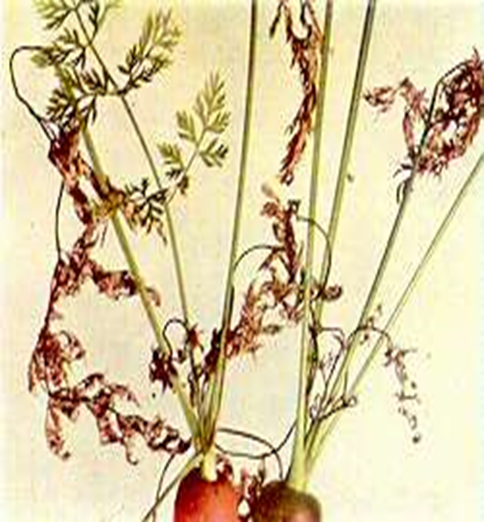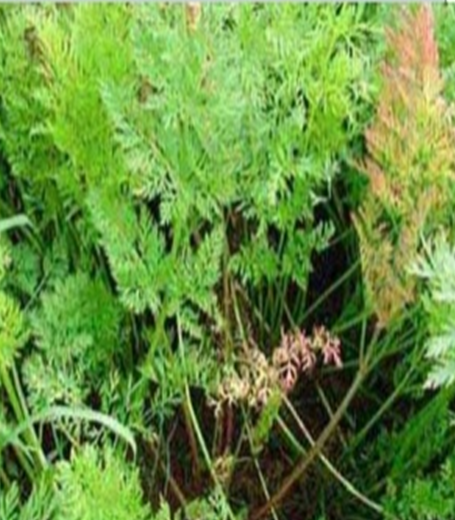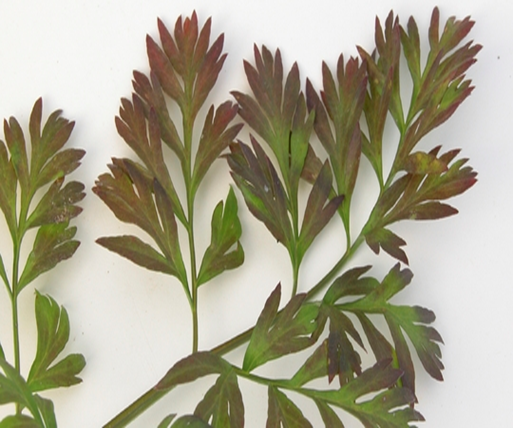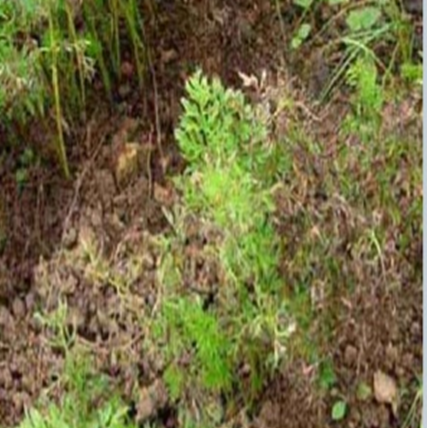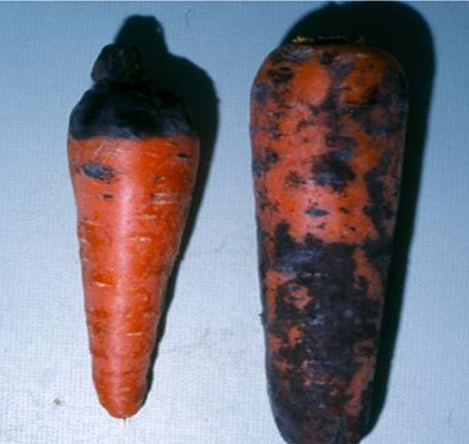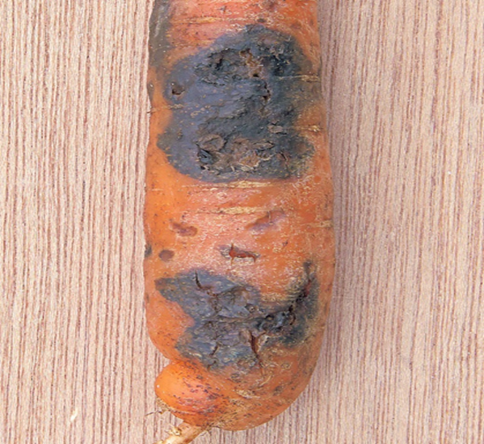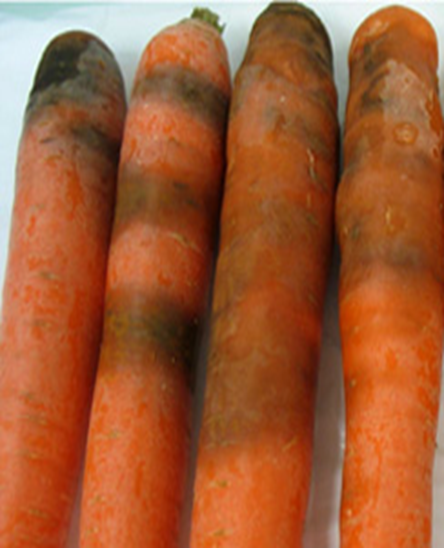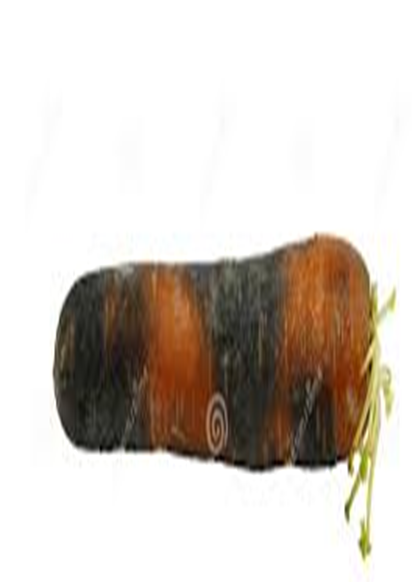
- Carrot is a member of the family Apiaceae.
- Carrot is one of the most important root vegetables.
- It is a rich source of alpha and beta carotene.
- Uttarpradesh has maximum production, Bihar has the highest area of carrots in India.
- It is a biennial plant.
• Soil- Carrot required deep, loose loamy soils.
• pH- pH of the soil should be in the range of 5.5 to 7 (a pH of 6.5 is ideal for good yield).
• Temperature- Carrots grow best in temperatures between 16°-20°C.
• Climate- Cold weather crop, and it also does well in warm climates.
- Applying first irrigation after sowing will aid in germination.
- Irrigation should be done every five days.
- Apply remaining irrigations at intervals of 6-7 days in summer and 10-12 days in winter, depending on soil type and climate.
- Carrots required 3-4 irrigations in total.
- Stop irrigation 2-3 weeks before harvesting to help the carrots become sweeter and more flavorful.
- Beds should be covered with moist gunny bags after irrigation in the evening.
FOR IRRIGATION :
Irrigate your field with Power Plant Bhoomi power, Premium, and Root guard.
BHOOMI POWER
4KG/ACRE

POWER PLANT PREMIUM
1 LITRE/ ACRE

ROOT GUARD
2 KG/ACRE

HOW TO USE IT?
Use Bhoomi power by following methods.
1. By broadcasting over the field.
2. Use in slurry.
3. Give it in cow dung.
4. you can also give it in dry soil.
Note: Repeat Bhoomi power and Root guard every 3 months.
- Prior to planting, thoroughly water the area.
- 4 seeds per 2cm, direct sow the small seeds 5mm (14") deep.
- Carrots are harvested in August in the plains.
Spacing
- Rows are indicated with a 25-to-30-centimeter space between them. Seeds should be blended with sand at a ratio of one part seed to four parts sand.
- Hills should be thinned to a depth of 10cm between plants.
Plains: The distance between plants should be 5cm.
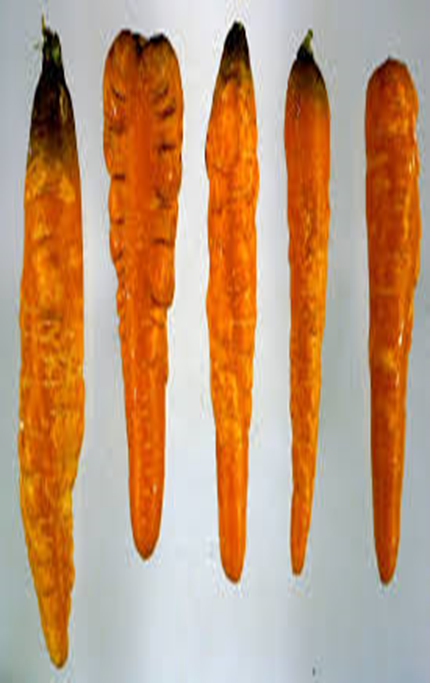
DEFICIENCY OF NITROGEN
TREATMENT :
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
DEFICIENCY OF PHOSPHORUS
TREATMENT :
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water. |
 |
|
Use BLOOM 2 ml per litre of water. |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water. |
 |
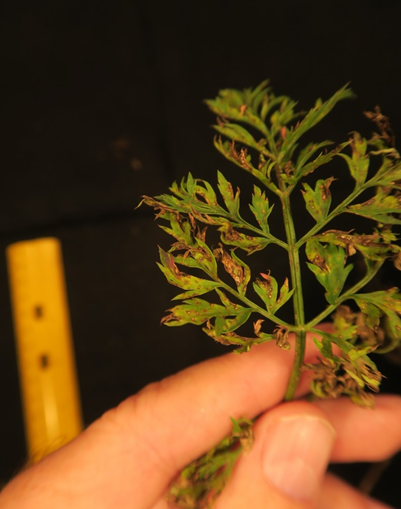
DEFICIENCY OF POTASSIUM
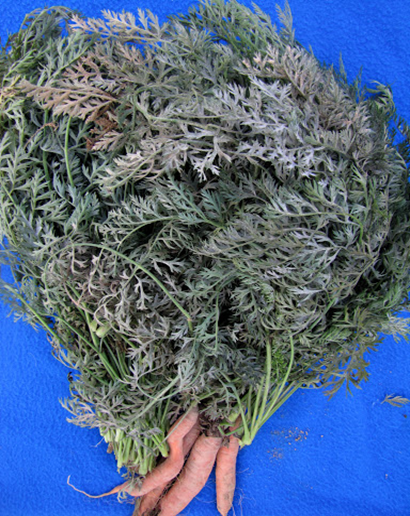
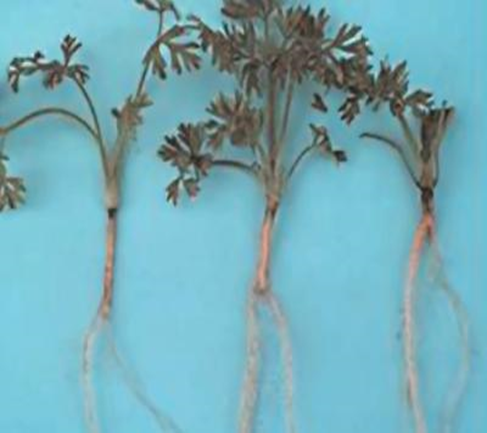
´Potassium deficiency causes reddish foliage discoloration, starting on older leaf margins.
TREATMENT :
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
TREATMENT :
|
Use Ferric EDTA 0.5-01 gm per litre of water. |
.png) |
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water. |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water. |
 |
DEFICIENCY OF SULPHUR
´Chlorosis occurs in young leaves.
TREATMENT :
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
DEFICIENCY OF BORON
TREATMENT :
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water. |
 |
|
Use BLOOM 2 ml per litre of water. |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water. |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES (i) CONTACT BASED
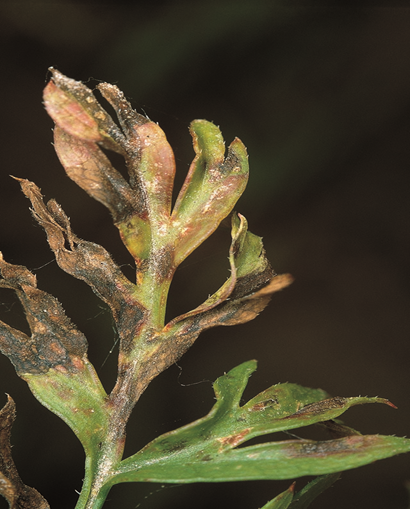
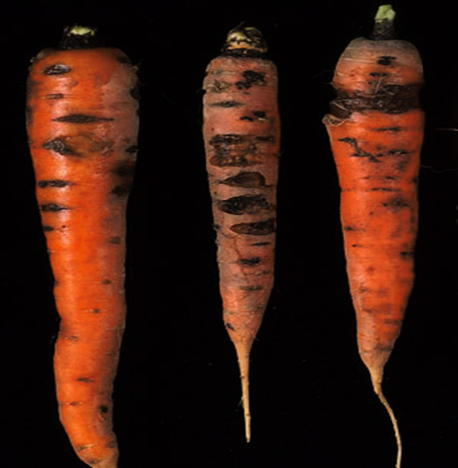
1. ALTERNARIA LEAF BLIGHT ( Alternaria dauci)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
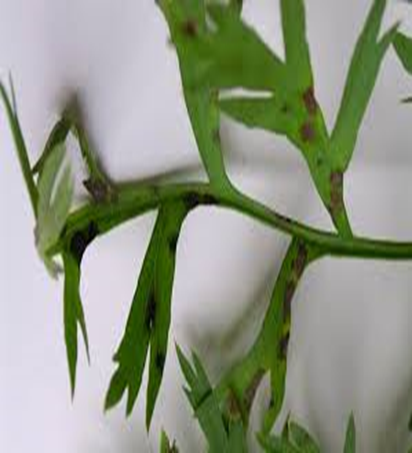
2.CERCOSPORA LEAF SPOT (Cercospora carotae)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
|
3. POWDERY MILDEW (Erysiphe heraclei)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
4. CAVITY SPOT (Pythium sulcatum)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES(ii) SYSTEMIC BASED
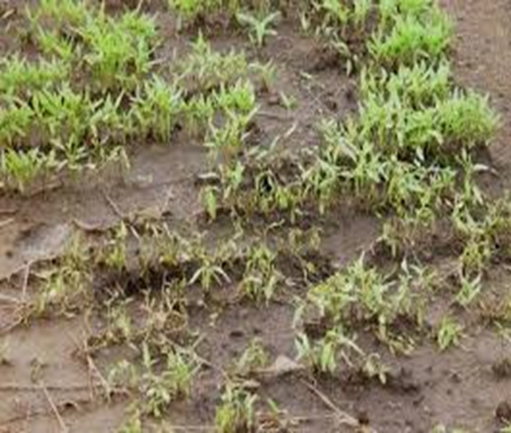
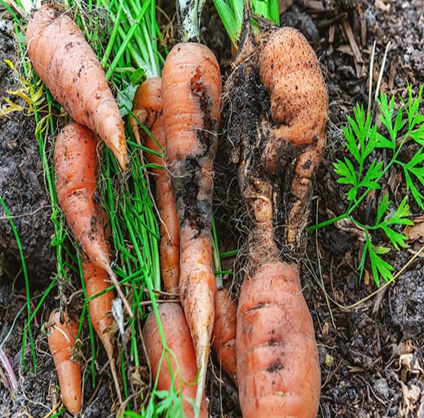
1. DAMPING OFF (Rhizoctonia solani)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
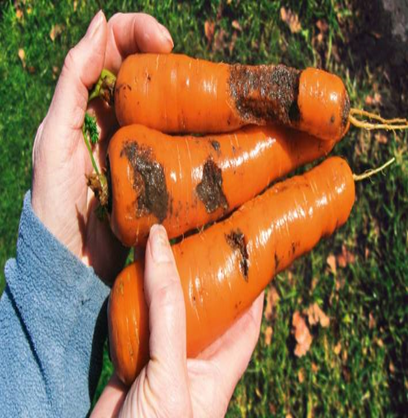
2.BLACK ROOT ROT (Thielaviopsis basicola)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
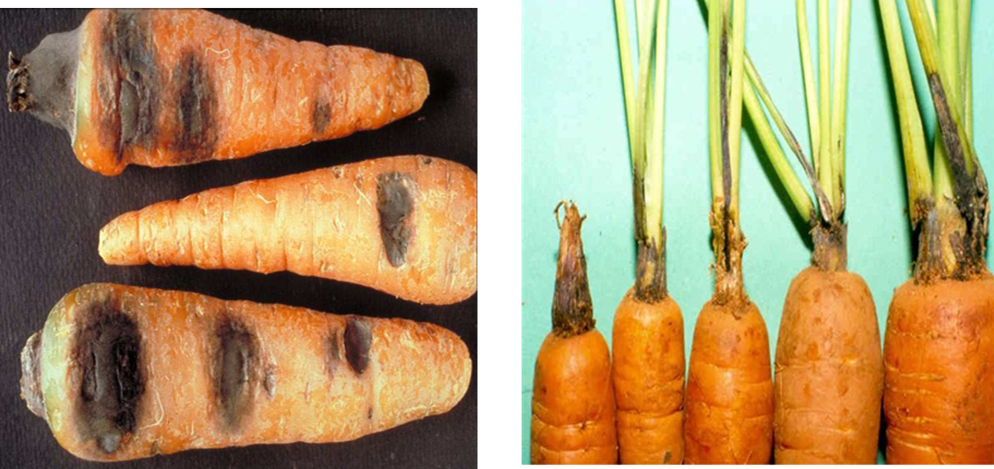
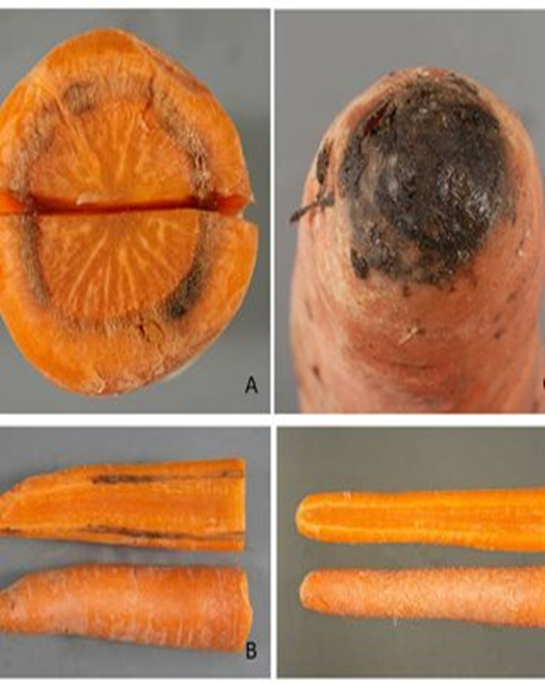
3. BROWN ROT (Phytophthora porri)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
B.VIRAL DISEASES
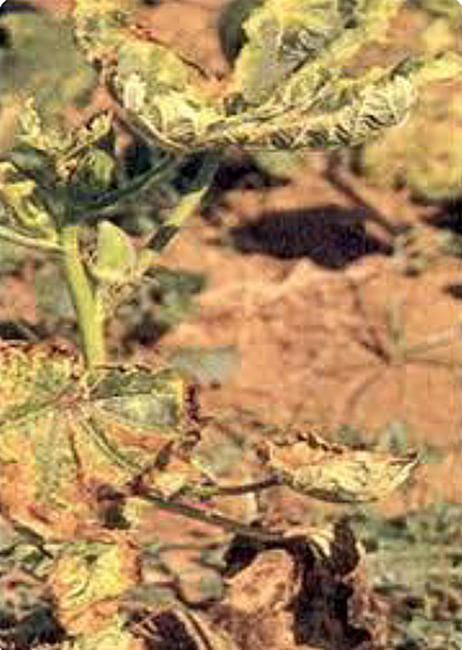
1. CARROT RED LEAF
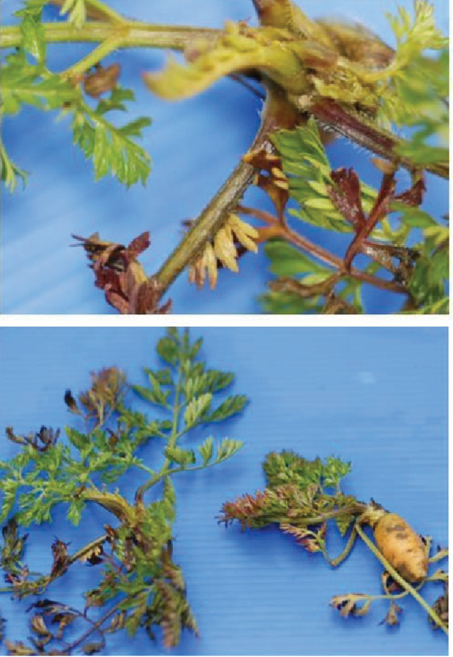



TREATMENT :
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
2. CARROT YELLOW LEAF
TREATMENT :
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C.PESTS: (i) CHEWING PESTS
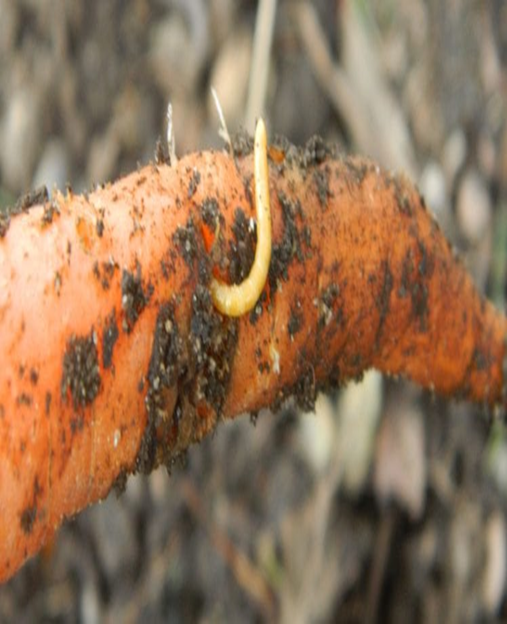
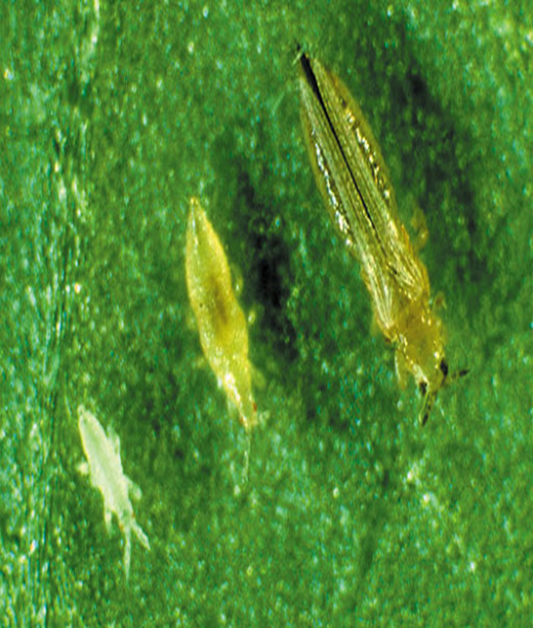
1. CARROT RUST FLY (Psila rosae)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
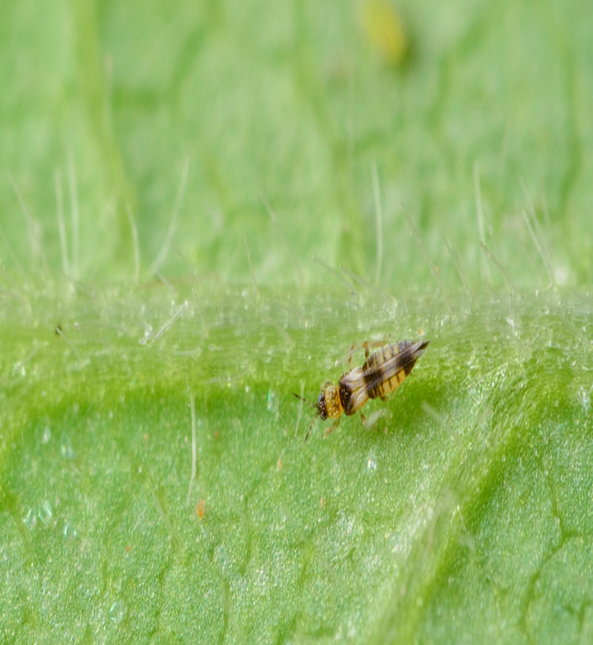
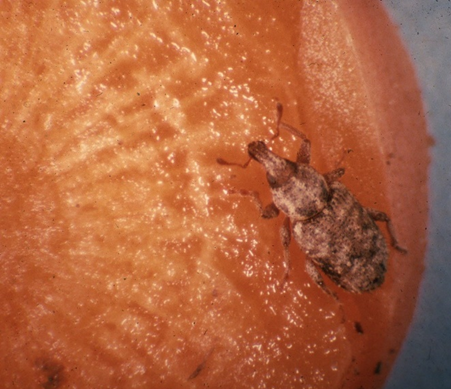
2.CARROT WEEVIL( Listronotus oregonensis)


TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
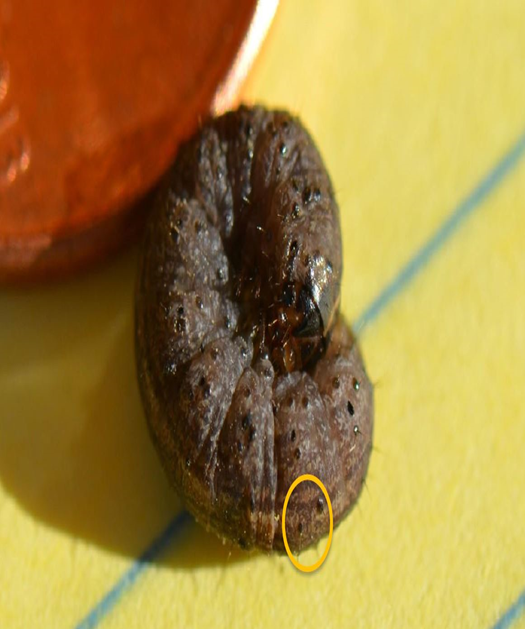
3. CUTWORM( Agrotis spp.)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
C.PESTS : (ii) SUCKINGPESTS
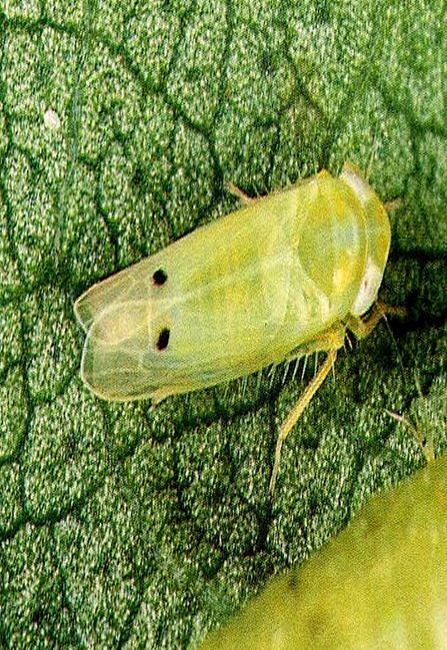
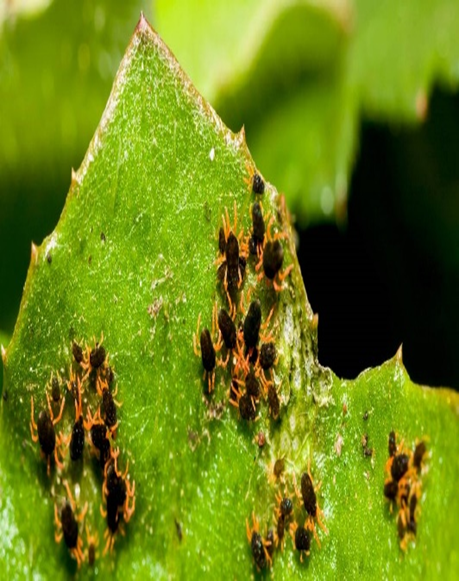
1. WILLOW CARROT APHID(Cavariella aegopodii)



TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
3.RED LEGGED EARTH MITE(Halodytus destructor)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |









































