INTRODUCTION

Apricot: A Popular Fruit in India
- Apricot is a popular fruit in India’s arid temperate and moderate highland areas.
- In India, this fruit belongs to the Rosaceae family and the genus Prunus.
- In the hills of Shimla and Himachal Pradesh, this fruit grows wild.
- When compared to other fruits, apricots are high in vitamin A and niacin.
- Apricots are used in jams, and squash, and they can also be dried and canned.
- In India, commercial apricot growing is minimal.
REQUIREMENTS
Soil & Climate Requirements
- Soil: Well-drained deep soils with good organic matter.
- pH: 6.0 to 6.8.
- Temperature: 0° to 8°C.
- Climate: Long cool winters with frost-free conditions and warm springs.
IRRIGATION
- Apricots require irrigation, particularly during the fruit growth stage in April and May.
- Irrigation frequency is determined by soil type, tree age, and weather conditions.
- Irrigation should be given every 8 to 10 days under extremely hot and dry conditions (May to June).
- Because these trees are sensitive to waterlogging, the soil should be emptied off in the event of severe rainfall.
FOR IRRIGATION :
Irrigate your field with Power Plant Bhoomi power, Premium, and Root guard.
" style="width:370px">
|
BHOOMI POWER 4KG/ACRE |
 |
|
POWER PLANT PREMIUM 1 LITRE/ ACRE |
 |
|
ROOT GUARD 2 KG/ACRE |
 |
HOW TO USE IT?
Use Bhoomi power by following methods.
1. By broadcasting over the field.
2. Use in slurry.
3. Give it in cow dung.
4. you can also give it in dry soil.
Note: Repeat Bhoomi power and Root guard every 3 months.
CULTIVATION
- The apricot plants are planted during the dormant season i.e. end of December to February, but early planting gives better establishment of plants.
- Undesirable trees and shrubs should be removed from the land during its initial preparations by digging and ploughing.
- On the flat land, a regular planting layout system such as square and triangular is followed, while on the hill slopes, contour system is generally practiced
- The spacing of plants varies with the soil, climate and vigour of variety and rootstocks.
- The plants are generally planted at a spacing of 6mx6m
- The pits of 1x1x1m dimension are dug about a month before planting.
PRODUCT RECOMMENDED:
Treat the bulbs of the banana plants with Power Plant Seed Treatment.
NUTRIENT DEFICIENCY
Deficiency of Iron
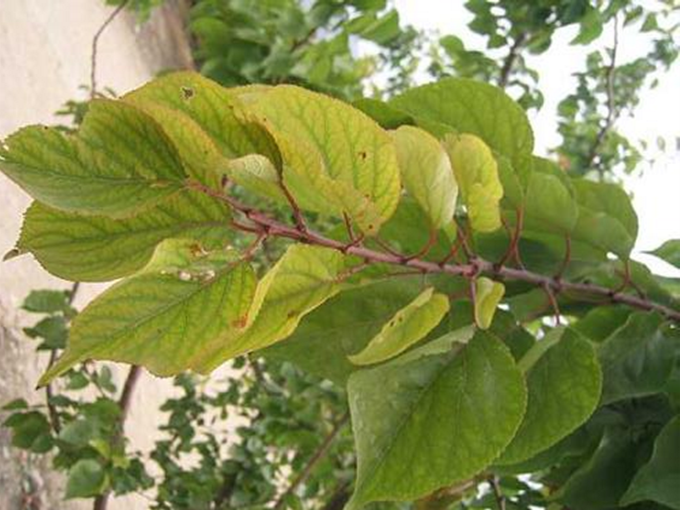
- Fe deficiency leads to characteristic chlorotic yellowing, and sometimes bleaching, of new leaf growth.
- The severity of the chlorosis increases towards the youngest leaves at the shoot tip. Under severe deficiencies, leaves scorch.
Treatment
| Product Name | Dosage | Image |
|---|---|---|
| Ferric EDTA | 0.5-1 gm per litre of water |
.png)
|
| NITROKING | 2-3 ml per litre of water |

|
| SPALL90 | 0.5 ml per litre of water |

|
DISEASES
Fungal Diseases: Contact-Based - Fusarium Wilt (Fusarium oxysporum)
Treatment
| Product Name | Dosage | Image |
|---|---|---|
| PPFC | 2-3 gm per litre of water |

|
| SpAll90 | 0.5 ml per litre of water |

|
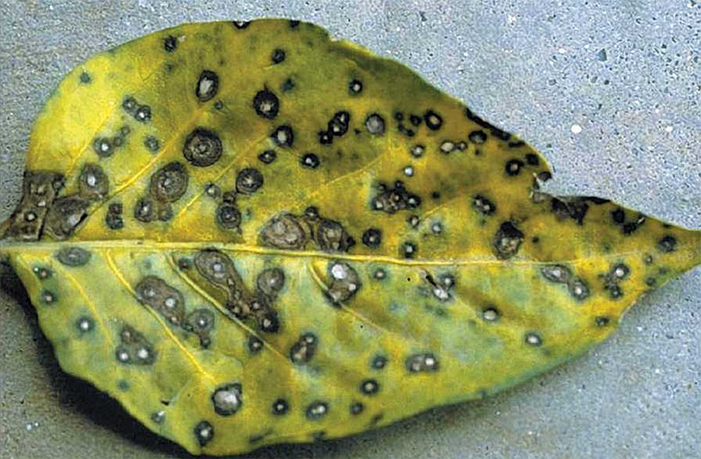
Gray Leaf Spot (Cercospora zeae-maydis)
Treatment
| Product Name | Dosage | Image |
|---|---|---|
| PPFC | 2-3 gm per litre of water |

|
| SpAll90 | 0.5 ml per litre of water |

|
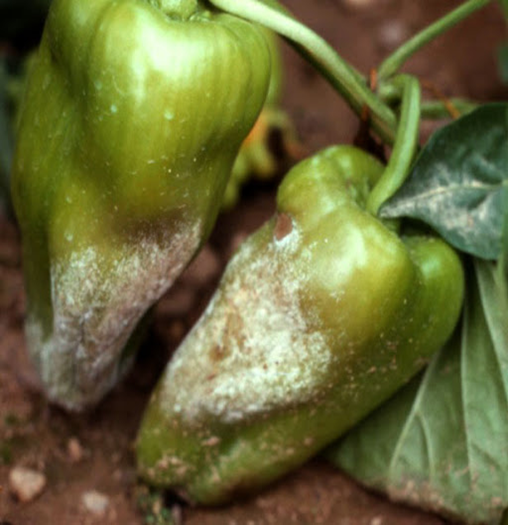
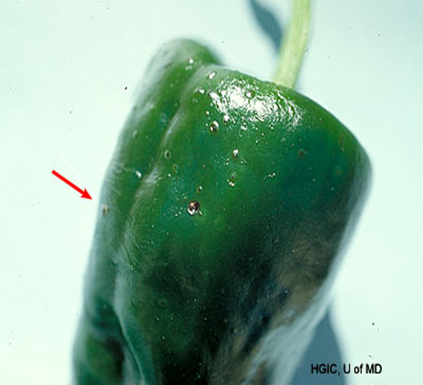
Phytophthora Blight (Phytophthora capsici)
Treatment
| Product Name | Dosage | Image |
|---|---|---|
| PPFC | 2-3 gm per litre of water |

|
| SpAll90 | 0.5 ml per litre of water |

|