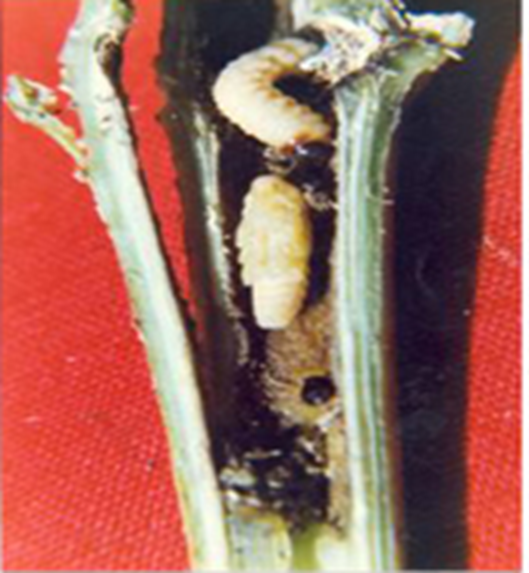
C. PESTS:(i)CHEWING PESTS
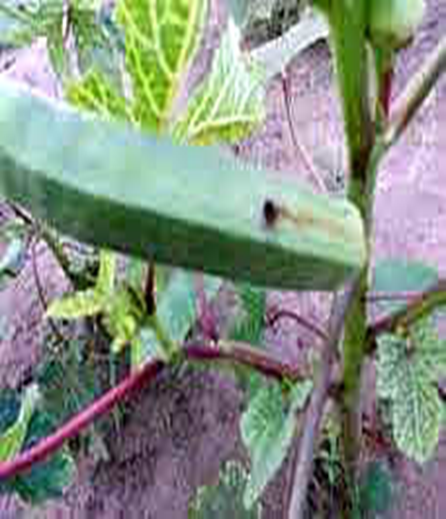
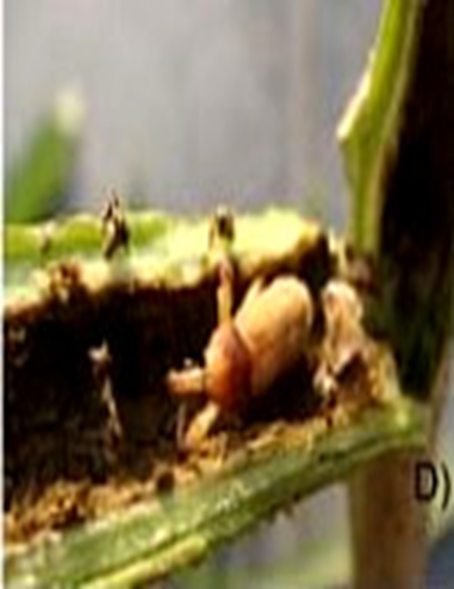
1.SHOOT BORER (Earias vitella)
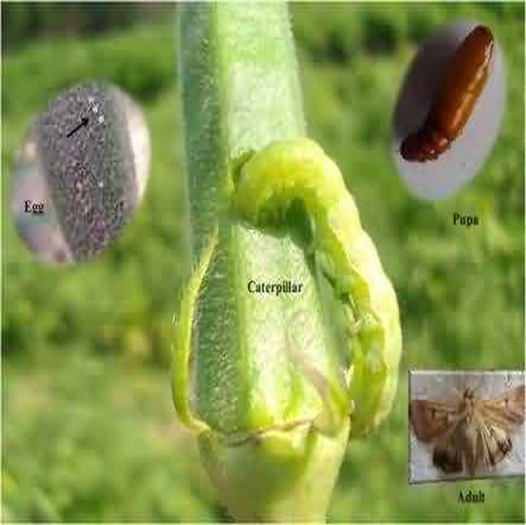
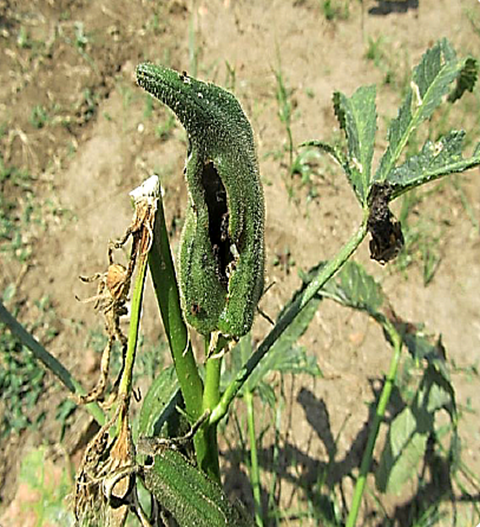


TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PESTS:(i)CHEWING PESTS
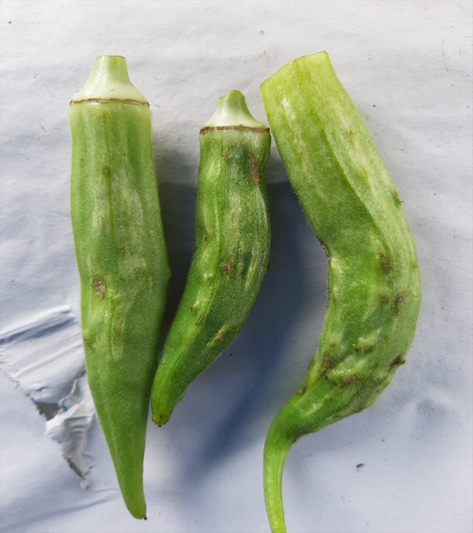
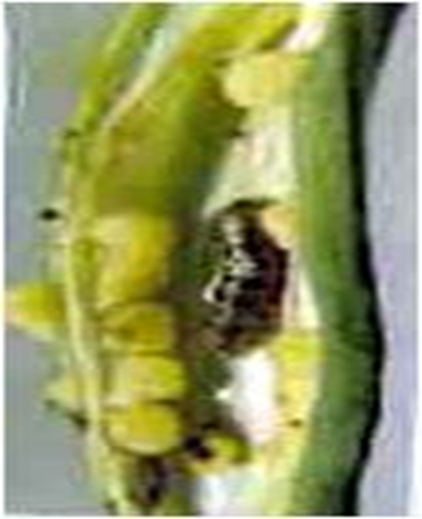
2.BHENDI FRUIT BORER (Helicoverpa armigera)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PESTS:(i)CHEWING PESTS
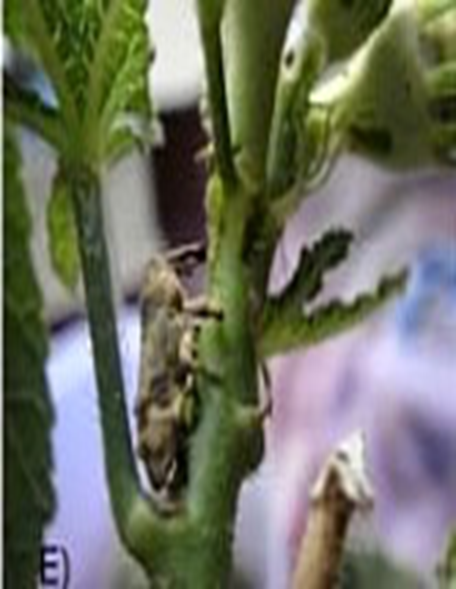
3.SHOOT WEEVIL (Alcidodes affaber)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PESTS:(i)CHEWING PESTS
4.STEM WEEVIL (Pempherulus affinis)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PESTS:(i)CHEWING PESTS
5. SEMILOOPER (Anomis flava)
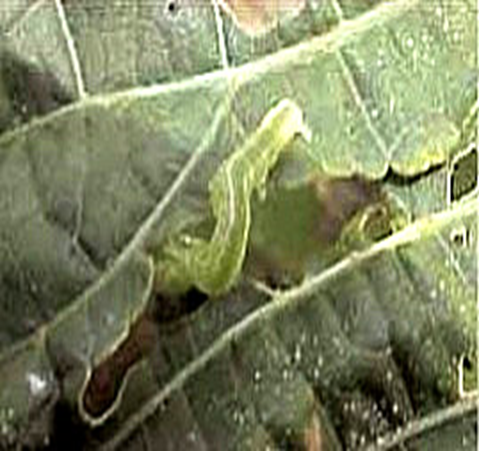
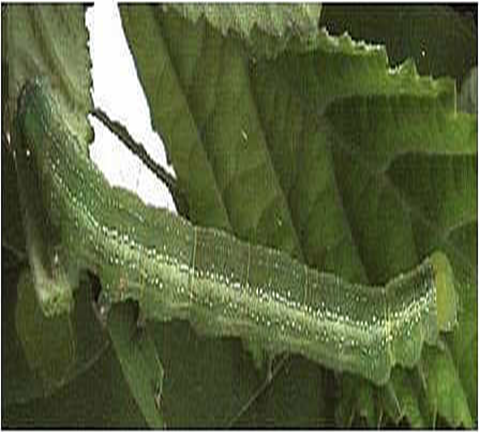


TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
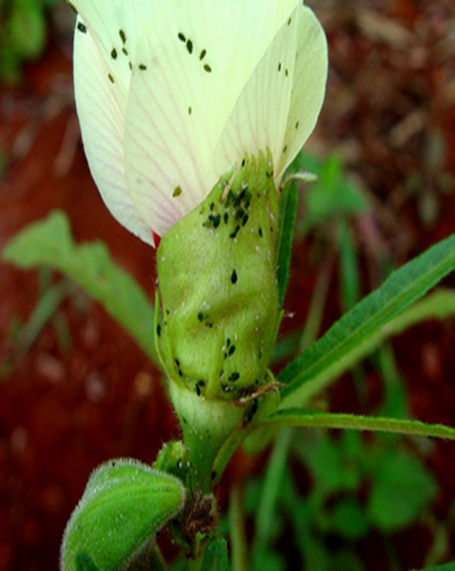
C. PESTS :(ii) SUCKING PESTS
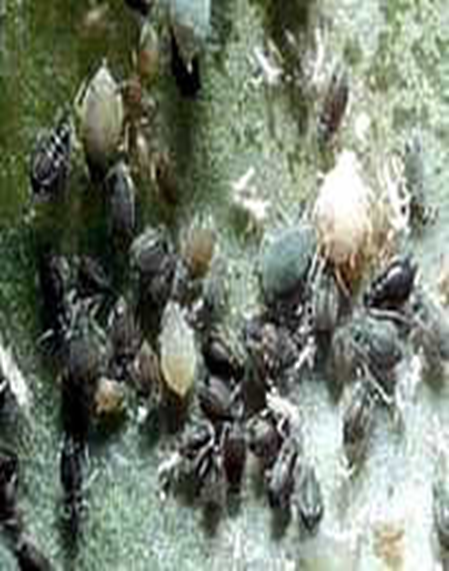
1. APHID (Aphis gossypii)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
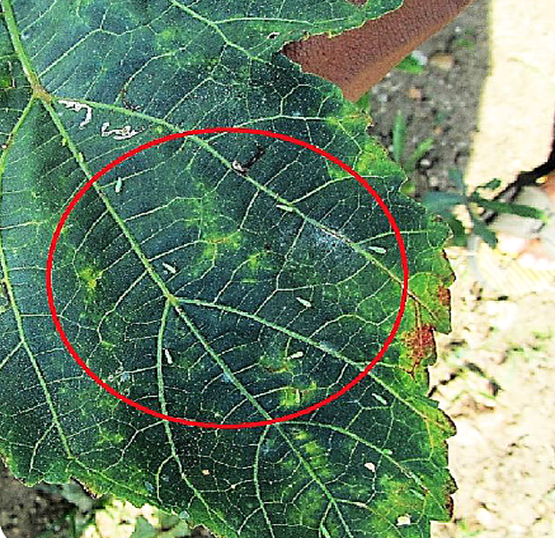
C.PESTS : (ii) SUCKINGPESTS
2. JASSID (Amrasca devastans)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |