- Arachis hypogaea are the scientific name for groundnut, which belongs to the Fabaceae family.
- Groundnut is a valuable crop that can be grown as a floor crop in a coconut garden as a catch crop after the second crop paddy is irrigated.
- Stones and clay should not be present in groundnut farming soil, as this would reduce yield.
- Groundnut farming is not ideal for high altitudes, cold, or frost.
- Groundnuts thrive in climates with long periods of warm weather.
• Soil- Sandy loam or clay loam soil.
• Cultivation- Preparatory cultivation.
• pH- 6.0- 6.5
• Temperature- Vegetative growth=26 to 30 ºC depending on the cultivar, Reproduction growth=24-27 ºC.
• Rainfall- Annual rainfall between 450 to 1250 mm.
- Irrigation schedules for summer groundnut have revealed that 11-12 irrigations are ideal.
- After sowing, one irrigation at 0-10 days, one at 10-30 days, two at 30-50 days, three at 50-80 days, one at 80-90 days, two at 90-105 days, and one at 105-120 days has been determined to be the most effective.
- Groundnut is drought-resilient in terms of life, but its pod output is greatly reduced if appropriate soil moisture is not maintained, especially during critical growth stages (flowering, pegging of pod development)
- The potential evapotranspiration during the crop period, as well as the degree of soil cover, dictate the amount of water consumed by the crop.
- The amount of water required peaks during flowering and continues until pod development.
- The seeds are placed in the soil at a depth of 5-6 cm and lightly pressed to maintain the moisture in place for uniform and quick germination.
- The soil temperature for sowing should be around 18ºC.
- Under rain-fed conditions, the best row and plant spacing is 90 cm and 4-7 cm, respectively.
- If the area is reliant on irrigation, the spacing between rows should be 30 to 35 cm.
- In order to plant one hectare of land, 100 to 160 kg of seeds are necessary.
- Seeds are used to propagate groundnuts. Only two weeks before planting, the seeds should be shelled.
- Groundnut seeds are grown in a nursery before being transplanted to the main field, or they are sown directly in the main field.
- Because the seeds are easily damaged, they must be handled with care.
- Seeds that have been exposed to the sun for an extended period of time are also thought to have a low germination rate.
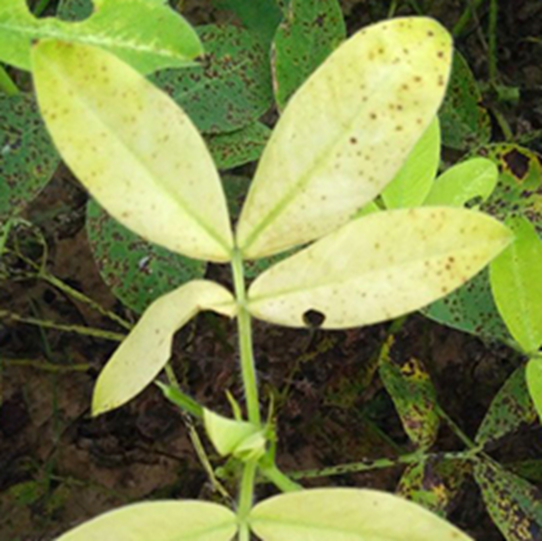
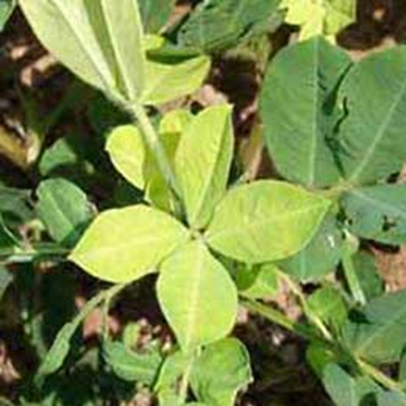
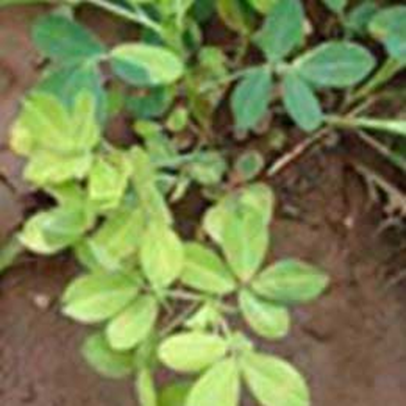
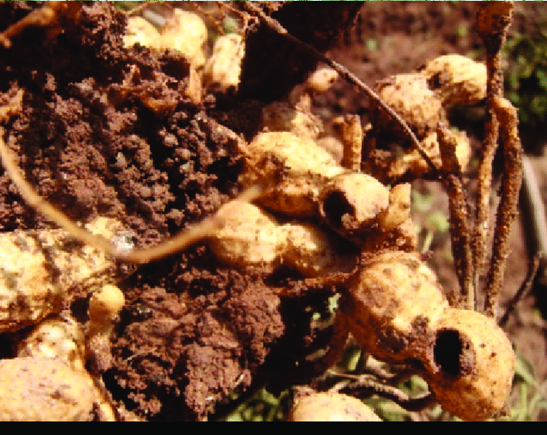
DEFICIENCY OF NITROGEN
´Yellowing that starts at the tip and moves along the center of older leaves.
TREATMENT :
|
Use Calcium EDTA 0.5g per litre of water |
 |
|
Use BLOOM 2 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5ml per litre of water |
 |
TREATMENT :
|
Use Manganese EDTA 0.5 gm per litre of water |
.png) |
|
Use Grow 2 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
TREATMENT :
|
Use Ferric EDTA 0.5-01 gm per litre of water |
.png) |
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
TREATMENT :
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use BLOOM 2 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
TREATMENT :
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
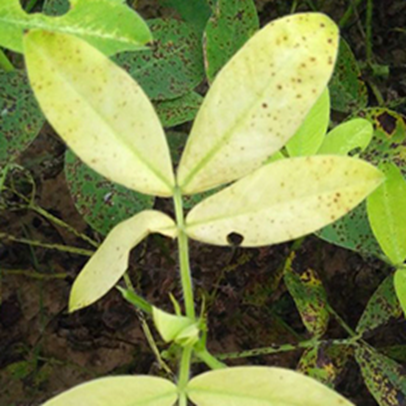
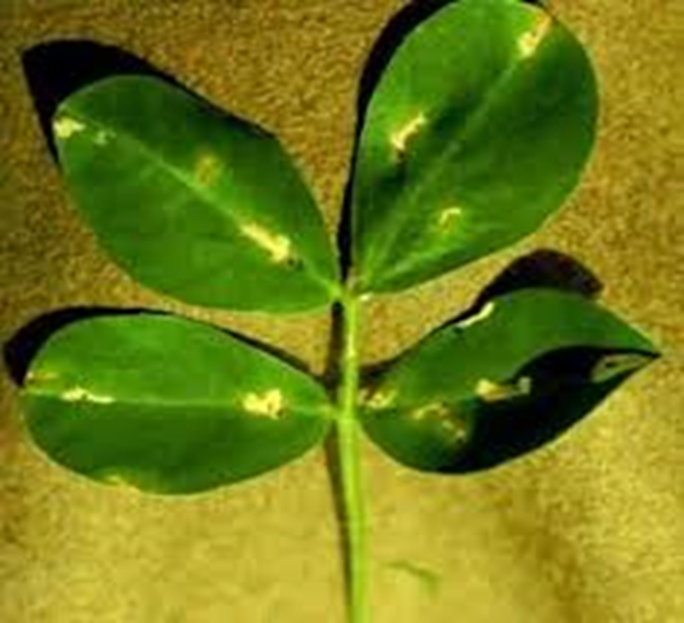
DEFICIENCY OF ZINC
Stunted growth while young leaves are smaller than normal.
The leaf lamina will be uneven on both sides.
The leaf becomes chlorotic.
TREATMENT :
|
Use Zinc EDTA 0.5-01 gm per litre of water. |
 |
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
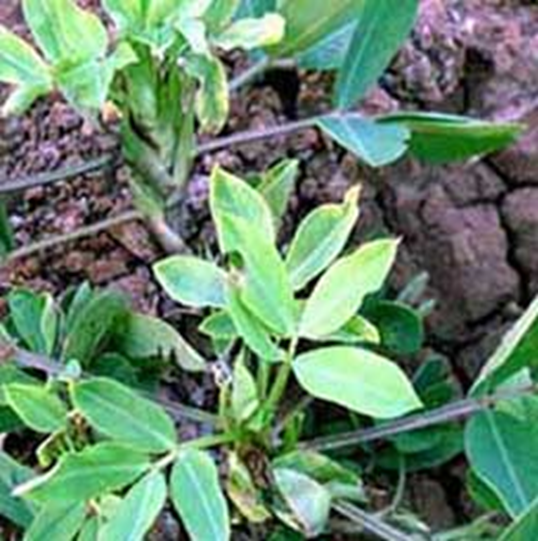
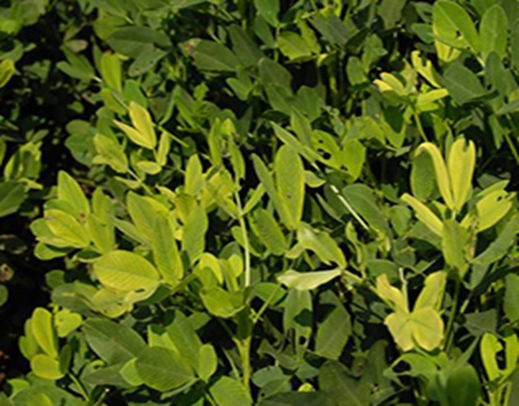
DEFICIENCY OF MAGNESIUM
´Oldest leaves turn yellow between the veins.
´In severe cases, younger leaves may be affected and older leaves may drop off.
´May occur on acid soils, sandy soils, or soils with high potassium levels.
TREATMENT :
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
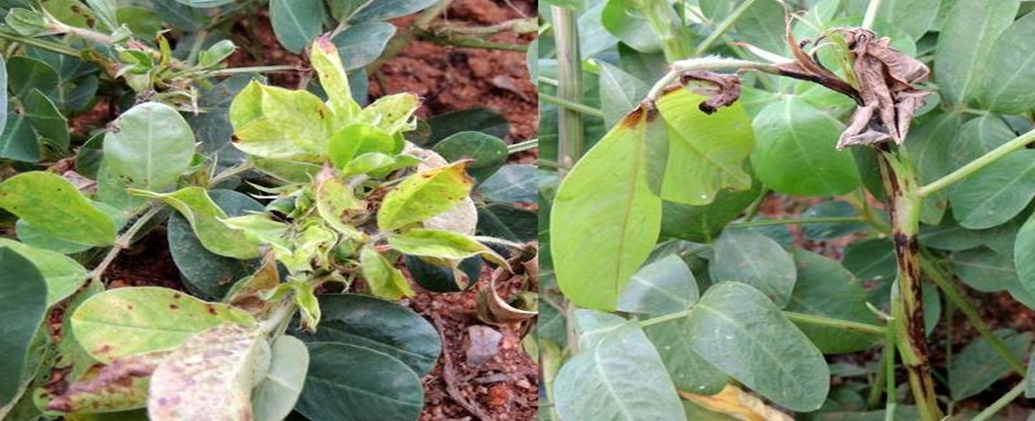
1. ANTHRACANOSE (Colletotrichum gloeosporioides)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (i) CONTACT BASED
2. ALTERNARIA LEAF SPOT
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (i) CONTACT BASED
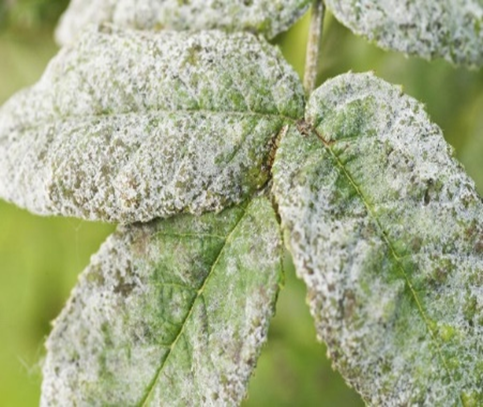
3. RUST (Puccinia arachidis Speg)



TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (i) CONTACT BASED
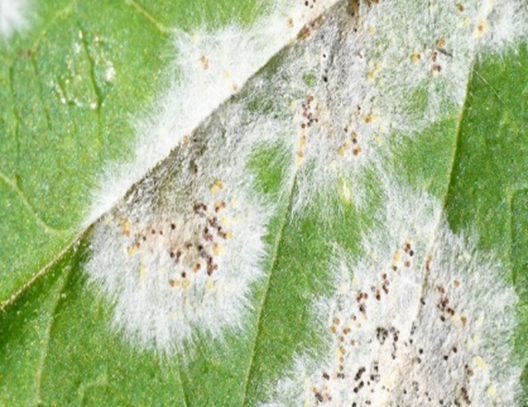
4. POWDERY MILDEW (Cercospora arachidicola Hori)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (i) CONTACT BASED
5. CERCOSPORIDIUM PERSONATUM (Cercospora personata)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (ii) SYSTEMIC-BASED
1. CYLINDROCLADIUM PARASITICUM (Cercospora personata)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (ii) SYSTEMIC BASED
2.SCLEROTINIA MINOR (Sclerotinia minor)
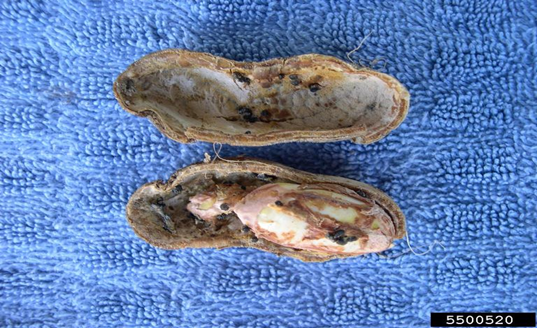


TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (ii) SYSTEMIC BASED
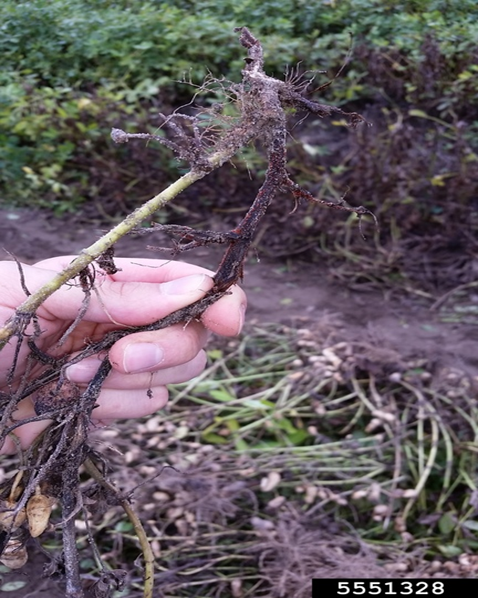
3.PYTHIUM MYRIOTYLIUM (Soft Root Rot)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
B. VIRAL DISEASE
1. PEANUT STUNT VIRUS (PSV)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
B. VIRAL DISEASE
2. PEANUT BUD NECROSIS VIRUS
TREATMENT :
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PEST:(i) CHEWING PESTS
1. CATTERPILLAR (Lepidopteran)
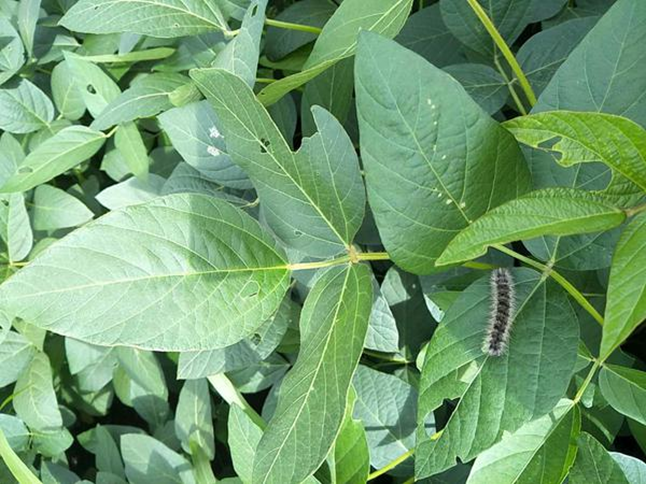



TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PEST:(i) CHEWING PESTS
2. LEAF MINER (LIRIOMYZA BRASSICAE)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PEST:(i) CHEWING PESTS
3. WHITEGRUB (Holotrichia serrata)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PEST:(i) CHEWING PESTS
4. TERMITE (Isoptera)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
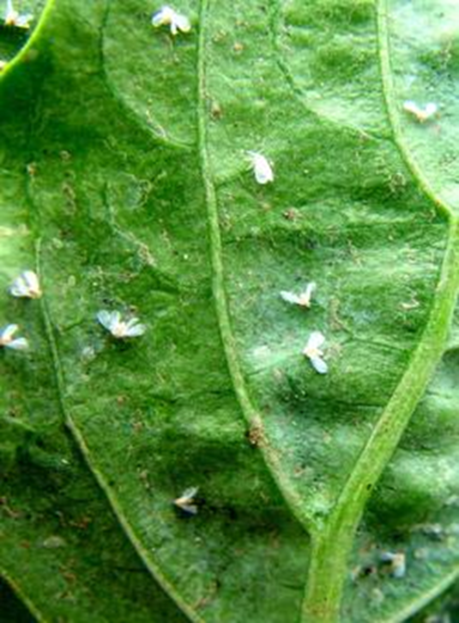
C. PEST:(ii) SUCKING PESTS
1. WHITEFLY (Aleyrodidae)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PEST:(ii) SUCKING PESTS
2. APHID (Aphidoidea)
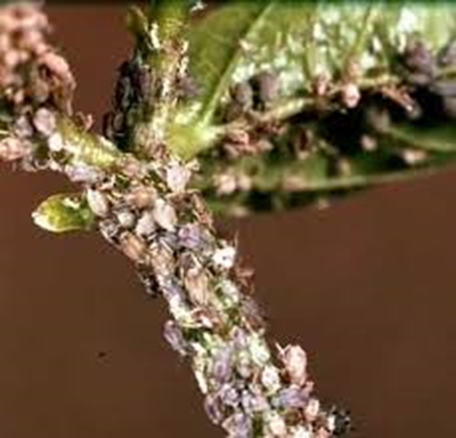
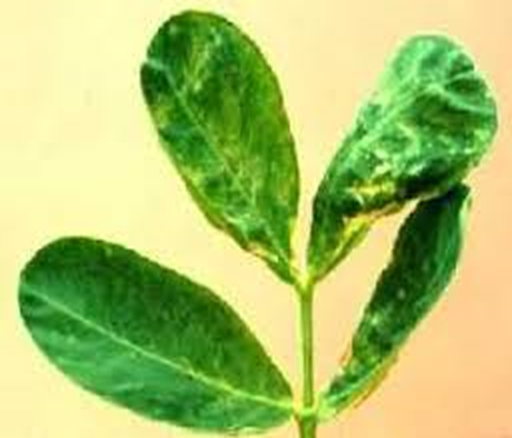
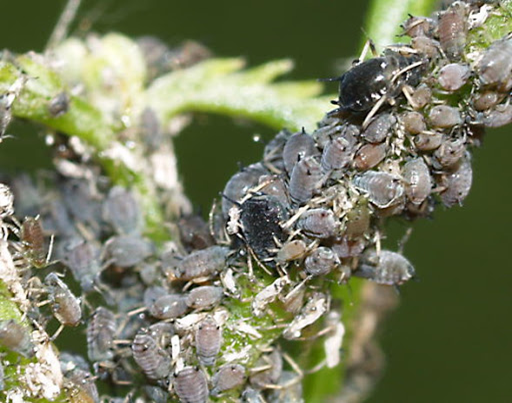



TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C.PEST:(ii) SUCKING PESTS
3. THRIP (Thysanoptera)
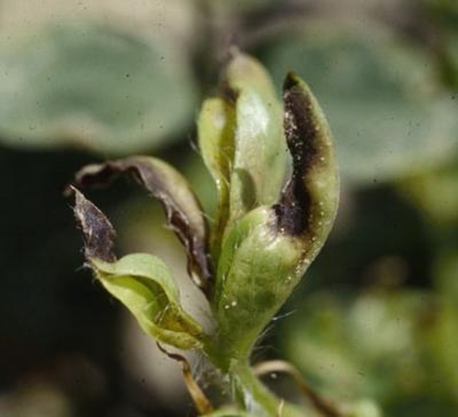
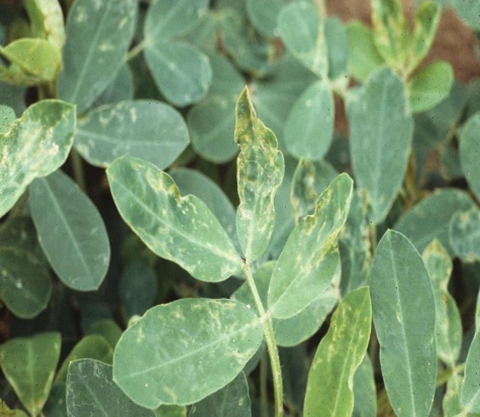



TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PEST:(ii) SUCKING PESTS
4. MEALYBUG (Pseudococcidae)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |