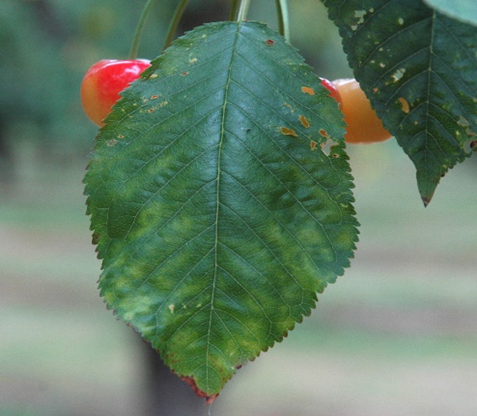
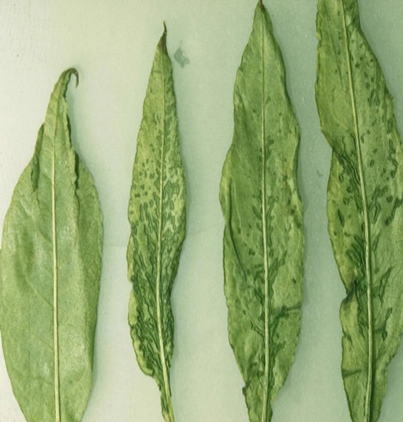
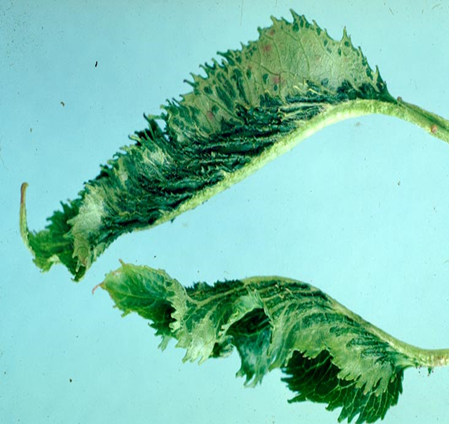
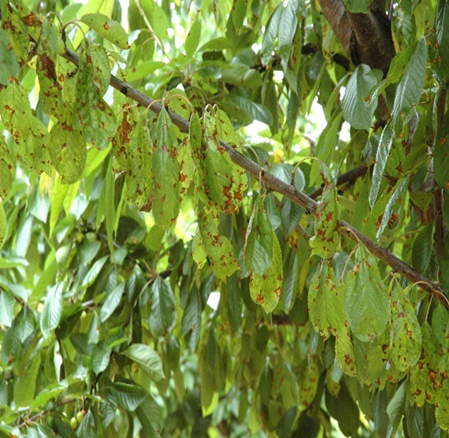
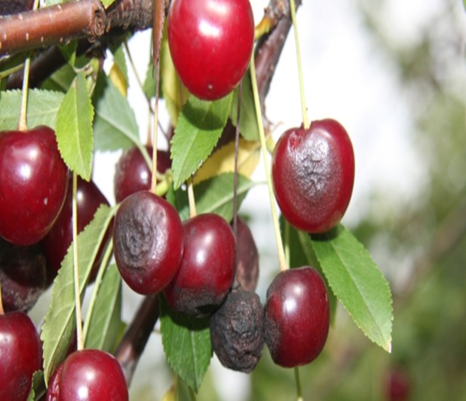
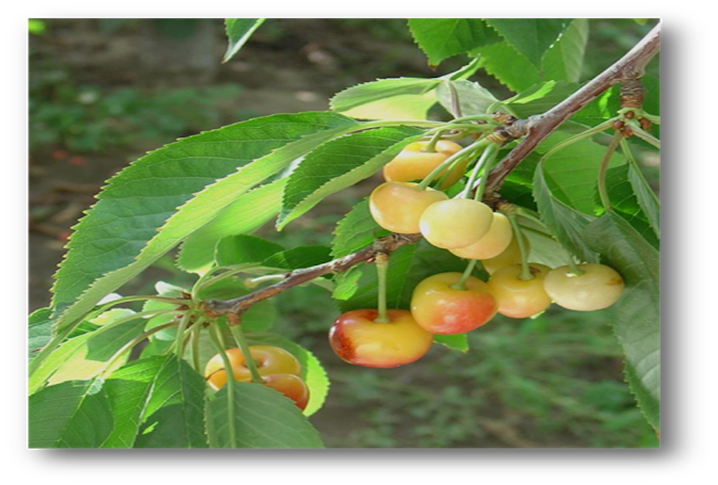
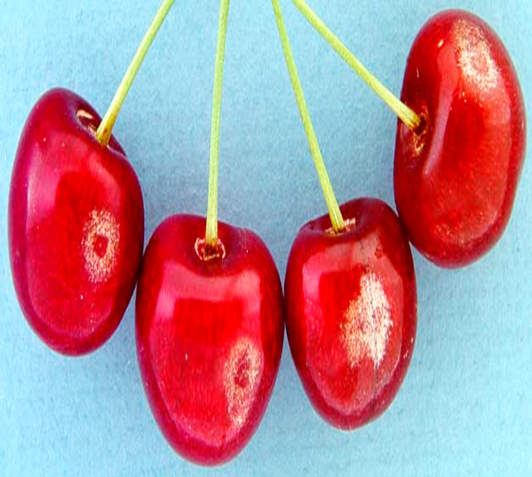
- Rosaceae is a family that includes cherries.
- The majority of sweet cherries are self-fertile and require pollination from another plant.
- Cherries are high in fiber, vitamins, and minerals such as potassium, calcium, vitamin A, and folic acid, among others.
- Prunus avium and Prunus cerasus varieties are used to make commercial cherry.
• Soil- The ideal soil for cherries would be reasonably fertile but also deep, especially where the ground is dry.
• pH- 5.5 to 7
• Temperature- •Cherry grows best in temperatures between 5-7º C.
- It's critical to water cherry trees adequately the first year after they've been planted.
- In The first week, they should be watered deeply every other day; in the second week, they can be irrigated thoroughly 2-3 times; and after the second week, they can be watered deeply 2-3 times.
- For the balance of the first season, water cherry trees thoroughly once a week.
- Cherry trees that have been established for a long time don't require much watering.
- Your cherry trees should be getting enough water if you get at least an inch (2.5 cm) of rain every ten days in your area.
- In times of drought, though, it is critical to provide them with more water.
FOR IRRIGATION :
Irrigate your field with Power Plant Bhoomi power, Premium, and Root guard.
BHOOMI POWER
4KG/ACRE

POWER PLANT PREMIUM
1 LITRE/ ACRE

ROOT GUARD
2 KG/ACRE

HOW TO USE IT?
Use Bhoomi power by following methods.
1. By broadcasting over the field.
2. Use in slurry.
3. Give it in cow dung.
4. you can also give it in dry soil.
Note: Repeat Bhoomi power and Root guard every 3 months.
- The best period to plant cherries is between December and January, and this fruit is grown primarily in steep places with sloppy soil.
- The rootstock selected determines the plant spacing. Plants raised from seedlings, on the other hand, should be spaced 6 x 6 metres apart.
- Fill a small container with planting media and two to three trenches, then water the seeds in.
- When the cherry seedlings have grown to a height of two inches (5cm).
- Indoors, keep the seedlings in bright locations.
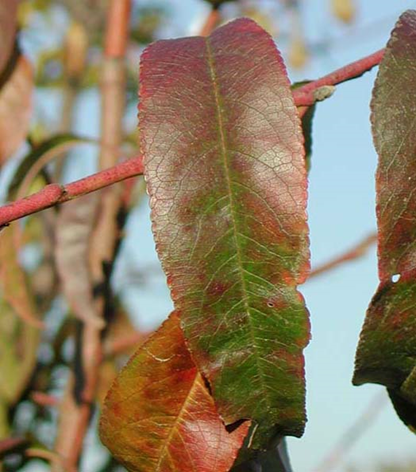
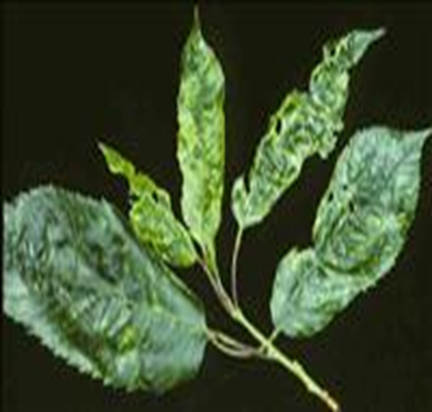
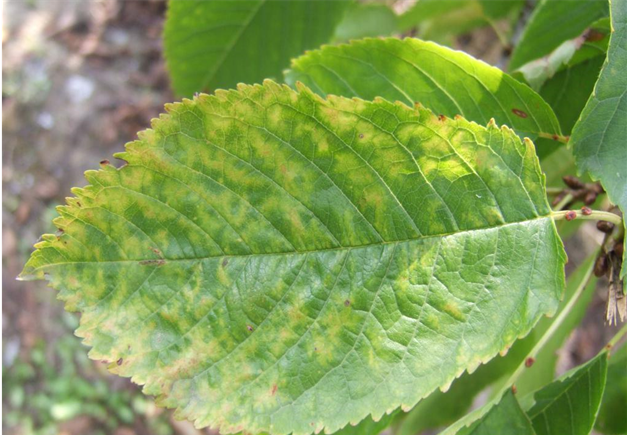
DEFICIENCY OF NITROGEN
TREATMENT :
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water. |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water. |
 |
DEFICIENCY OF PHOSPHORUS
DEFICIENCY OF POTASSIUM
TREATMENT :
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water. |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water. |
 |
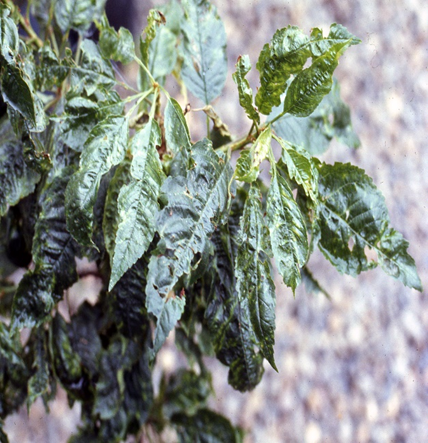
DEFICIENCY OF IRON
TREATMENT :
|
Use Ferric EDTA 0.5-01 gm per litre of water |
.png) |
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
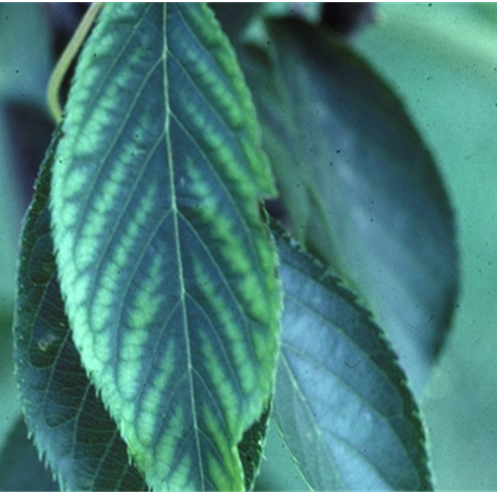
DEFICIENCY OF ZINC
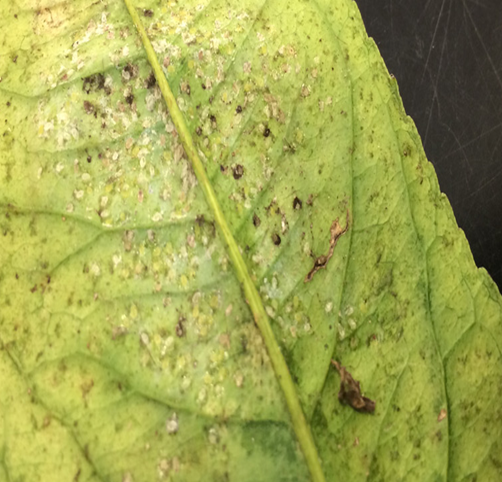
A. FUNGAL DISEASES (i) CONTACT BASED
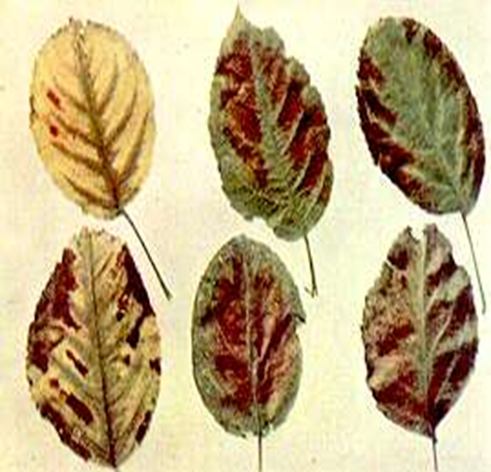
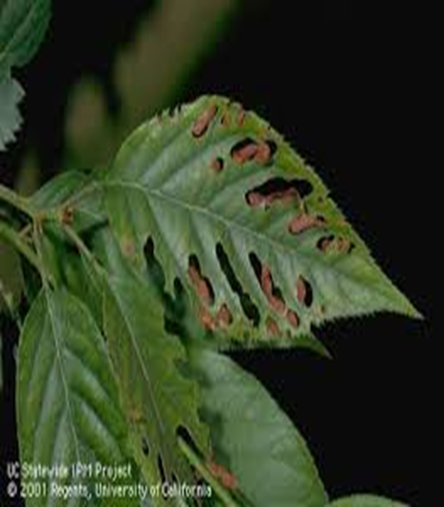
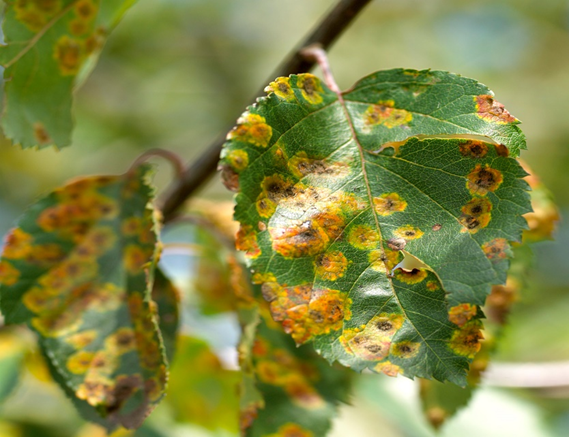
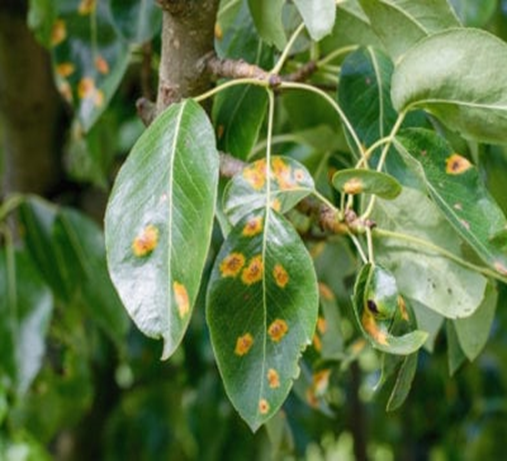
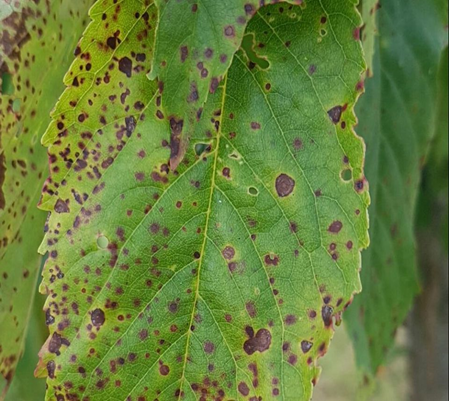
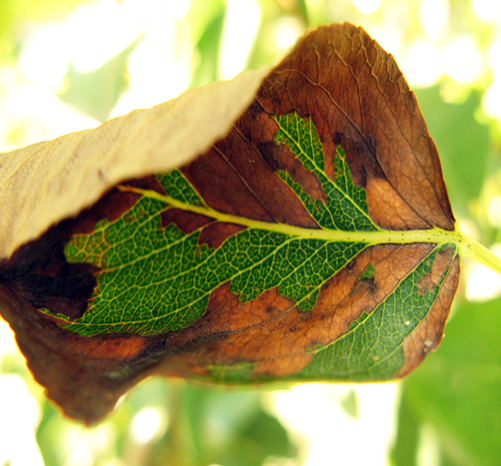
1. CHERRY LEAF SPOT (Coccomyces hiemalis)
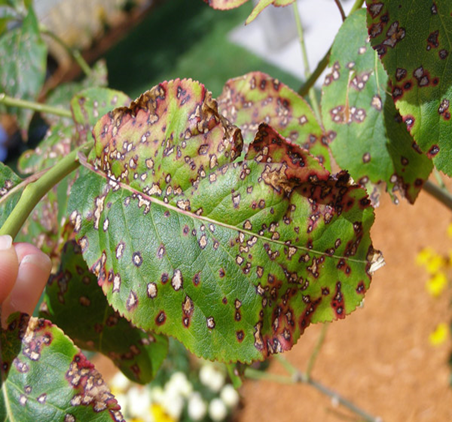
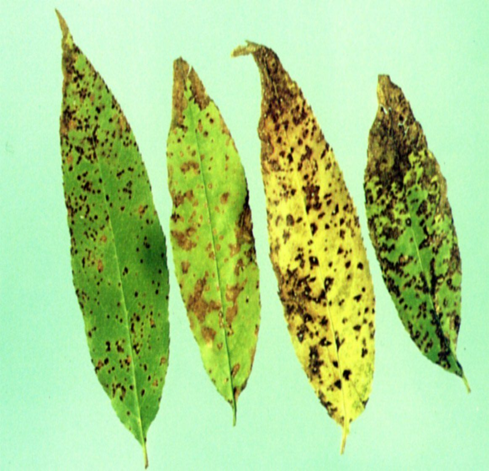
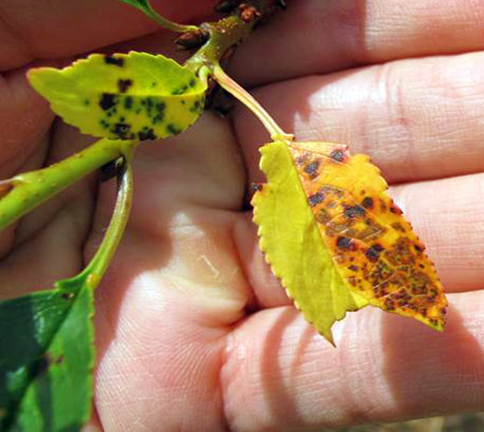



TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES (i) CONTACT BASED
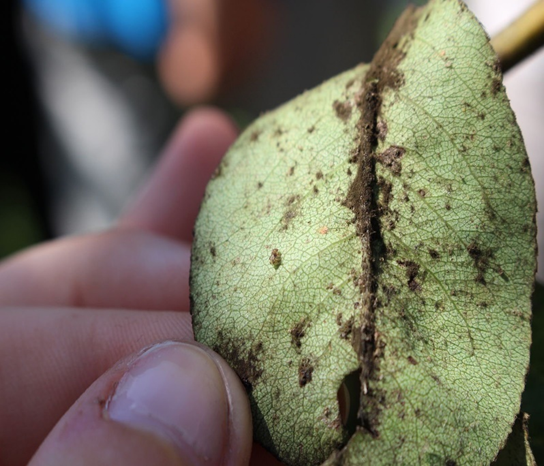
2. POWDERY MILDEW (Apiosporina morbosa)
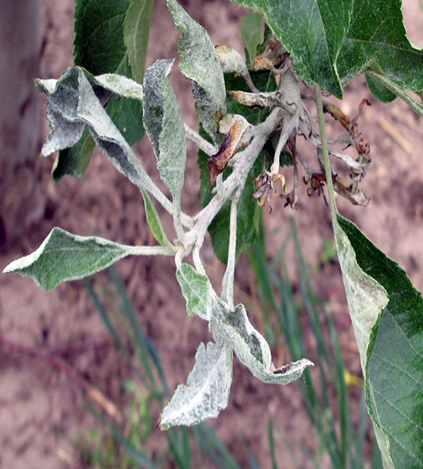
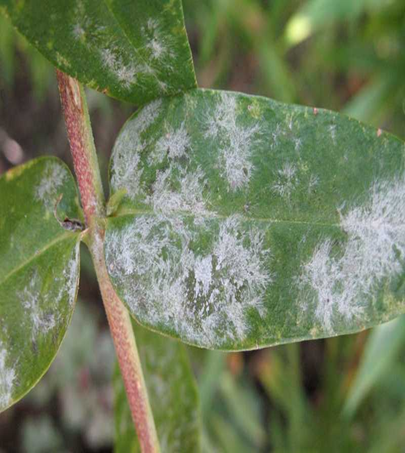
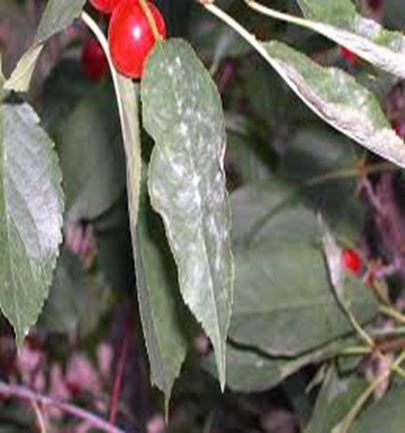



TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES (i) CONTACT BASED
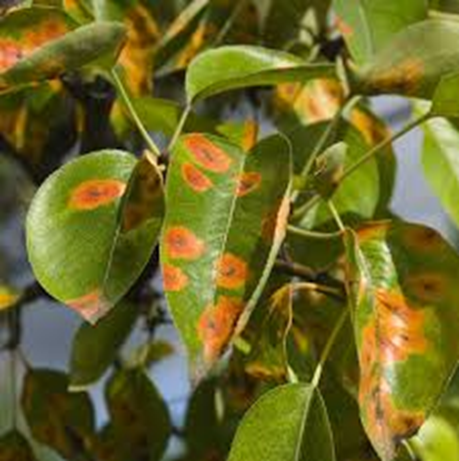
3. RUST (Tranzschelia discolor)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES (ii) SYSTEMIC BASED
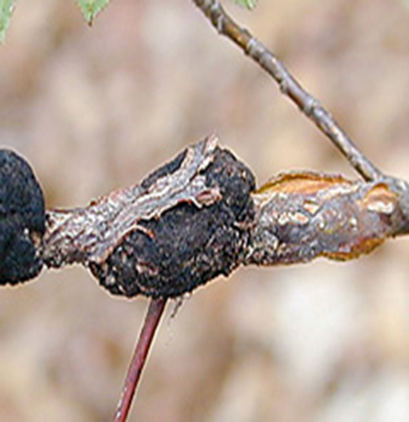
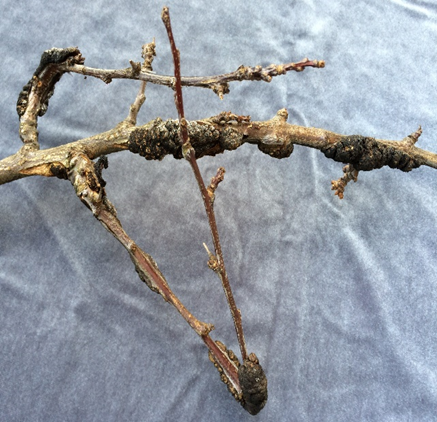
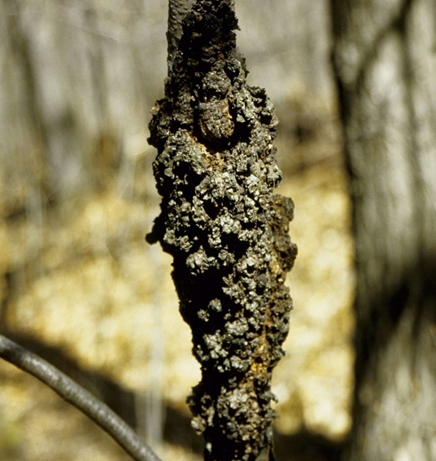
1. BLACK KNOT (Apiosporina morbosa)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES (ii) SYSTEMIC BASED
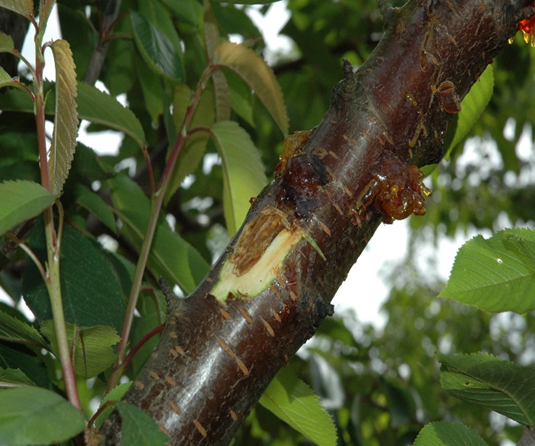
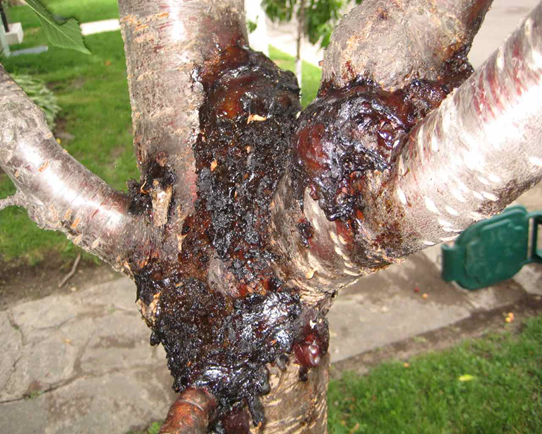
2. CANKER (Pseudomonas syringae)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES(ii) SYSTEMIC BASED
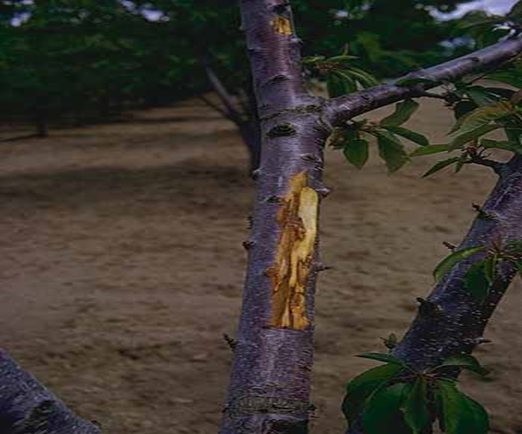
3. ROOT ROT ( Phymatotrichum omnivorum)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
B. VIRAL DISEASES
1. PRUNUS NECROTIC RING SPOT VIRUS
TREATMENT :
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water. |
 |
B. VIRAL DISEASES
2. CHERRY LEAF ROLL VIRUS
TREATMENT :
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water. |
 |
B. VIRAL DISEASES
3. CHERRY MOTTLE LEAF VIRUS
TREATMENT :
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water. |
 |
B. VIRAL DISEASES
4. CHERRY TWISTED LEAF VIRUS
TREATMENT :
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water. |
B. VIRAL DISEASES
5.CHERRY RASP LEAF VIRUS
TREATMENT :
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water. |
B. VIRAL DISEASES
6.NECROTIC RUSTY MOTTLE VIRUS
TREATMENT :
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water. |
B. VIRAL DISEASES
7. PRUNE DWARF VIRUS
TREATMENT :
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water. |
C.PESTS: (I) CHEWING PESTS
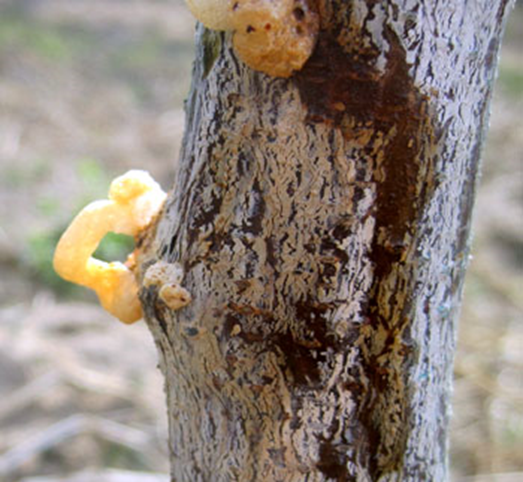
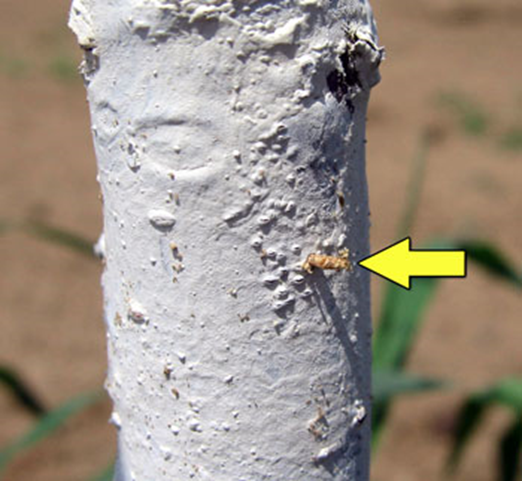
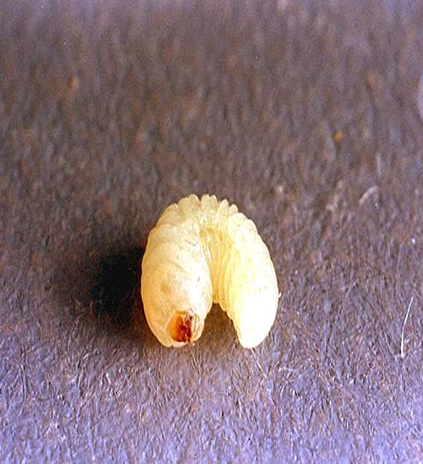
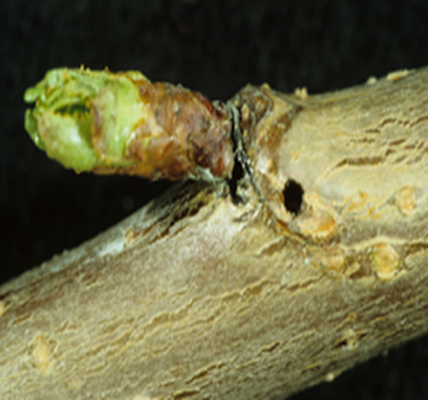
1. STEM BORER ( Scirpophaga incertulas)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C.PESTS: (I) CHEWING PESTS
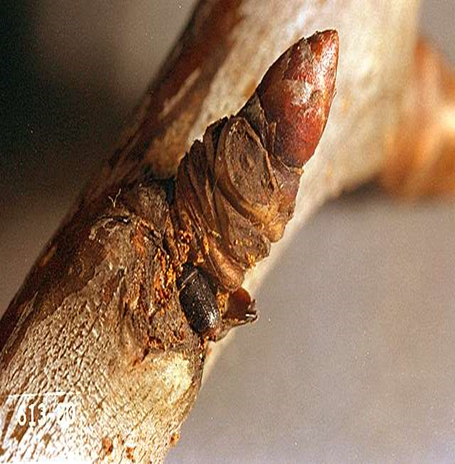
2. SHOT HOLE BORER (Xyleborus perforans)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
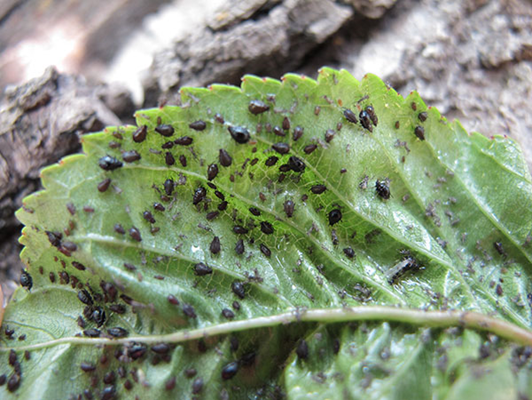
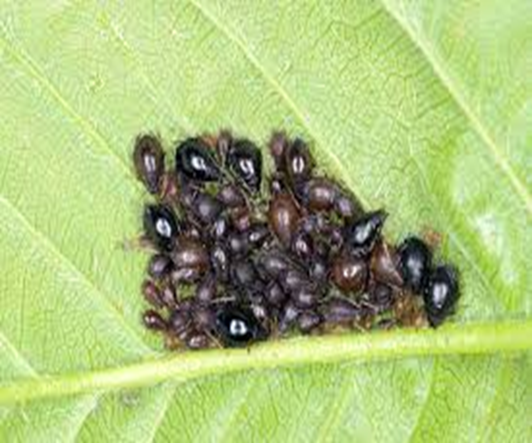
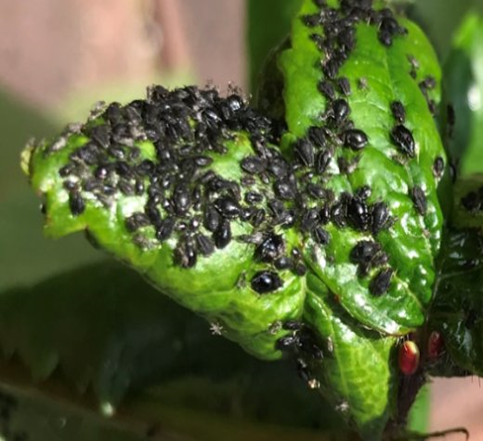
C.PESTS:(II) SUCKING PESTS
1. APHIDS (Aphidoidea)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C.PESTS:(II) SUCKING PESTS
2. THRIPS (Helicothrips indicus)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C.PESTS: (II) SUCKING PESTS
3. PEAR PSYLLA (Cacopsylla pyri)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |