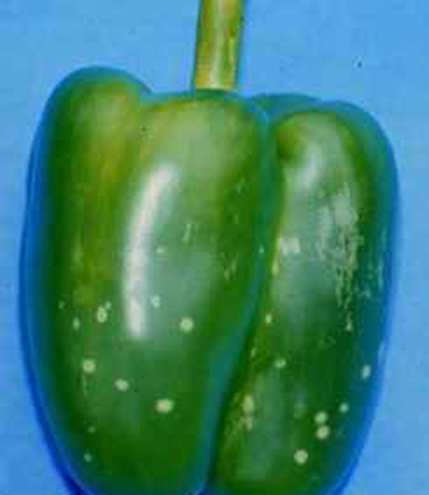
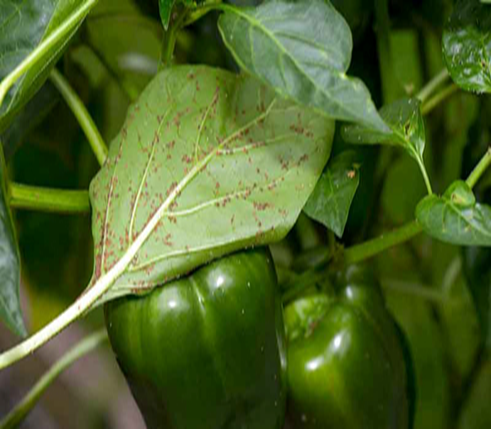
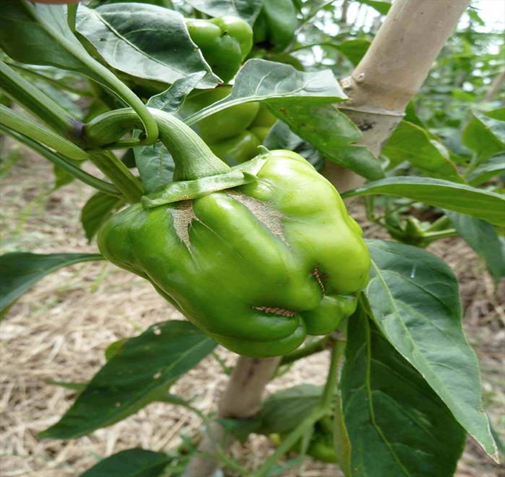
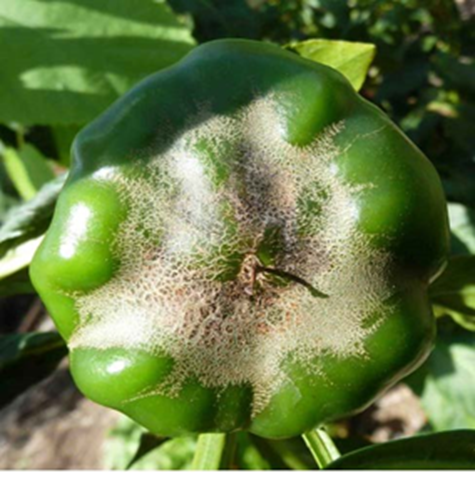
Capsicum (Bell Pepper) Overview
- Capsicum, often known as sweet pepper, bell pepper, or Shimla Mirch, is a popular vegetable in India.
- They belong to the Solanaceae family and are perennial herbaceous plants.
- It reaches a maximum height of 75 cm and bears small white or purple flowers with white or purple petals.
- Rich in Vitamin A, Vitamin C, and minerals such as Calcium, Magnesium, Phosphorus, and Potassium.
- Capsicum is a cool-season crop but can be cultivated year-round in controlled environments with regulated temperature and relative humidity (RH).
Soil & Climate Requirements
| SOIL | Clayey to loamy soil |
| pH | 6 - 7 |
| TEMPERATURE | 21°C - 25°C |
| RAINFALL | 625 - 1500 mm |
| CLIMATE | Capsicum is a cool-season crop |
Irrigation Guidelines
- Immediately after seeding, light irrigation is applied.
- Irrigation every week or every ten days.
- Shortly after transplanting, the next irrigation is supplied, and later irrigation is administered if needed.
- Irrigation is required at regular intervals in dry and semi-arid zones.
For Irrigation:
Irrigate your field with Power Plant Bhoomi Power, Premium, and Root Guard.
| Product | Dosage | Image |
|---|---|---|
| BHOOMI POWER | 4KG/ACRE |

|
| POWER PLANT PREMIUM | 1 LITRE/ACRE |

|
| ROOT GUARD | 2 KG/ACRE |

|
How to Use It?
Use Bhoomi Power by following methods:
1. By broadcasting over the field.
2. Use in slurry.
3. Give it in cow dung.
4. You can also give it in dry soil.
Note: Repeat Bhoomi Power and Root Guard every 3 months.
Capsicum Planting Guidelines
- On the raised beds, sow capsicum seedlings in two rows.
- Capsicum planting can also be done on a raised bed with plastic mulch to conserve water and prevent weed growth.
- Water the seedlings daily using a rose can until they are fully established.
Nutrient Deficiencies in Plants
Deficiency of Nitrogen
- Yellowing starts at the tip and moves along the center of older leaves.
- Leaves are small, uniformly light green or yellowish.
- The bark appears yellowish-orange.
Treatment:
| Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |

|
| Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |

|
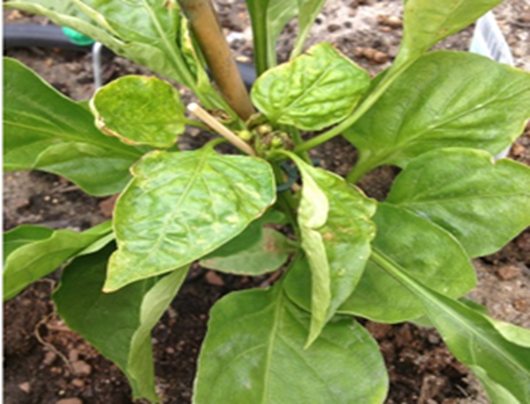
Deficiency of Potassium
- Drying along tips and margins of older leaves.
- Older leaves affected first, necrosis advancing from margins toward mid-rib.
- Margins first appear light green, later turning necrotic.
Treatment:
| Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |

|
| Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |

|
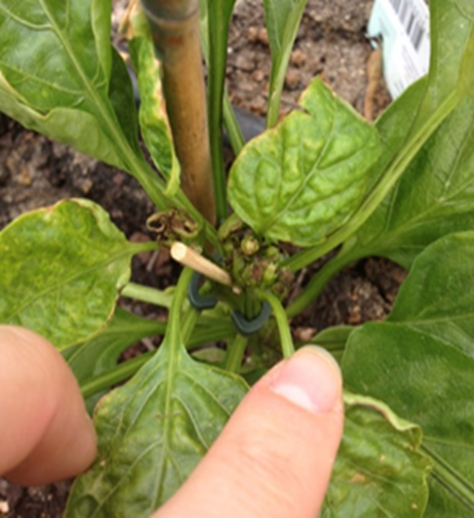
Deficiency of Magnesium
- Oldest leaves turn yellow between the veins.
- Severe cases affect younger leaves, causing older leaves to drop off.
- Occurs on acid soils, sandy soils, or soils with high potassium levels.
Treatment:
| Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |

|
| Use GROW 2 ml per litre of water |

|
| Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |

|
A.FUNGAL DISEASES: (i) CONTACT BASED
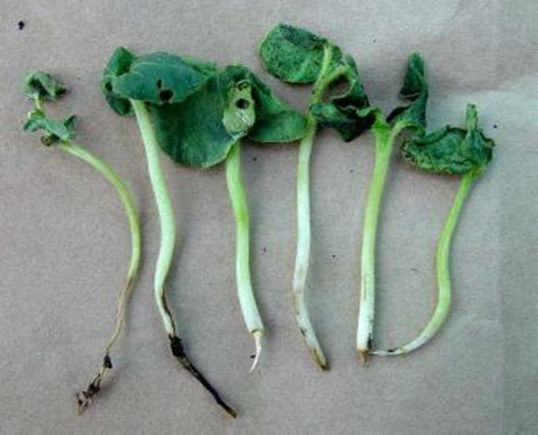
1. FUSARIUM WILT (Fusarium oxysporum)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
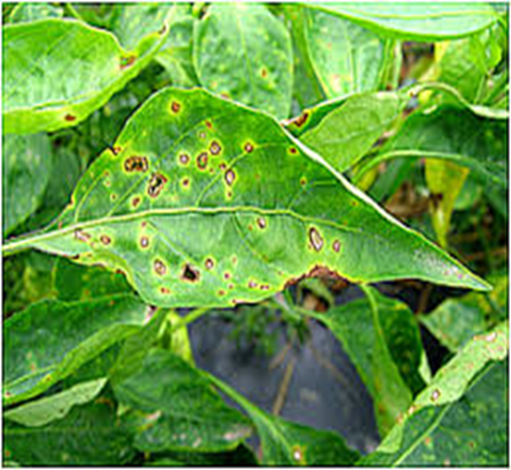
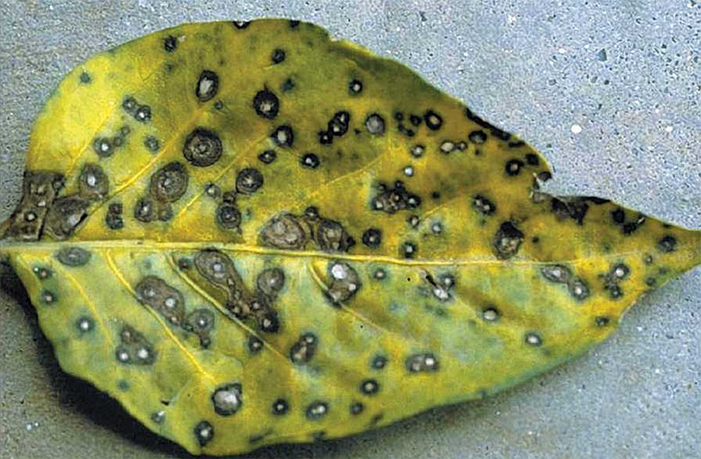
2. GRAY LEAF SPOT (Cercospora zeae-maydis)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
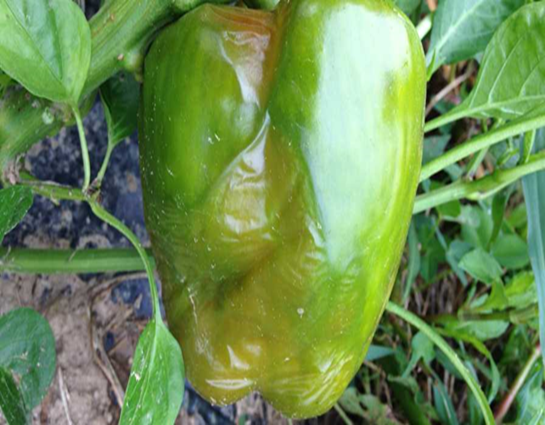
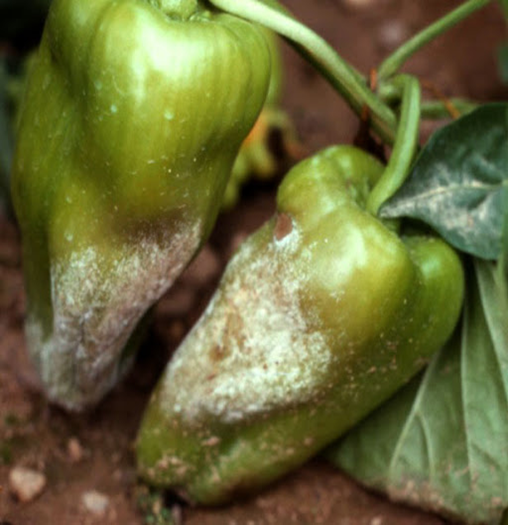
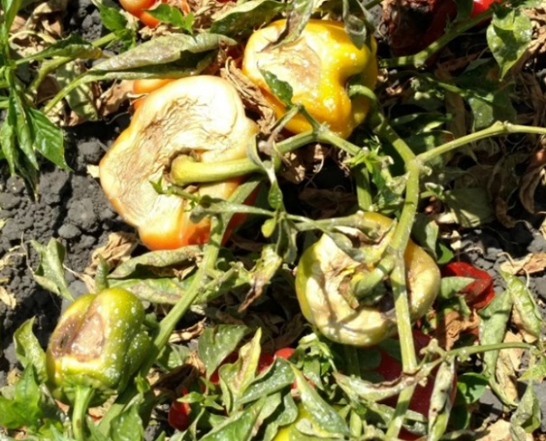
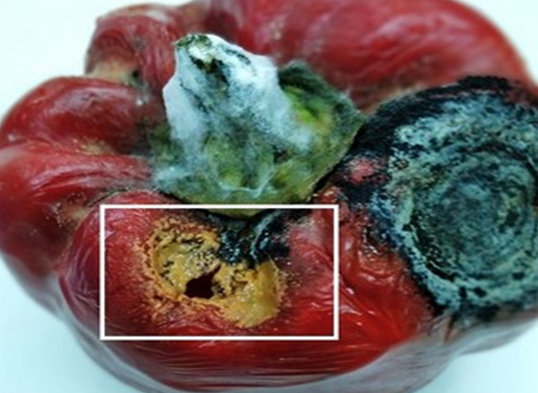
3.PHYTOPHTHORA BLIGHT(Phytophthora capsici)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
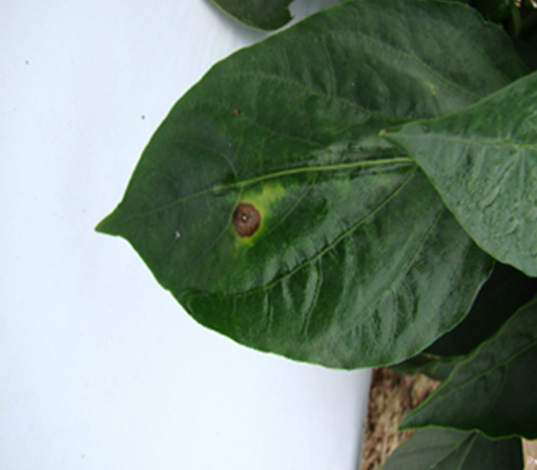
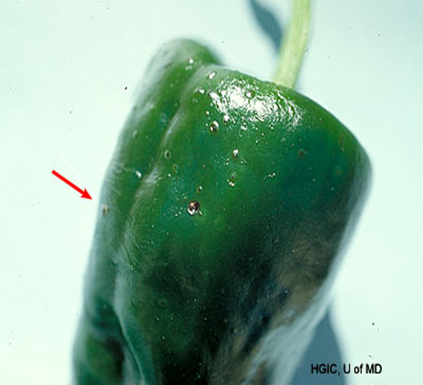
4. ANTHRACANOSE (Colletotrichum)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
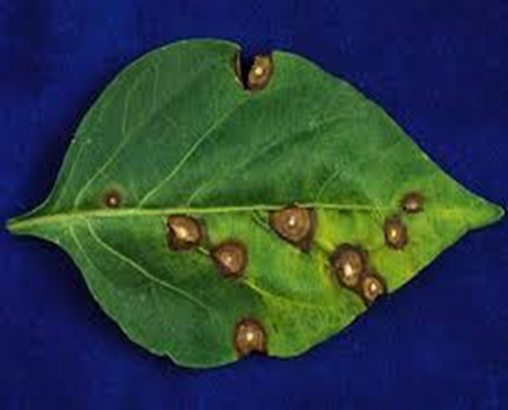
5.CERCOSPORA LEAF SPOT (Passaloracapsicicola)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
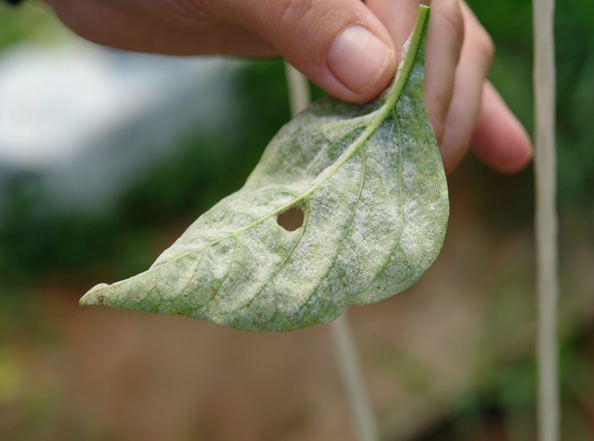
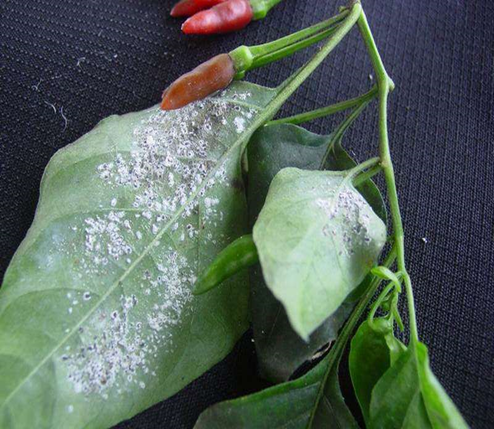
6. POWDERY MILDEW (Leveillula taurica)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (ii) SYSTEMIC-BASED
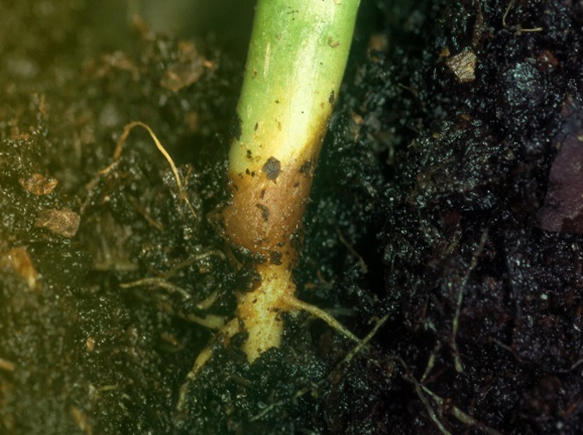
DAMPING OFF (Rhizoctonia solani)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
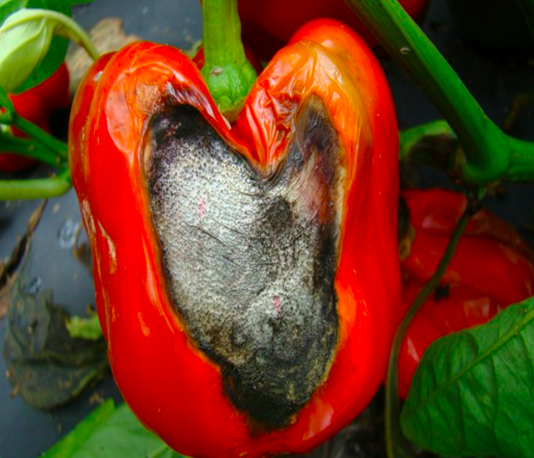
2. STEM END ROT (Phytophthora capsici)
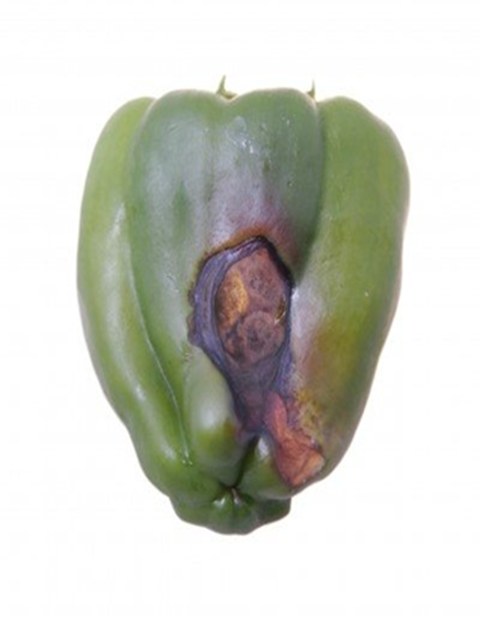
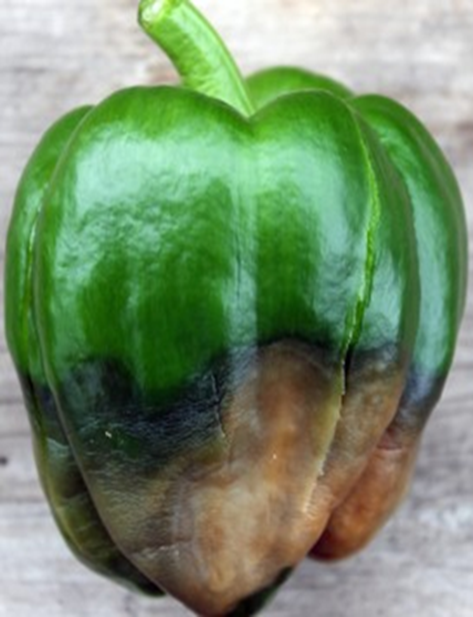


TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
B. VIRAL DISEASE:
1. CUCUMBER MOSAIC VIRUS
TREATMENT :
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water. |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water. |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water. |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water. |
 |
2. LEAF CURL VIRUS
TREATMENT :
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water. |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water. |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water. |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water. |
 |
3. PEPPER MILD MOTTLE VIRUS
TREATMENT :
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water. |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water. |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water. |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water. |
 |
C.PEST:(i) CHEWING PESTS
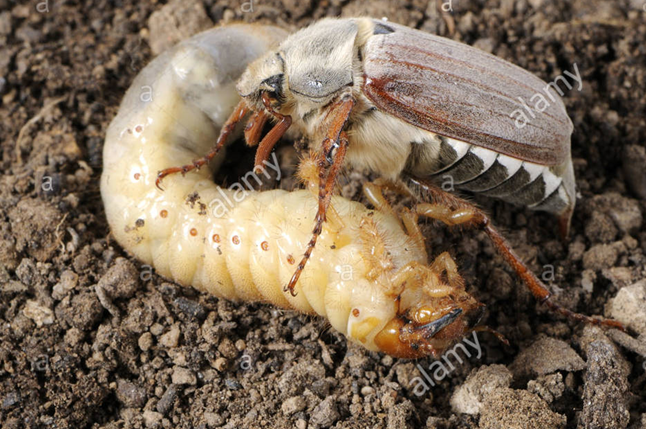
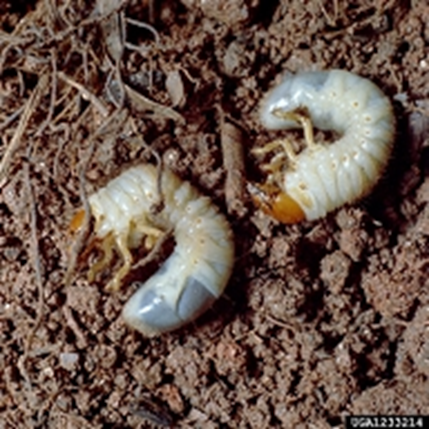
1. WHITEGRUB (Holotrichia)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
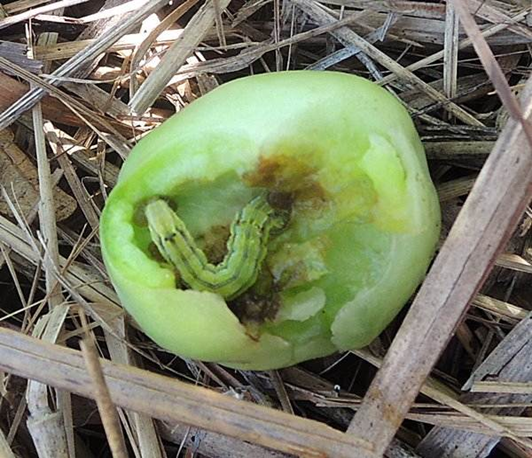
2. FRUITWORM (Helicoverpa zea)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
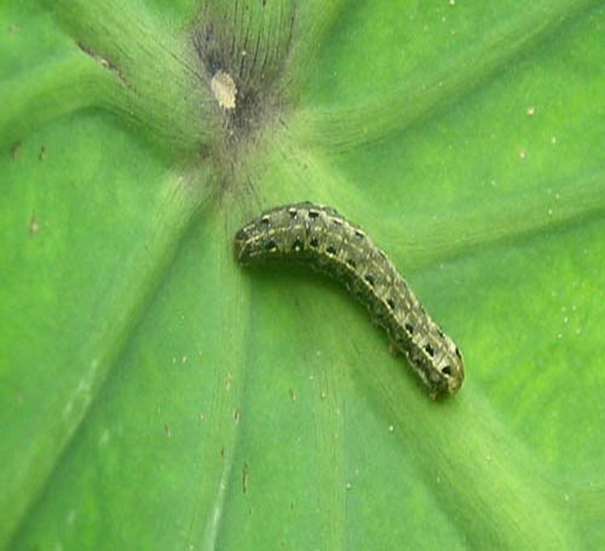
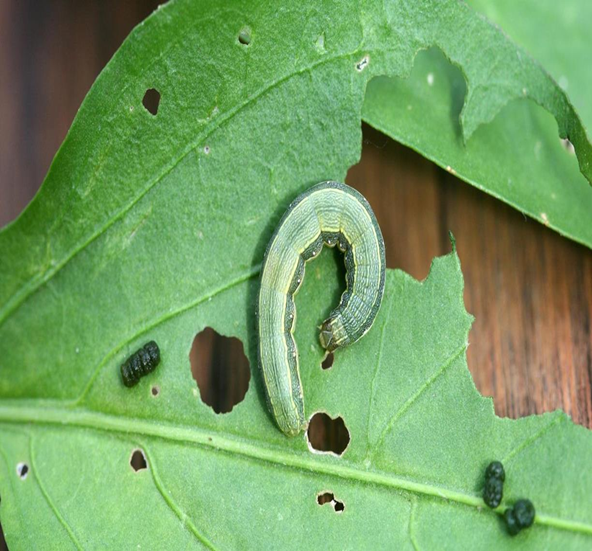
3. CATTERPILLAR (Lepidoptera)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PEST:(ii) SUCKING PESTS
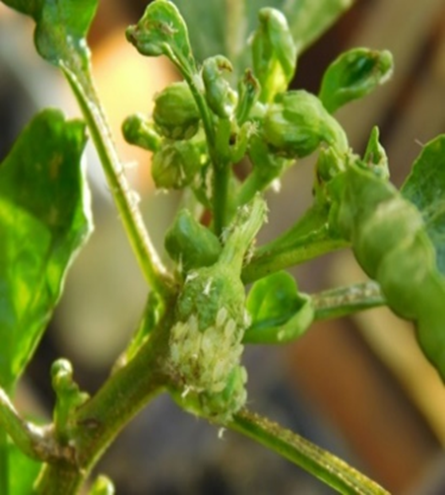
1.APHID (Aphidoidea)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
2. STINK BUG (Halyomorpha halys)
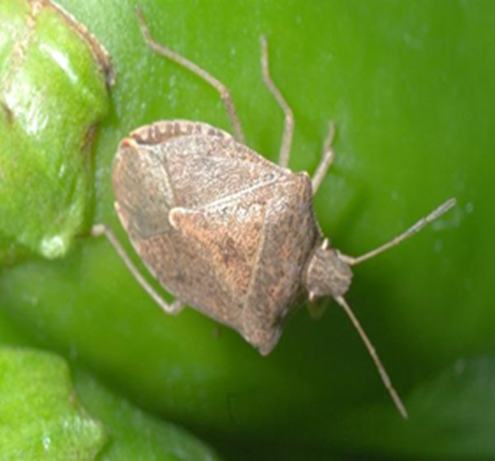
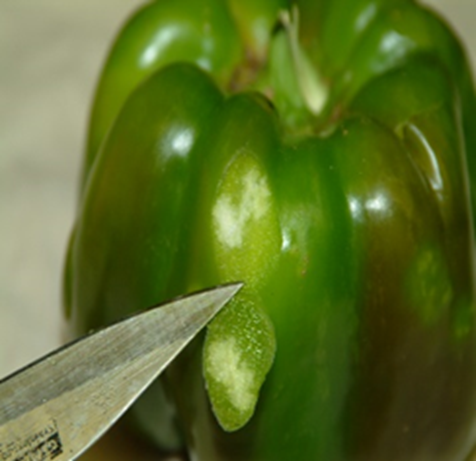
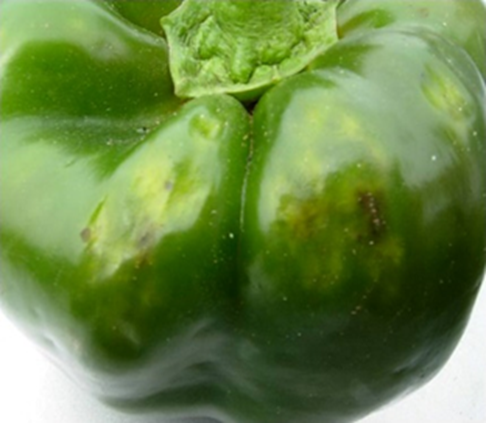



TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
3. WHITEFLY(Aleyrodidae)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
4. THRIP (Thysanoptera)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |