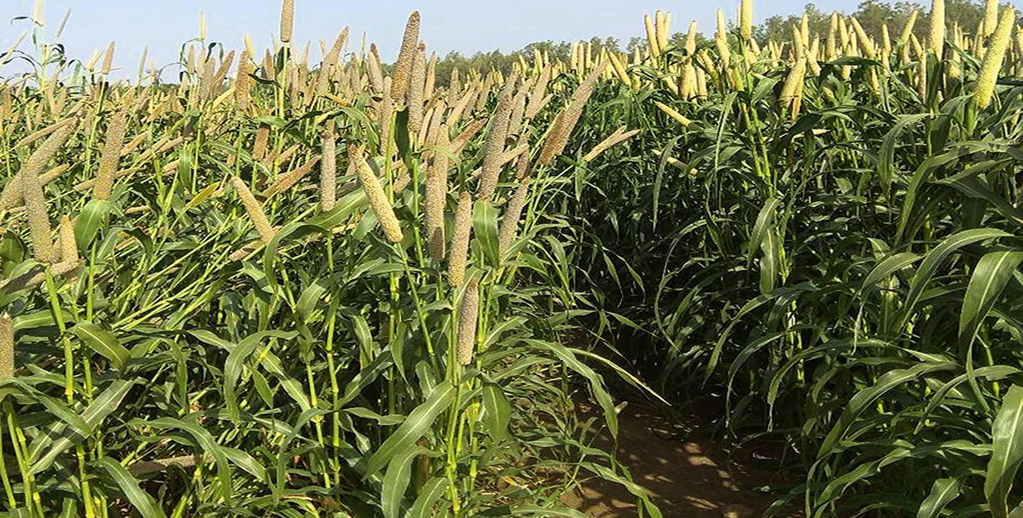
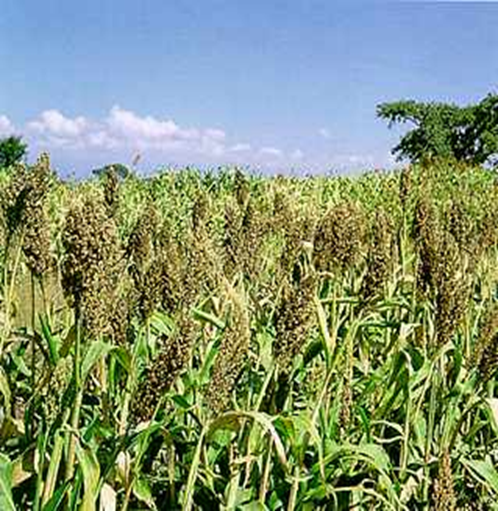
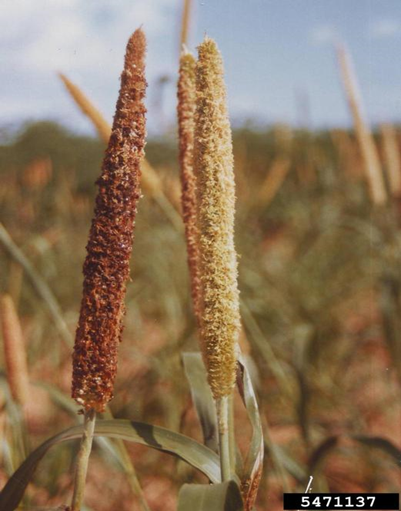
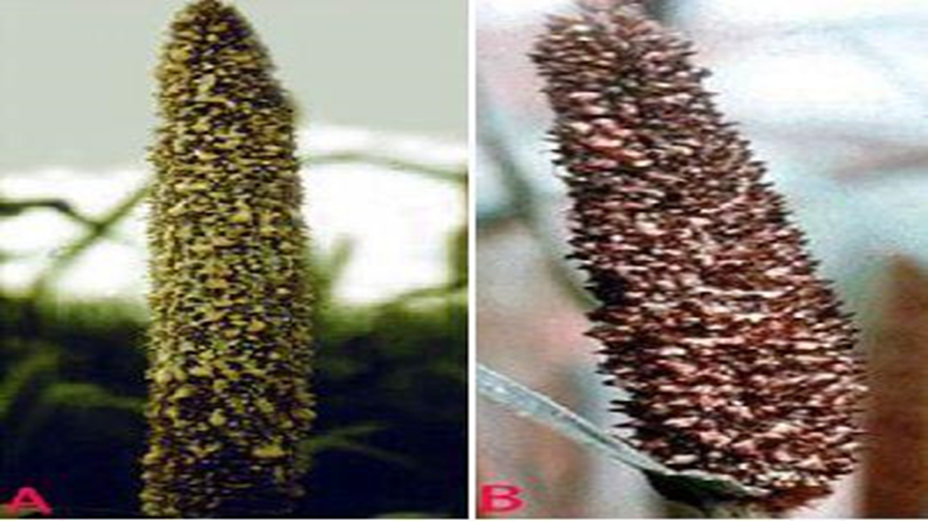
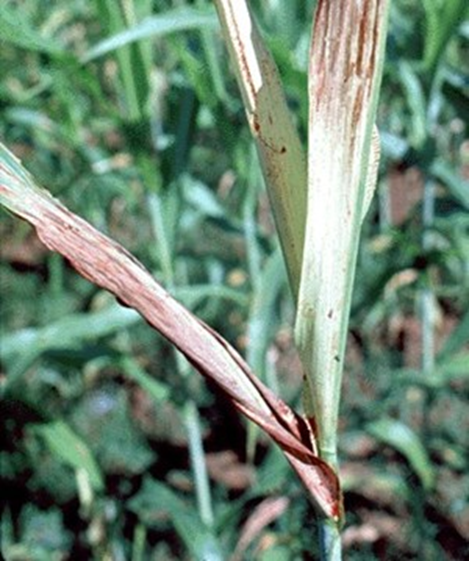
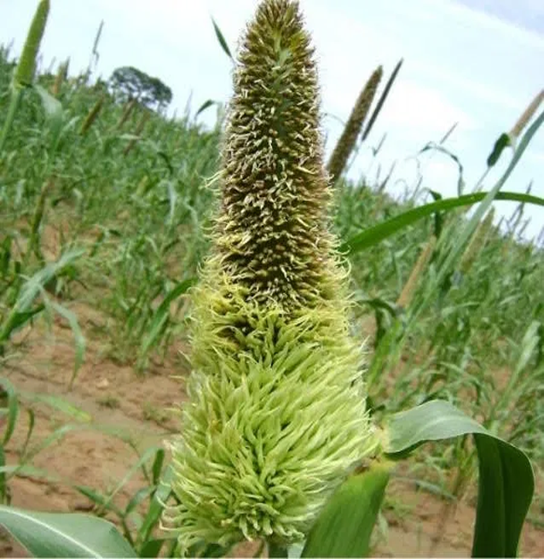
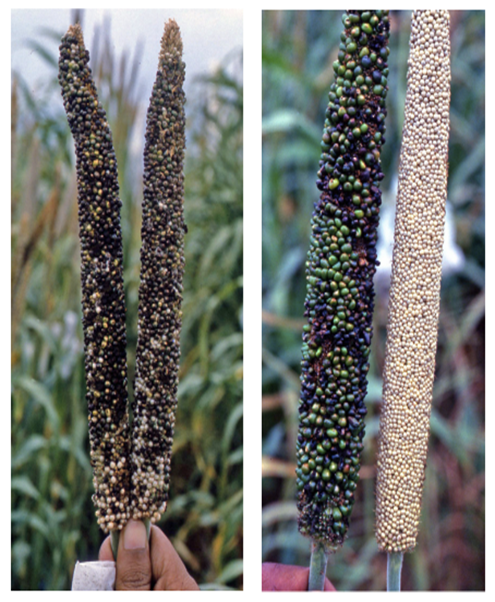
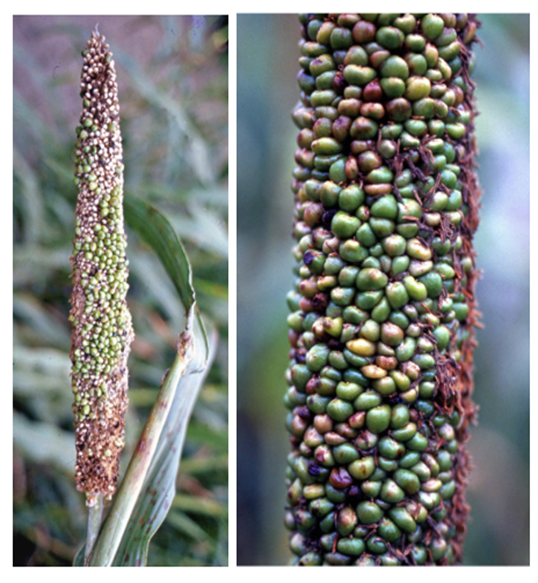
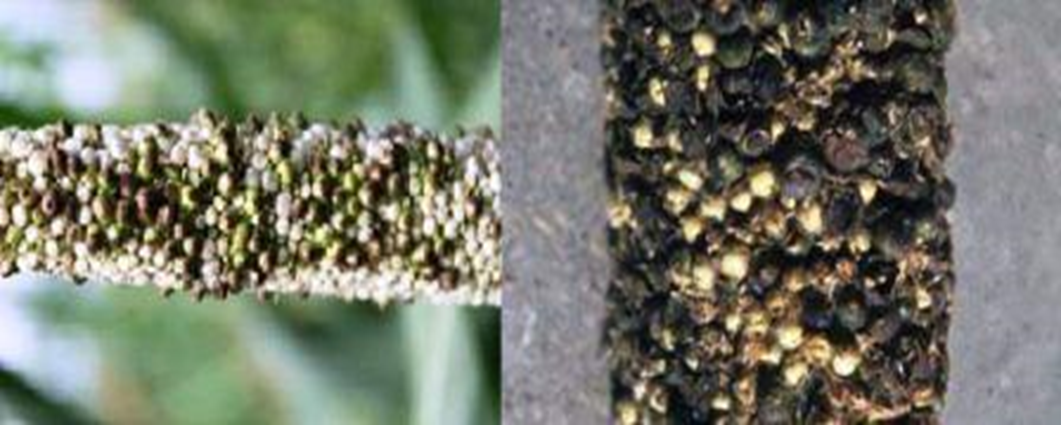
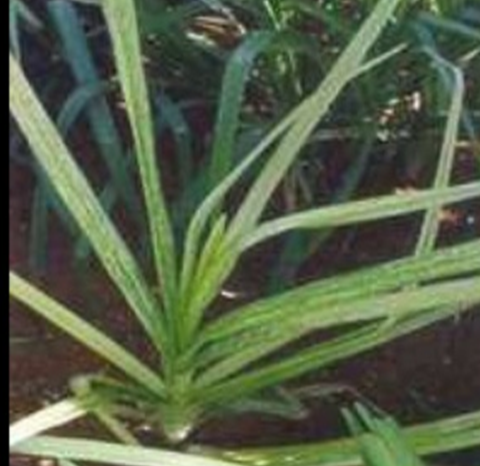
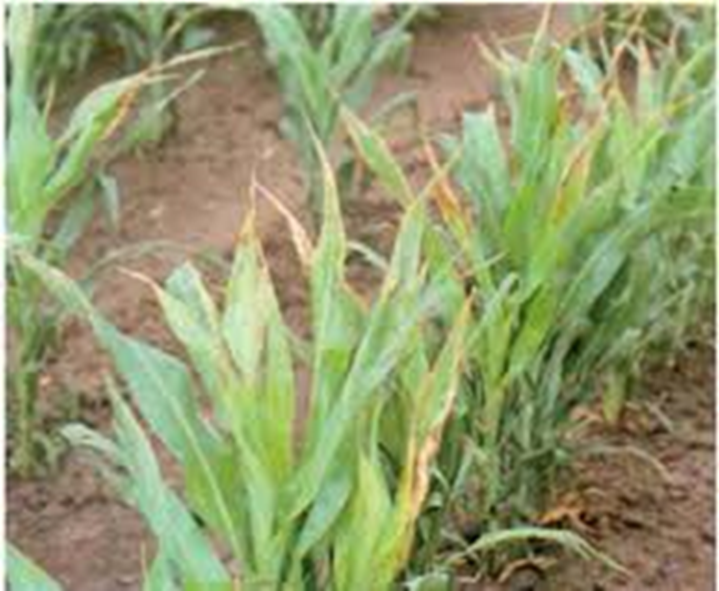
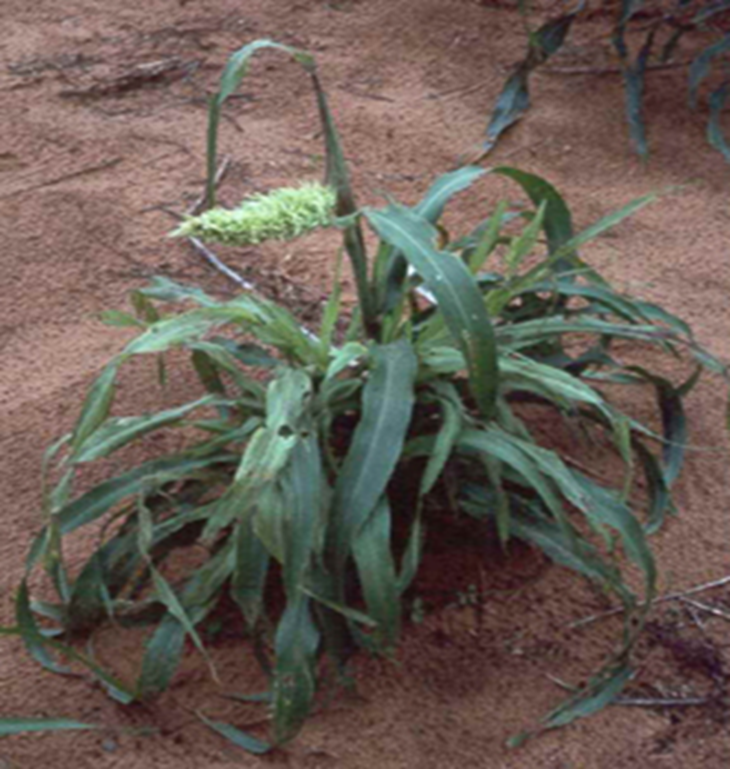
- Pennisetum glaucum is the scientific name for Pearl Millet, which belongs to the Grasses family.
- India is the world's leading pearl millet grower.
- Pearl millet is well-suited to conditions such as drought, low soil fertility, and high temperatures.
- Pearl millet is farmed on more than 26,000 square kilometers of land around the world.
- Pearl millet is a summer annual crop that is well-suited to double cropping and groundnut rotations.
• Soil- Clay loam soil.
• Cultivation- Arid-western plain.
• Susceptibility- Susceptible to pest diseases.
• Temperature- 33°–34°C.
• pH- 3.2
• Rainfall- Optimum rainfall requires 600 to 800 mm but pearl millet can be grown in areas that receive even less than 350mm of seasonal rainfall.
- If water is available during protracted dry spells, irrigation should be provided at important stages of crop growth, such as tillering, flowering and grain developmental stages.
- Pearl millet should be irrigated at regular intervals during the summer, depending on the crop's needs.
- Bajra is a rain-fed crop that requires little irrigation because of its drought resistance.
- It has been discovered that irrigating the crop at important growth stages such as maximal tillering, flowering, and grain filling will considerably improve production.
- Bajra can thrive in a variety of soil conditions.
- It grows best in black cotton soil, sandy loam soil with good drainage, and other similar conditions.
- This crop does not grow well in acidic or wet soil.
- When cultivating it, stay away from wet soil. It thrives in a low-pH environment.
- Bajra can be cultivated in areas where wheat and maize would fail.
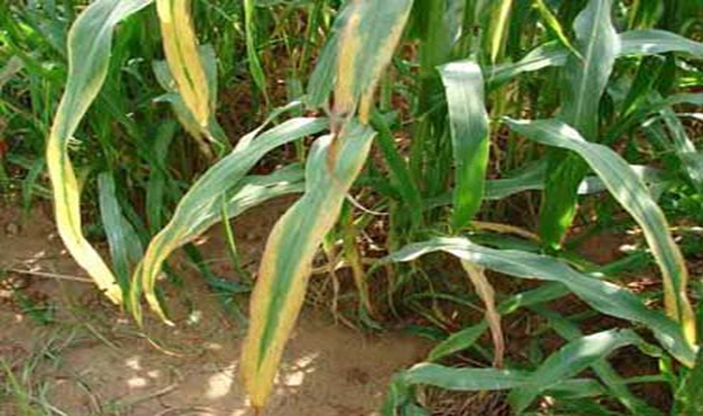
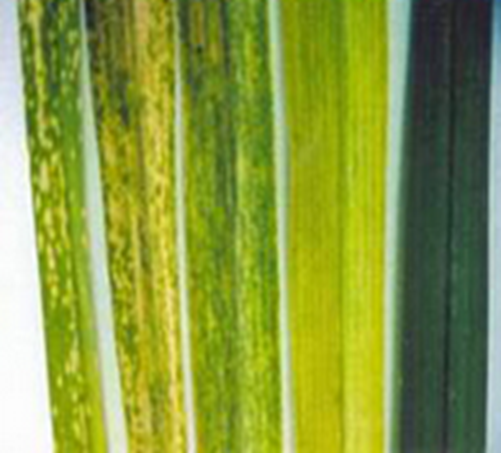
DEFICIENCY OF NITROGEN
´Yellowing that starts at the tip and moves along the center of older leaves.
´Older leaves affected first.
´Leaves are small , uniformly light green or yellowish.
´Bark is yellowish orange.
´Fruit set may be reduced.
TREATMENT :
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
DEFICIENCY OF SULFUR
´Sulphur deficiency is characterized by stunted growth, and general yellowing of plants.
´In some cases and interveinal pattern appears, the veins remaining green.
´Sulfur deficiency may also delay maturity of groundnut crop.
´ An acute sulfur deficiency causes the entire plant to turn yellow.
TREATMENT :
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
DEFICIENCY OF PHOSPHOROUS
´Small root systems; grain filling inhibited.
´Growth stunted, spindly, dark green / purple leaves with dark red coloration.
´ Leaf sheaths bend upward with red coloration leaf.
´Leave appear to be erect and leathery.
´Roots turn dark brown purple or black.
TREATMENT :
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
DEFICIENCY OF CALCIUM
´Growing points of plant may die.
´Younger leaves are affected.
´Root tip die and root growth is slow.
TREATMENT :
|
Use Calcium EDTA 0.5 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use Grow 2 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
DEFICIENCY OF IRON
´Under sever condition veins also may become chlorotic with white papery leaves.
´These areas later become brown and necrotic leading to death of the leaves and plant.
TREATMENT :
|
Use Ferric EDTA 0.5-01 gm per litre of water |
.png) |
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5ml per litre of water |
 |
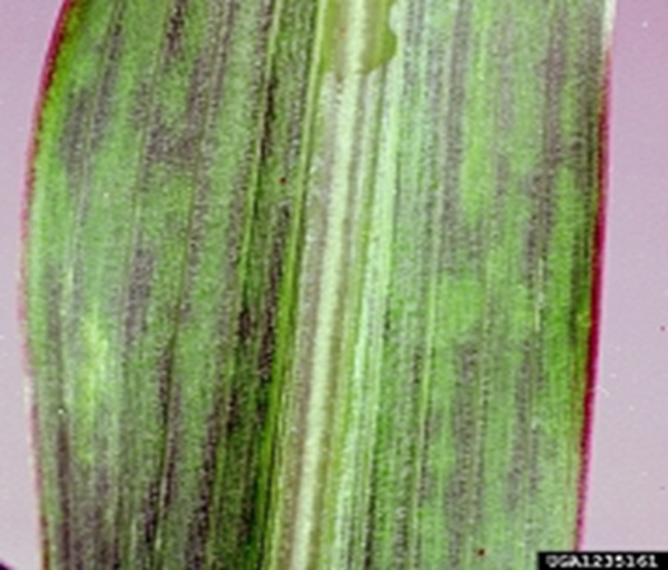
DEFICIENCY OF POTASSIUM
´Firing…drying along tips and margins of older leaves crinkled tissue within the veins and chlorotic margins.
´Older leaves affected first, necrosis advancing from margins toward mid-rib.
´Margins may first appear light green and later turn necrotic.
´Smaller, poorly coloured and low acidity fruit.
TREATMENT :
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
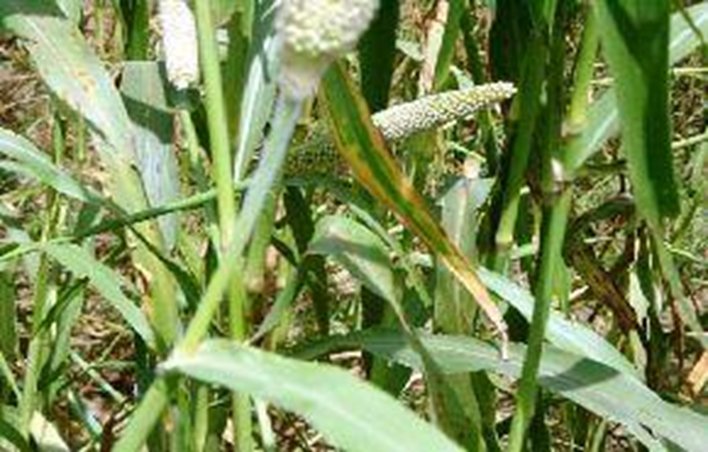
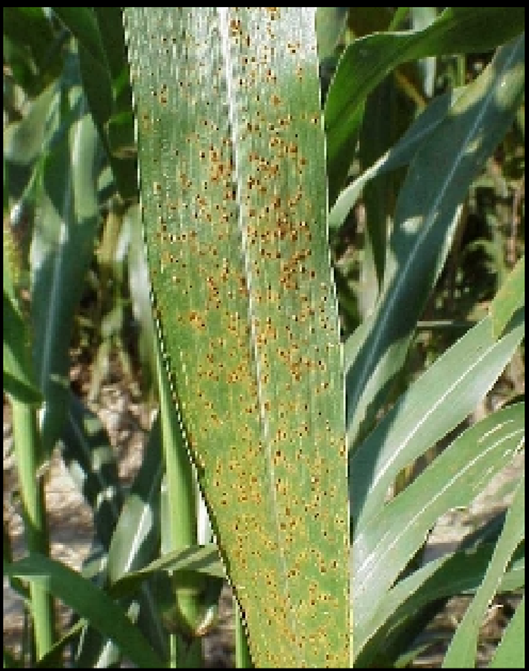
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (i) CONTACT BASED
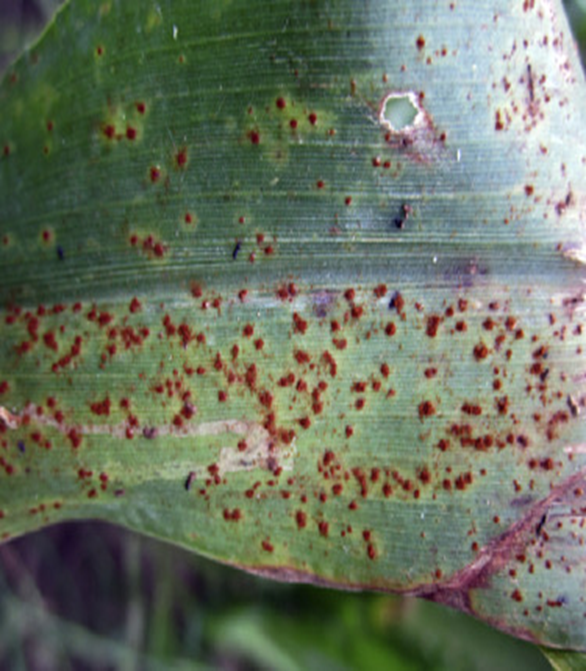
1. RUST (Puccinia substriata)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A.FUNGAL DISEASES: (i) CONTACT BASED
2. ERGOT (Claviceps)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A.FUNGAL DISEASES: (i) CONTACT BASED
3. DOWNY MILDEW (Sclerospora graminicola (Sacc.) Schroet)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (i) CONTACT BASED
4. SMUT (Tolyposporium penicillariae
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (ii) SYSTEMIC BASED
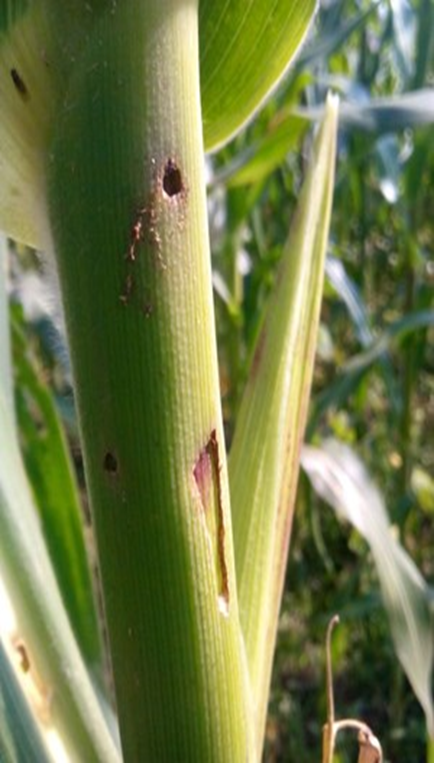
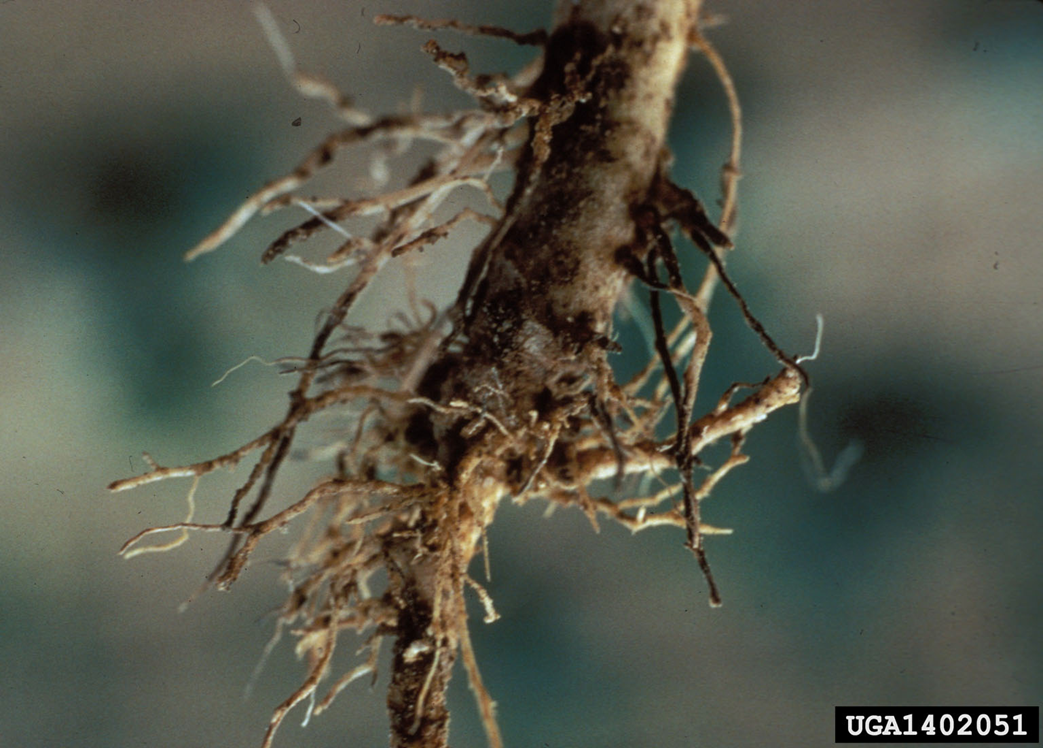
1. ROOT ROT (Phytophthora)

A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (ii) SYSTEMIC BASED
2. STEM END ROT (Pennisetum glaucum)
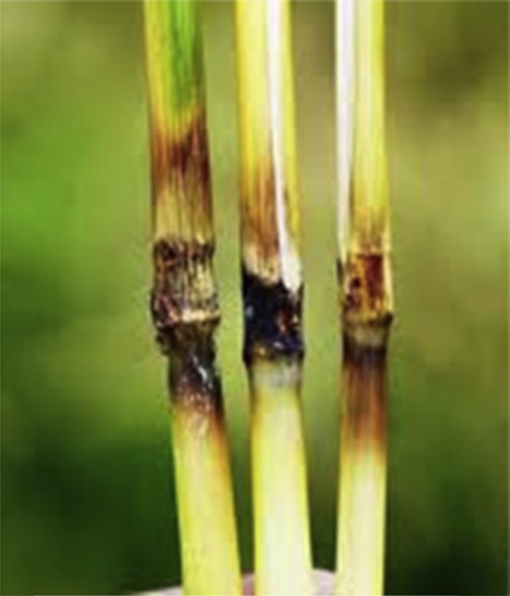
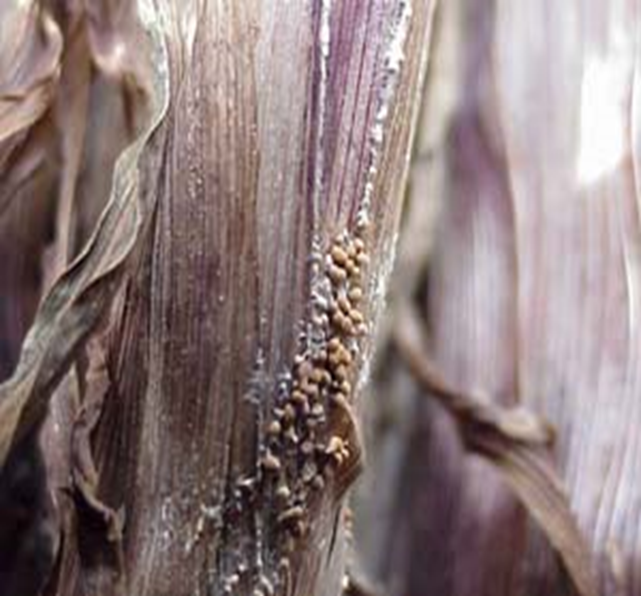
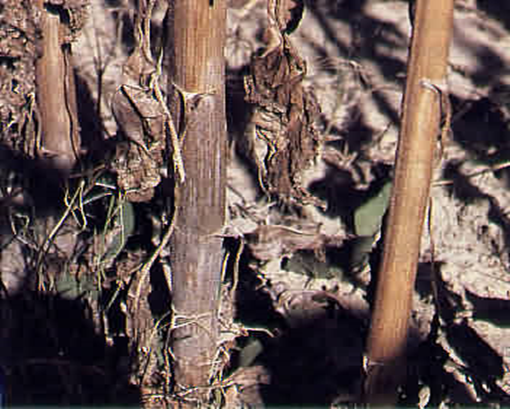



TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (ii) SYSTEMIC BASED
3. BLACK ROOT ROT (Mycosphaerella fijiensis)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
B.VIRUS ATTACK
1. RAGI MOTTLE STREAK VIRUS
TREATMENT :
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
B.VIRUS ATTACK
2. BLACK STREAKED DWARF VIRUS
TREATMENT :
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
B.VIRUS ATTACK
3. PANICUM MOSAIC VIRUS
TREATMENT :
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
B.VIRUS ATTACK
4. MAIZE DWARF MOSAIC VIRUS
TREATMENT :
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
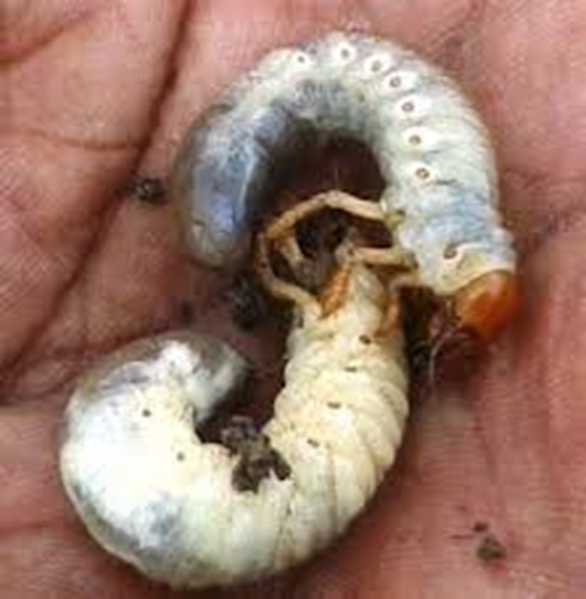
C. PEST:(i) CHEWING PESTS
1. WHITE GRUB (Holotrichia serrata)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PEST:(i) CHEWING PESTS
2. CUTWORM (Dark sword-grass)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
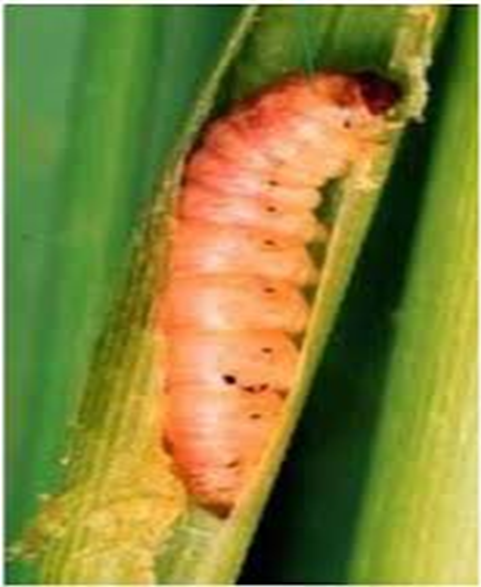
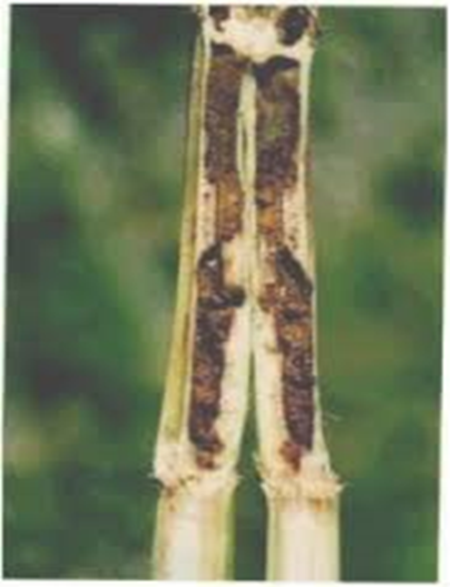
C. PEST:(i) CHEWING PESTS
3. STEM BORER (Scirpophaga incertulas)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PEST:(ii) SUCKING PESTS
1. APHID (Aphidoidea)
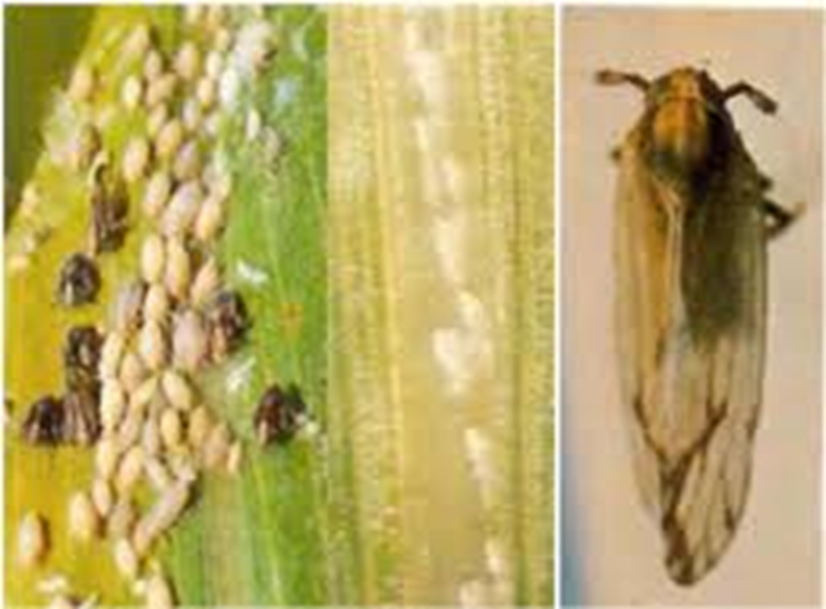

TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PEST:(ii) SUCKING PESTS
2. THRIP (Thysanoptera)
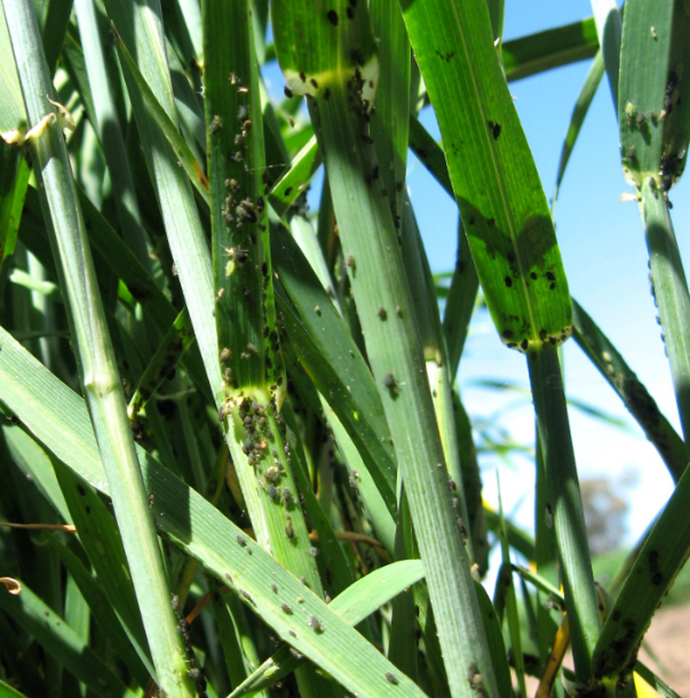

TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PEST:(ii) SUCKING PESTS
3. WHITEFLY (Aleyrodidae)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |