- Mango are a member of the family Anacardiaceae.
- Mango is the national fruit of India.
- Mango is a sweet tropical fruit as well as the name of the trees that produce it.
- Mango ranks first position in all fruit crops and occupies 43% area of total area under fruit crops in India.
- The availability of rain or artificial irrigation during important phases of tree growth and fruit development is critical to the success of mango plantations.
• Soil - Ideal soil for mango is red loamy.
• pH- 6.5-8.0
• Climate - warm weather
• Temperature- Mango prefers a warmer climate with an acceptable temperature range being between 23º- 26º C.
•Rainfall - 890-1,015 mm in a year
- Irrigation intervals are determined by the age of the tree, the soil, and the environment.
- The interval should be 2 to 6 days for the first six months after planting, weekly for 6 to 12 months old plants, and 7 to 20 days until the plants reach bearing age.
- The frequency of irrigation in light soils is higher than in heavy soils.
- For 30 days before flowering season, avoid irrigation and fertigation to induce stress.
- Grafting can be done in the months of March and April, as well as in the months of August and September.
- During the summer, the pits are dug and filled with 20-25 kg of well-rotten farm-yard manure and garden soil.
- The planting distance varies according to the cultivator. However, in all directions, an 8-10 m gap is recommended.
- Slit the hard husk of a fresh mango pit. Remove the seed from the inside and place it in a large pot with seed starter mix.
- Place the seed in a 14-inch hole.
- Irrigate the young fruit plants that have just been planted.
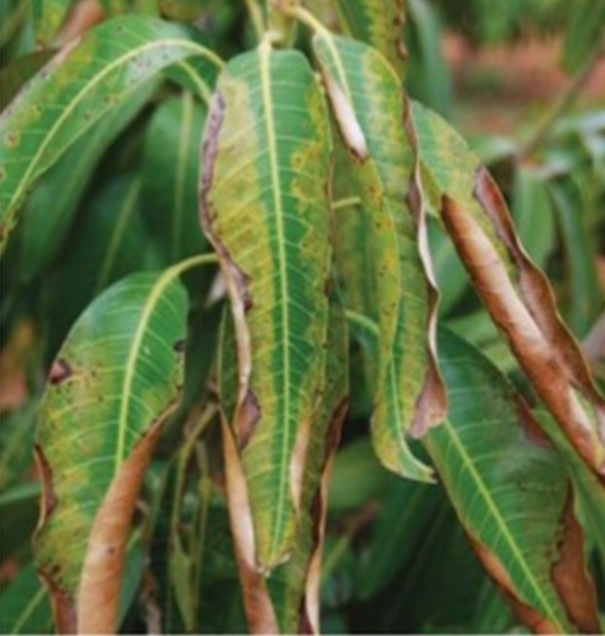
DEFICIENCY OF NITROGEN
TREATMENT :
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5ml per litre of water |
 |
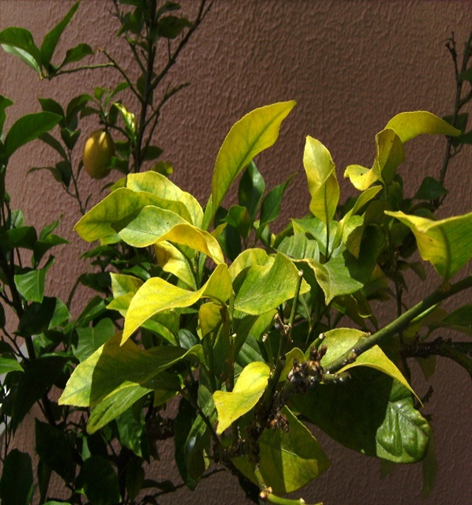
DEFICIENCY OF PHOSPHORUS
TREATMENT :
|
Use Ferric EDTA 0.5-01 gm per litre of water |
.png) |
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
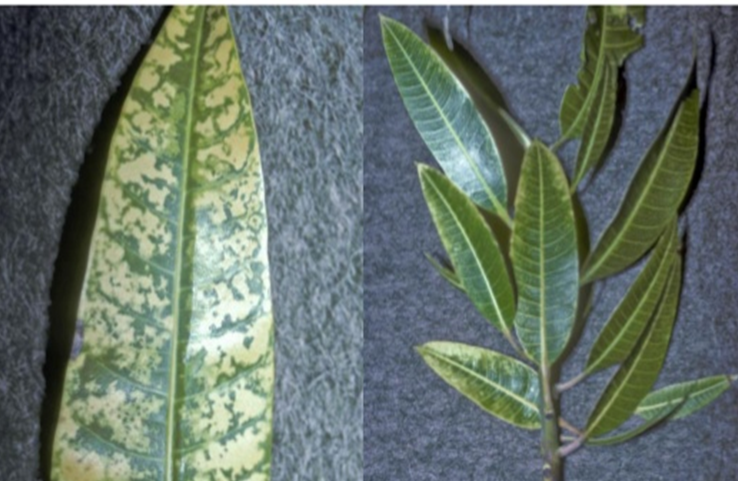
TREATMENT :
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use Grow 2 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
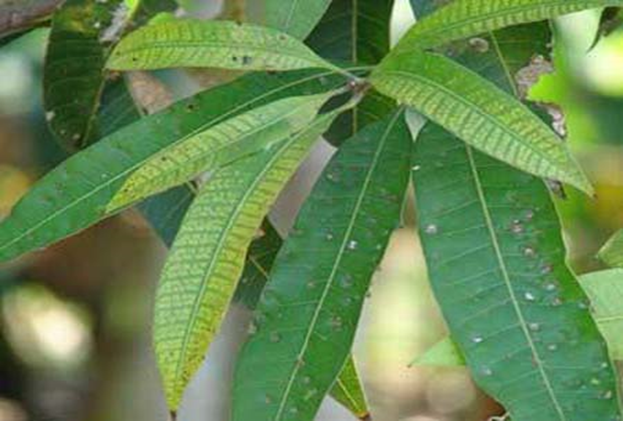
TREATMENT :
|
Use Manganese EDTA 0.5 gm per litre of water |
.png) |
|
Use Grow 2 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
TREATMENT :
|
Use Calcium EDTA 0.5g per litre of water |
 |
|
Use BLOOM 2 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES:(i) CONTACT BASED
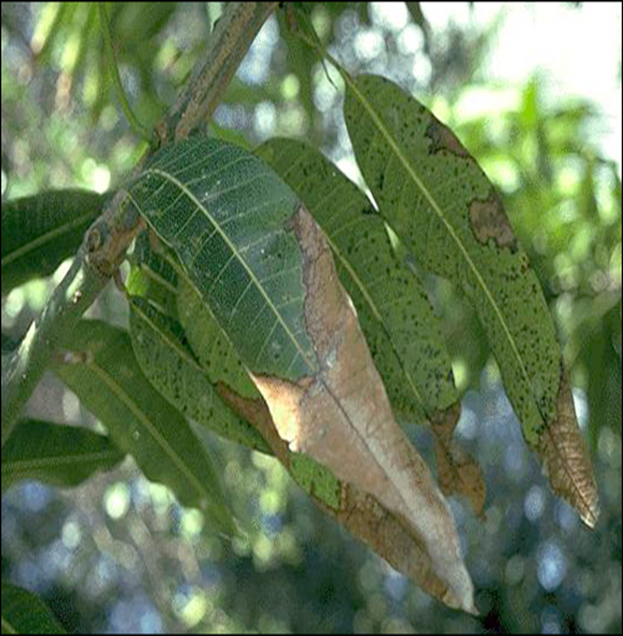
1. ANTHRACNOSE (Colletotrichum gloeosporioides)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (i) CONTACT BASED
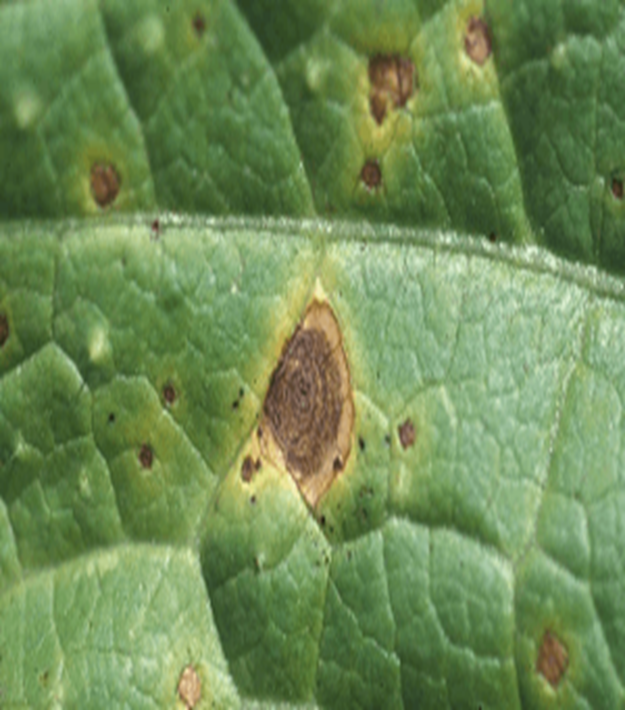
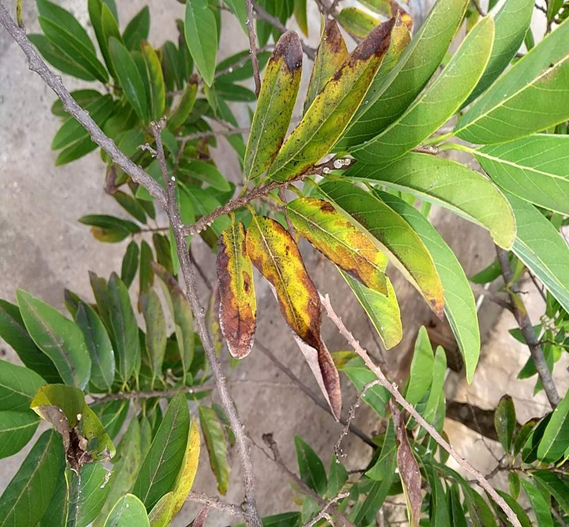
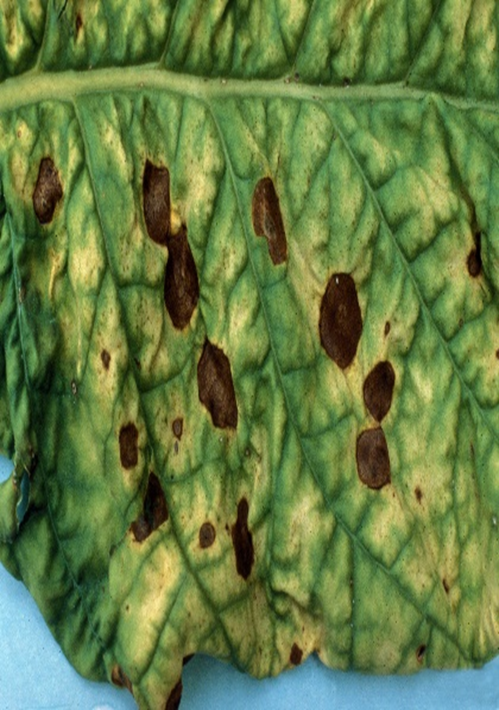
2. ALTERNARIA LEAF SPOT (Alternaria alternata)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (i) CONTACT BASED
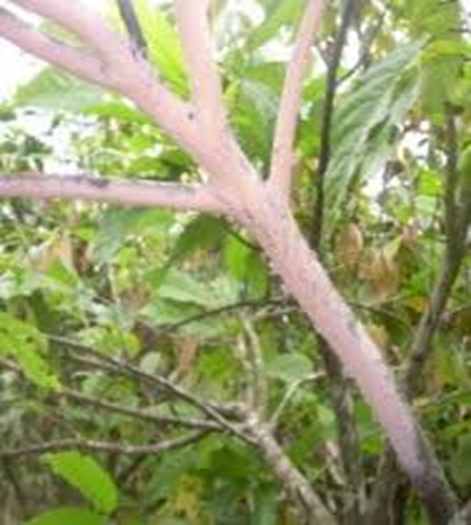
3. PINK DISEASE (Erythricium salmonicolor)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES:(i) CONTACT BASED
4. POWDERY MILDEW (Oidium mangiferae)
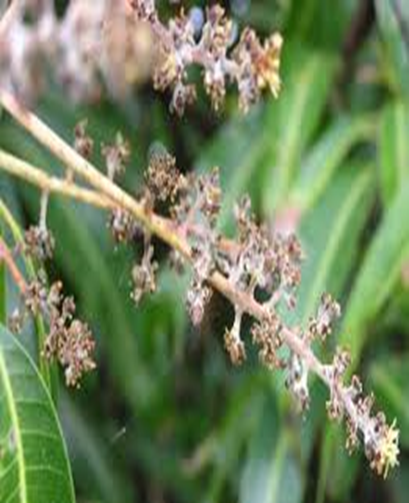
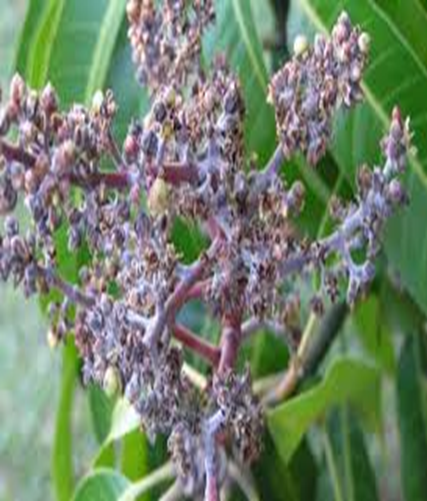



TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES:(i) CONTACT BASED
5. SOOTY MOULD(Capnodium mangiferae)
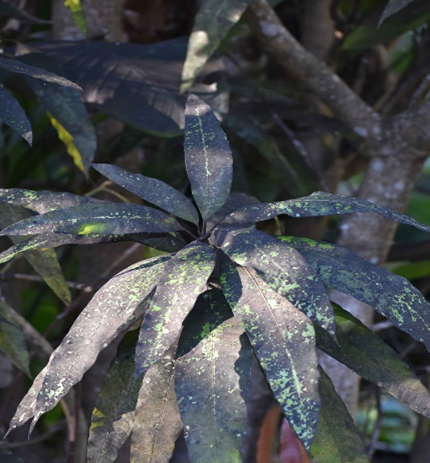
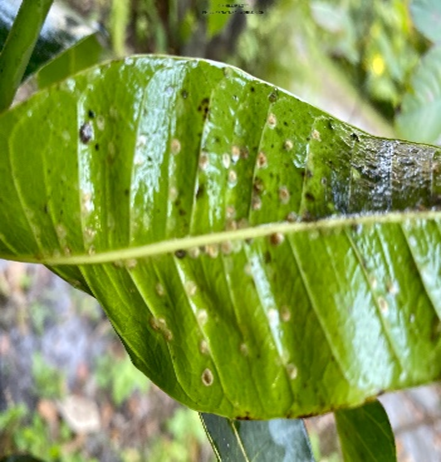
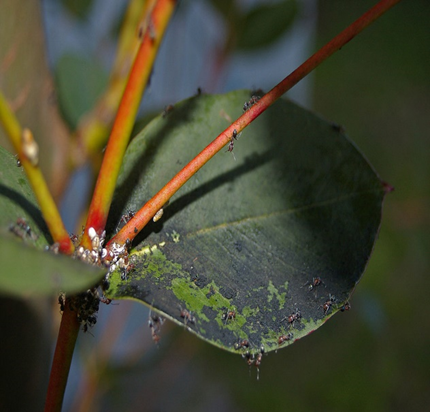



TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES:(i) CONTACT BASED
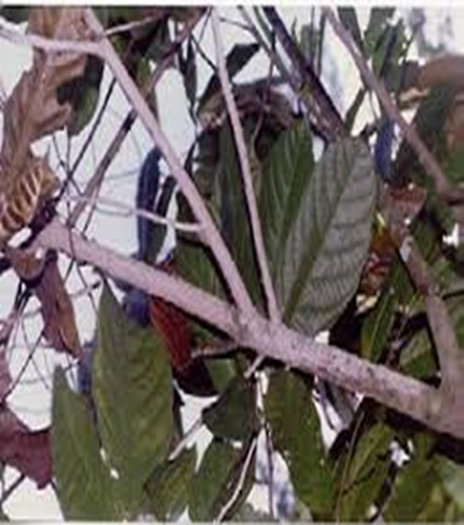
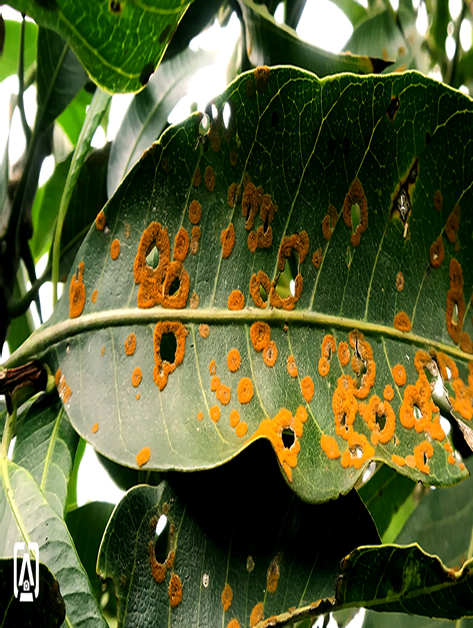
6. RED RUST (Cephaleuros virescens)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES:(i) CONTACT BASED
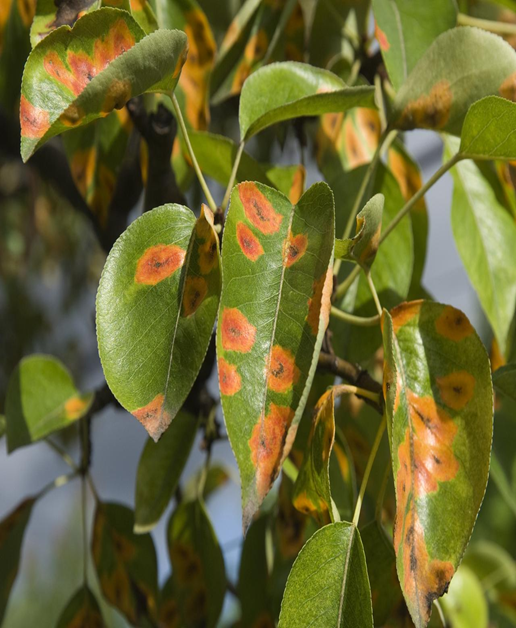
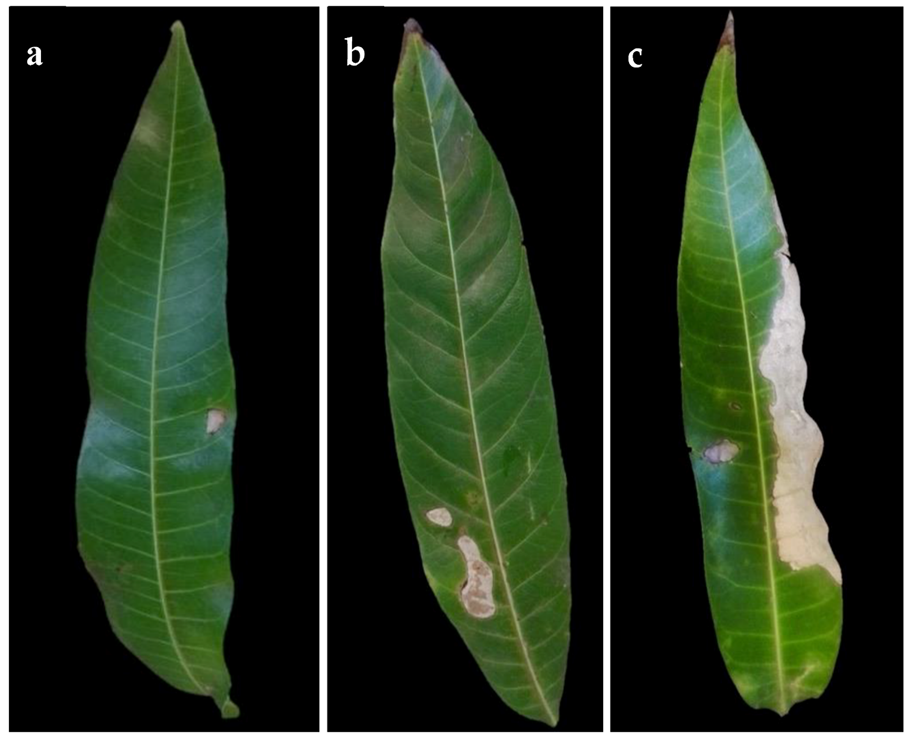
7. GREY BLIGHT (Pestalotia mangiferae)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES:(ii) SYSTEMIC BASED
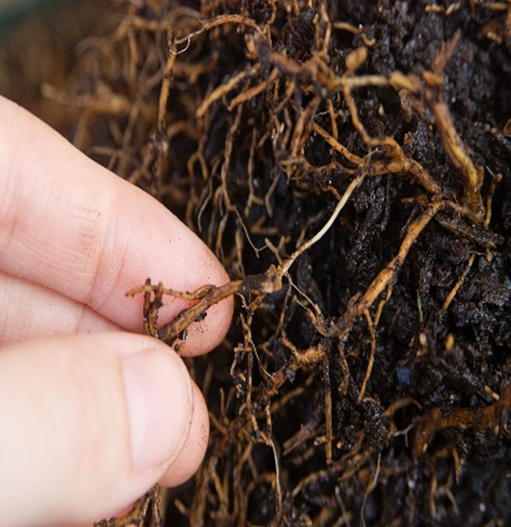
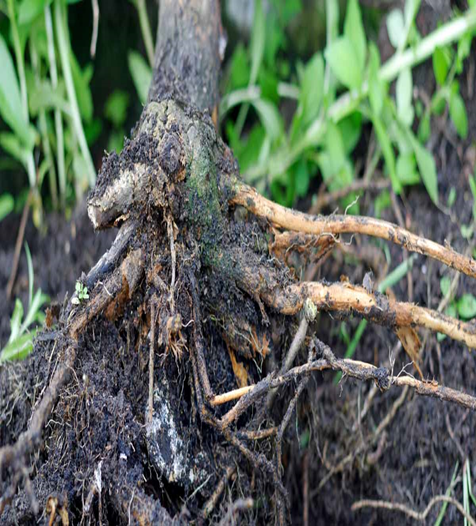
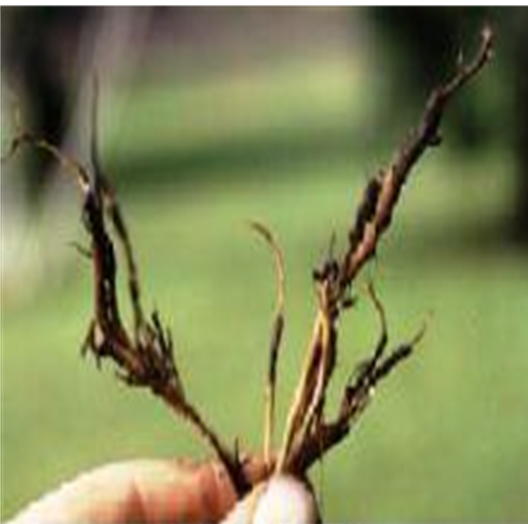
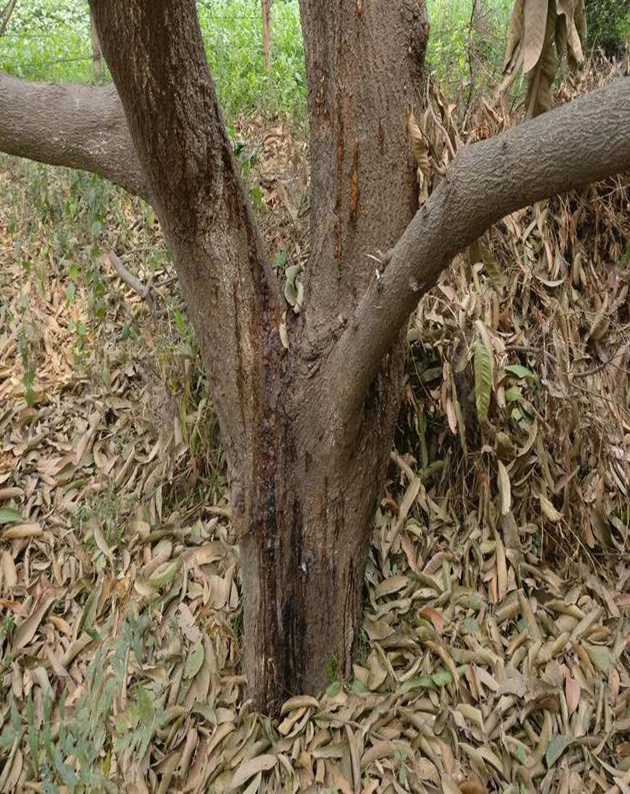
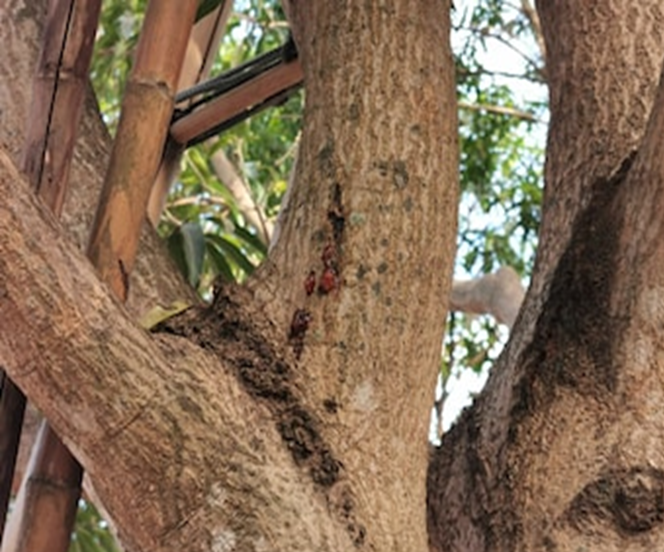
1. ROOT ROT(Phytophthora palmivora)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES:(ii) SYSTEMIC BASED
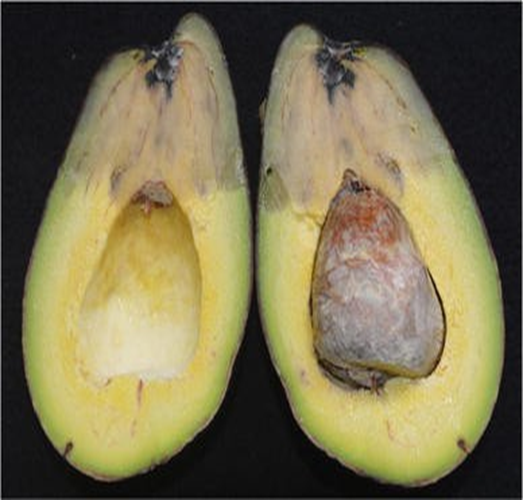
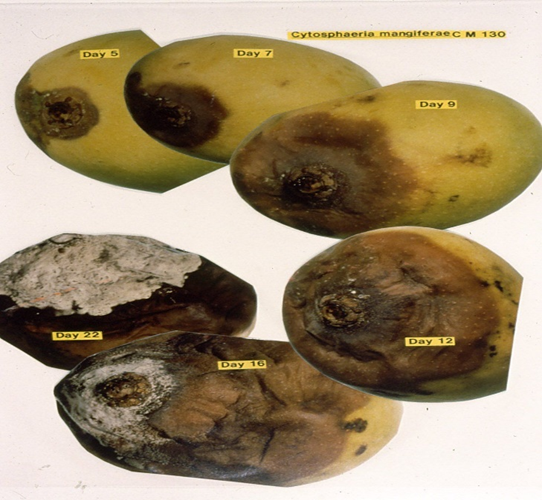
2. STEM END ROT (Diplodia natalensis)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES:(ii) SYSTEMIC BASED
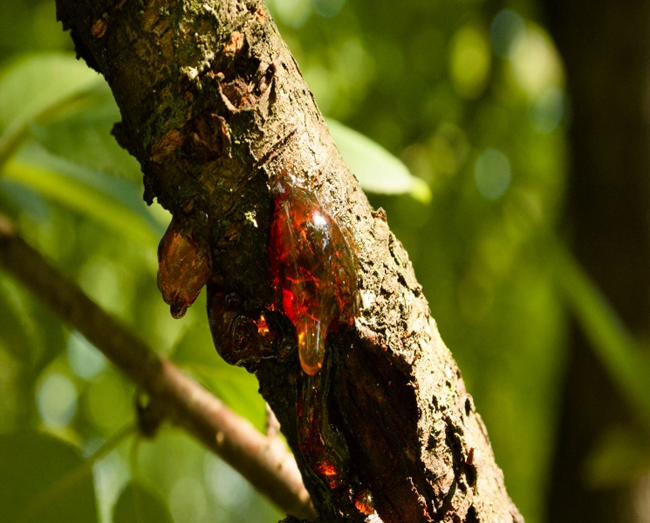
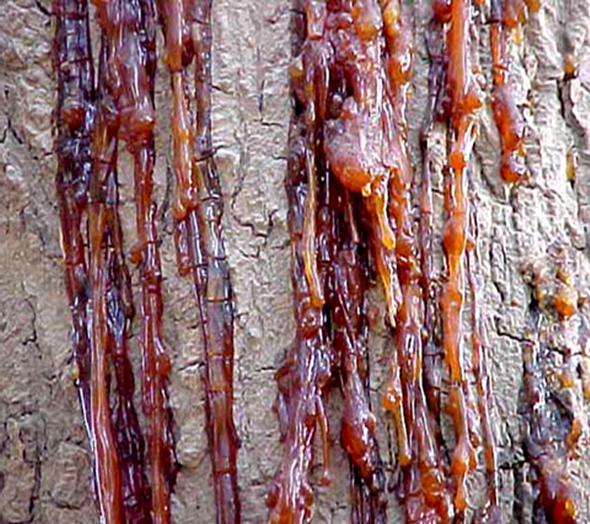
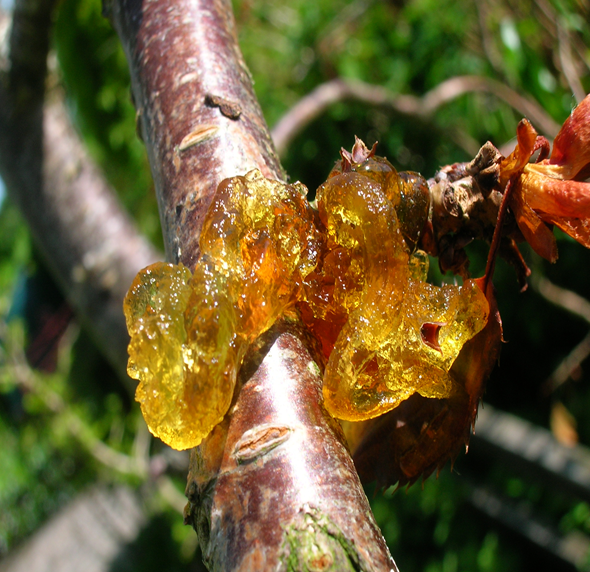
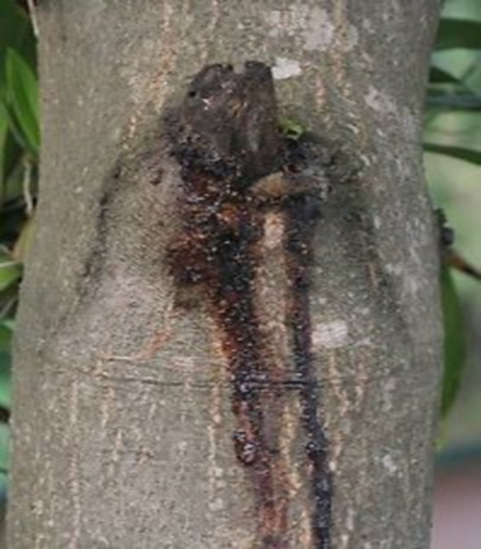
3. GUMMOSIS (Lasiodiplodia theobromae)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES:(ii) SYSTEMIC BASED
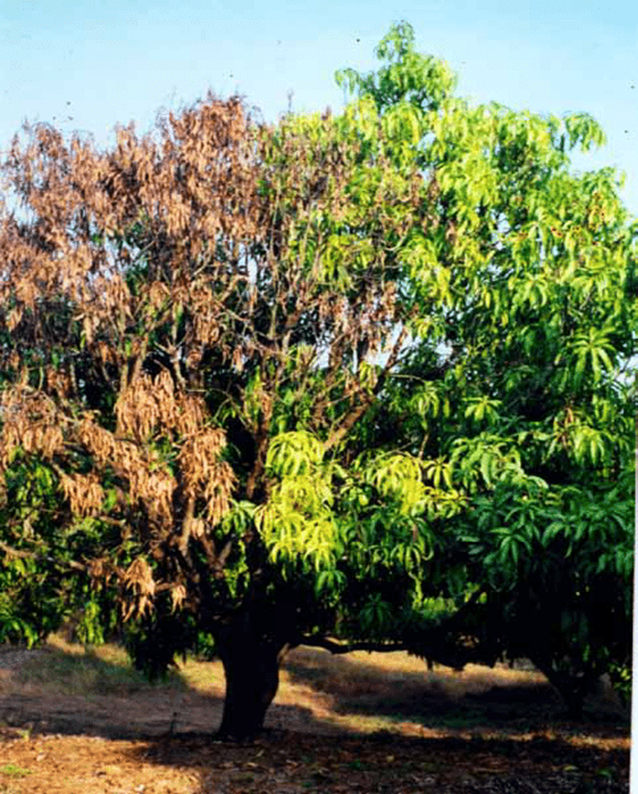
4. DIE BACK (Lasiodiplodia theobromae)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PESTS: (i)CHEWING PESTS
1. STEM BORER (Batocera rufomaculata)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PESTS: (i)CHEWING PESTS
2. BARK BORER (Indarbela tetraonis)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PESTS: (i)CHEWING PESTS
3. SHOOT BORER (Clumetia transversa)
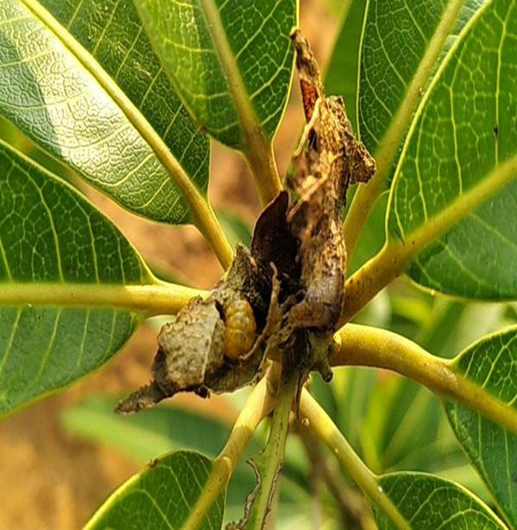
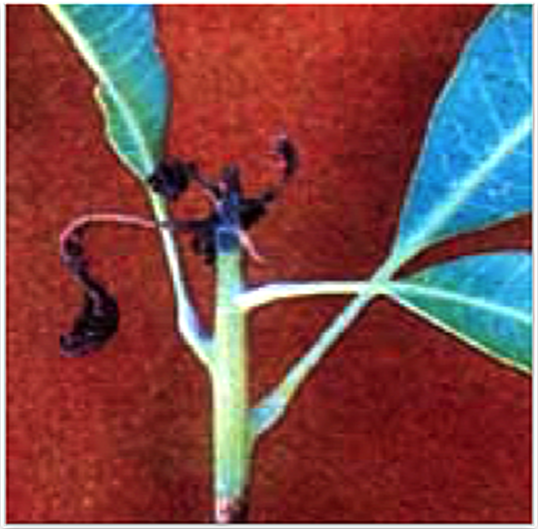
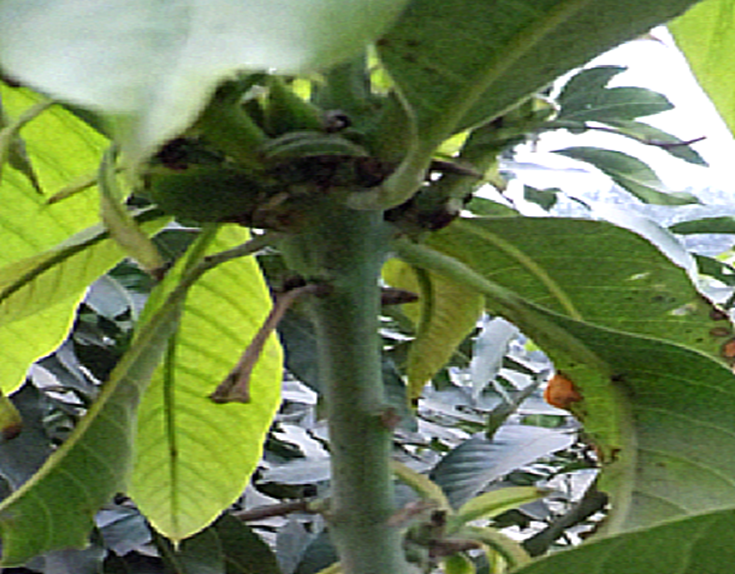



TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PESTS:(i)CHEWING PESTS
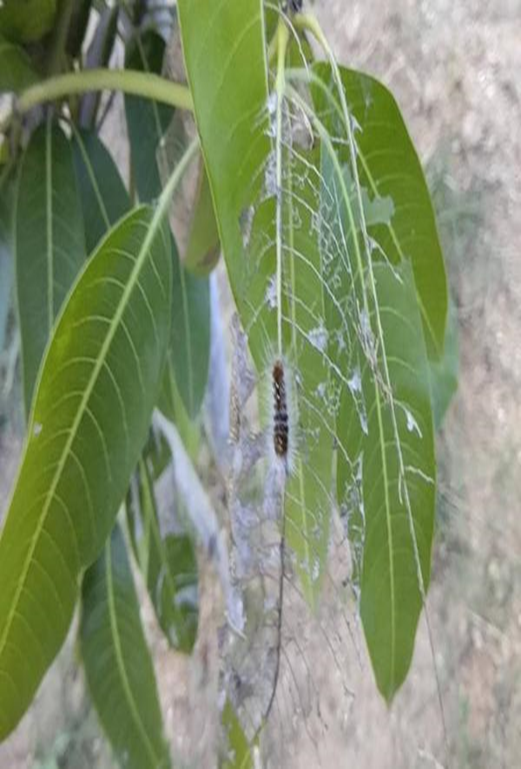
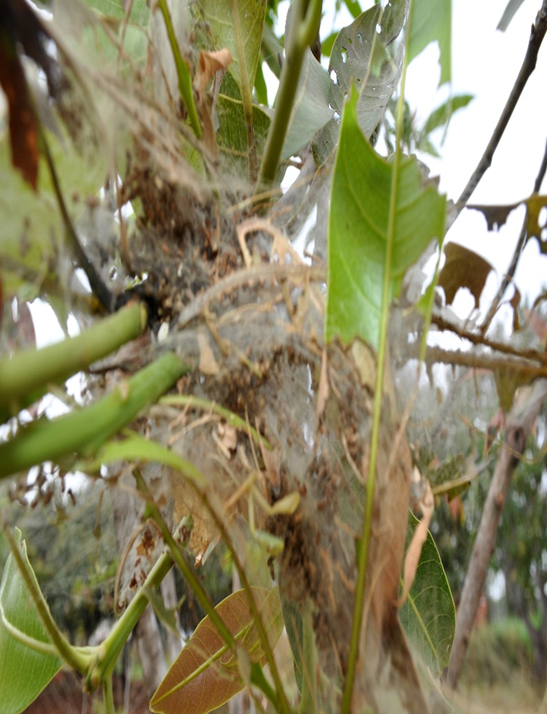
4. HAIRY CATERPILLAR (Amsacta albistriga)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PESTS: (i)CHEWING PESTS
5. SHOOT WEBBER (Orthaga exvinacea)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PESTS:(i)CHEWING PESTS
6. MANGO NUT WEEVIL (Sternochaetus mangiferae)
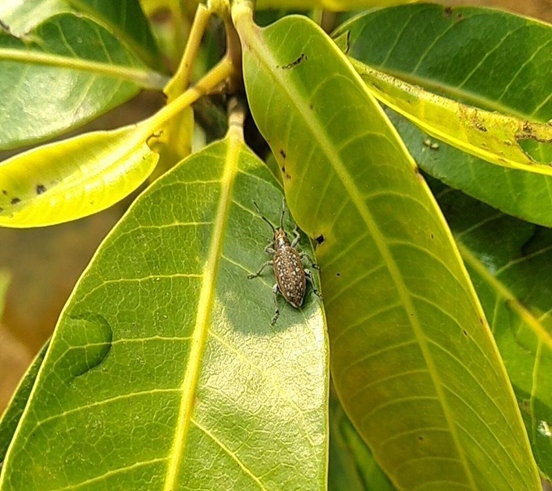
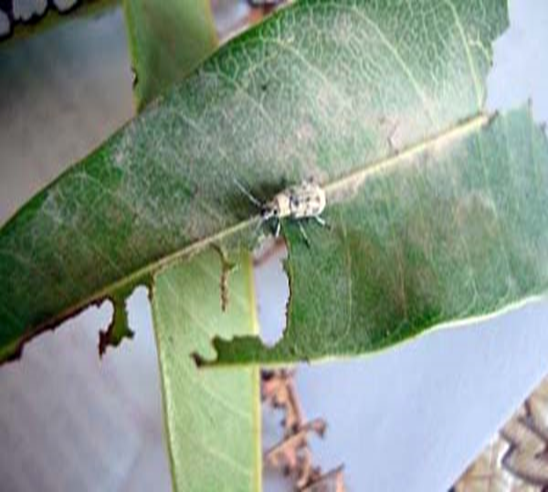
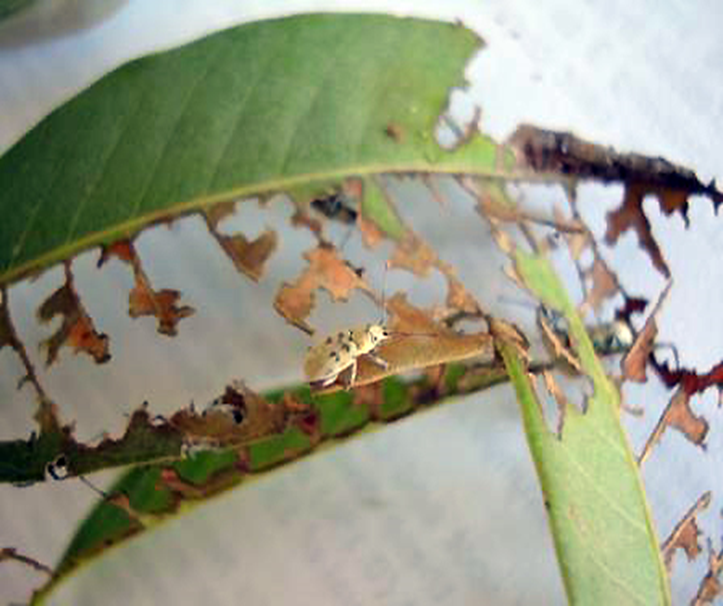



TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PESTS: (i)CHEWING PESTS
7. FRUIT FLY (Bactrocera (Dacus) dorsalis)
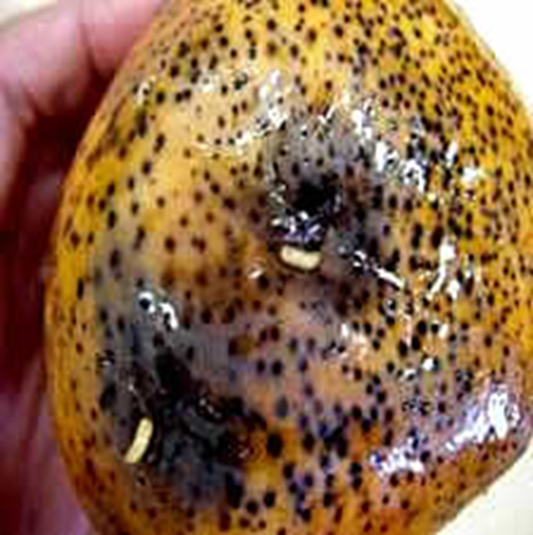
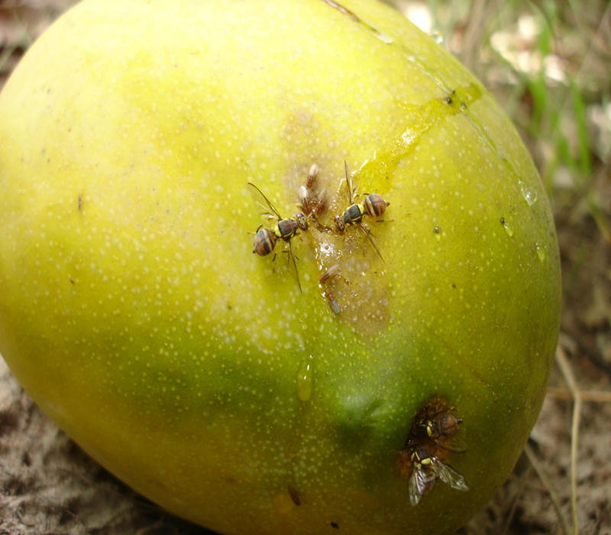
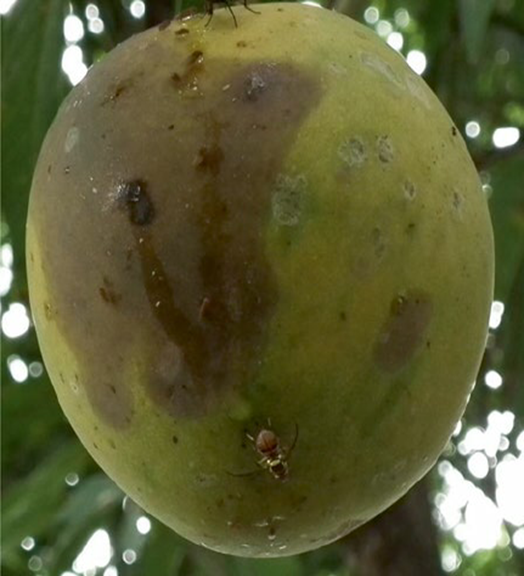



TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PESTS: (ii) SUCKING PESTS
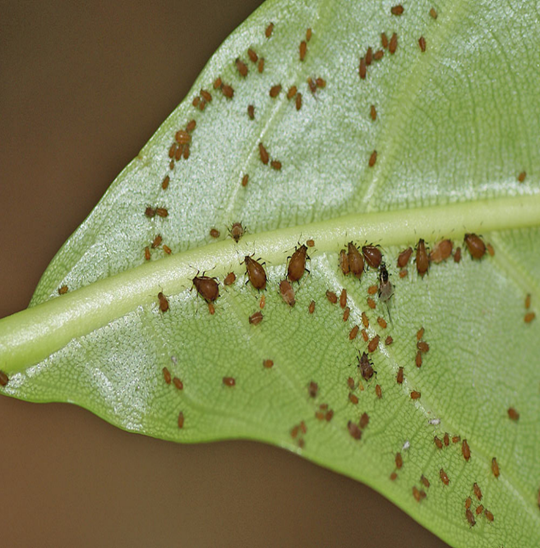
1. APHID (Toxoptera odinae)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PESTS: (ii)SUCKING PESTS
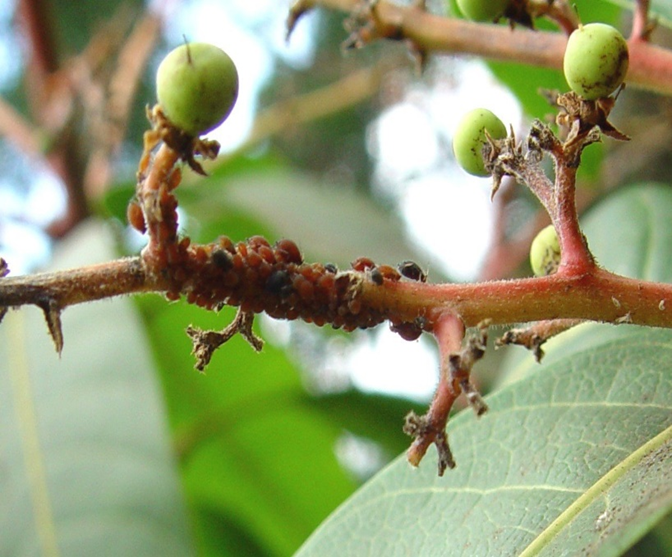
2. SCALE (Coccoidea)
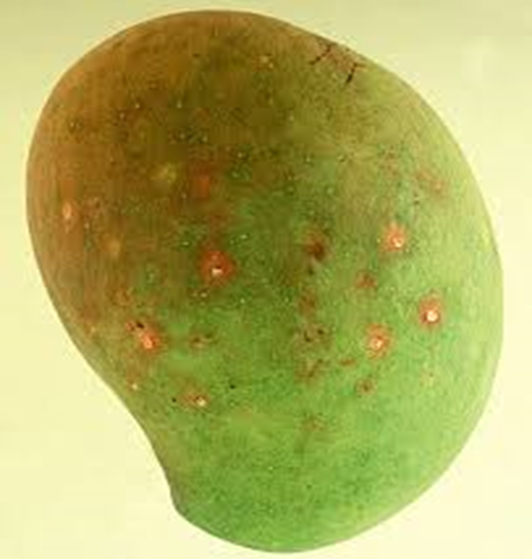
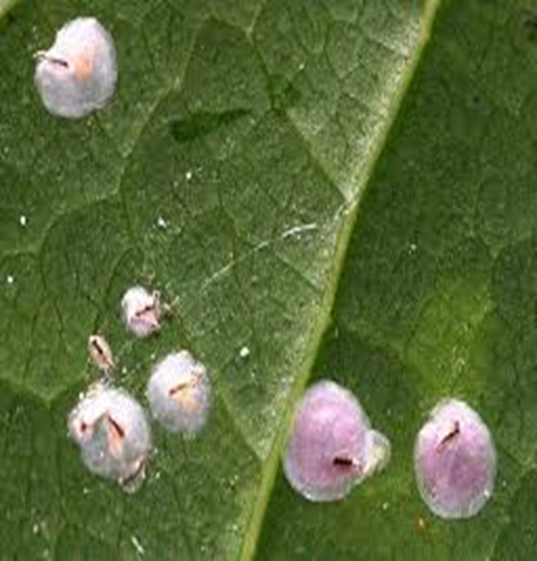
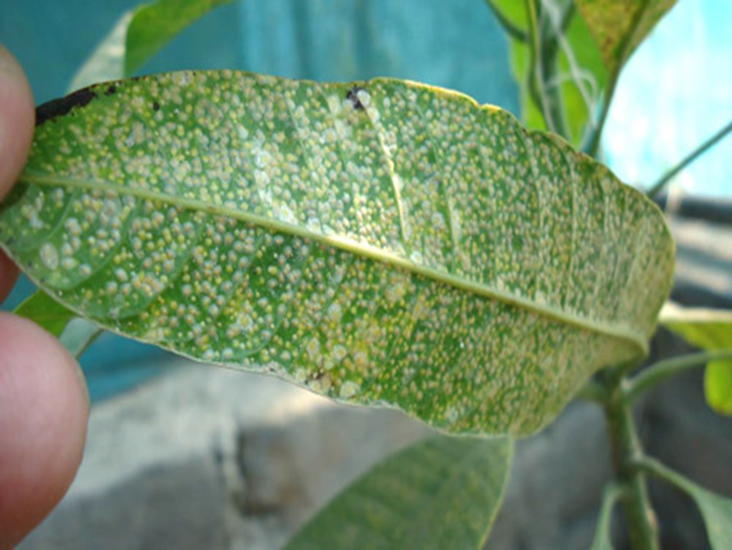



TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PESTS:(ii)SUCKING PESTS
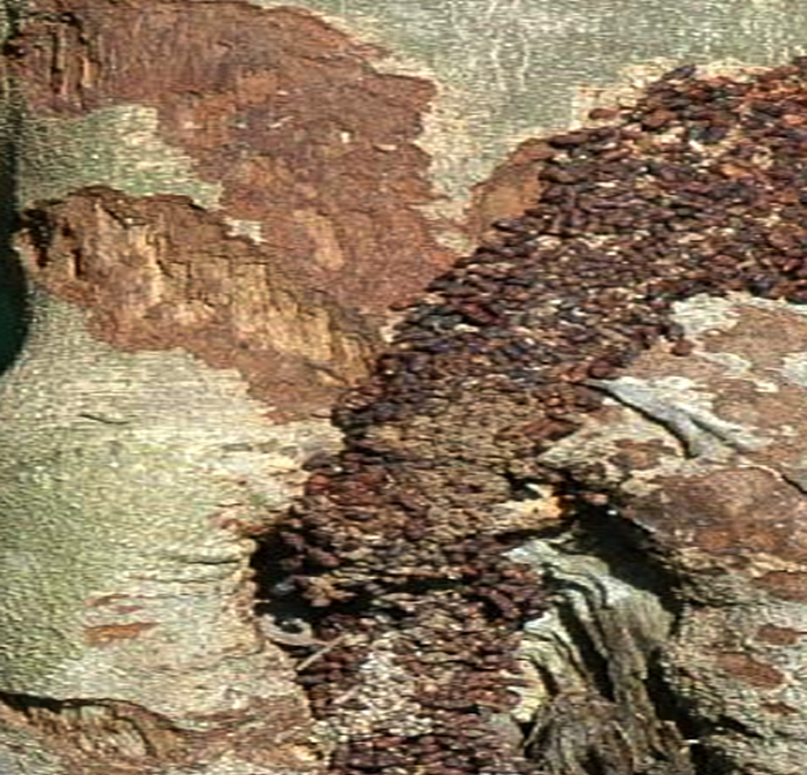
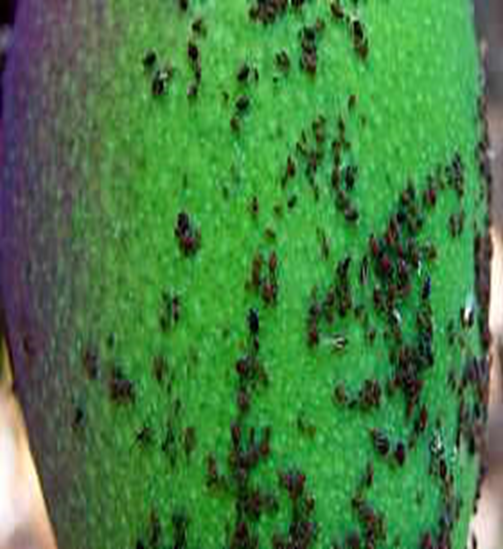
3. GAINT MEALY BUG (Drosicha mangiferae)
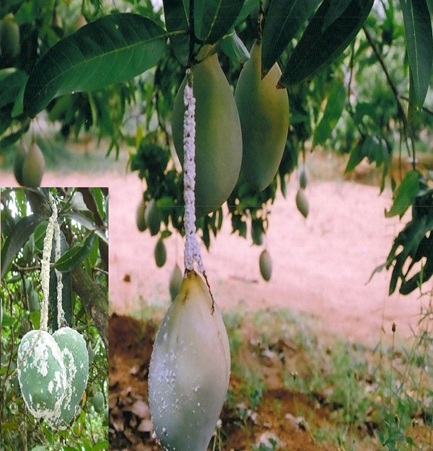
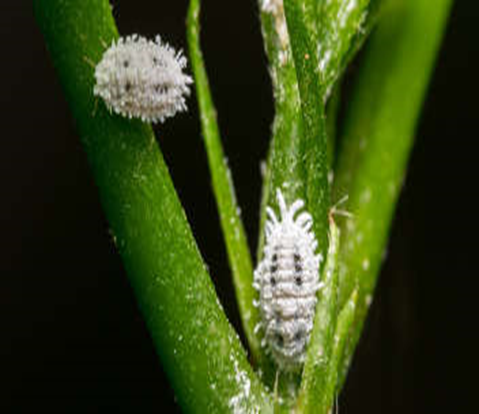



TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PESTS:(ii)SUCKING PESTS
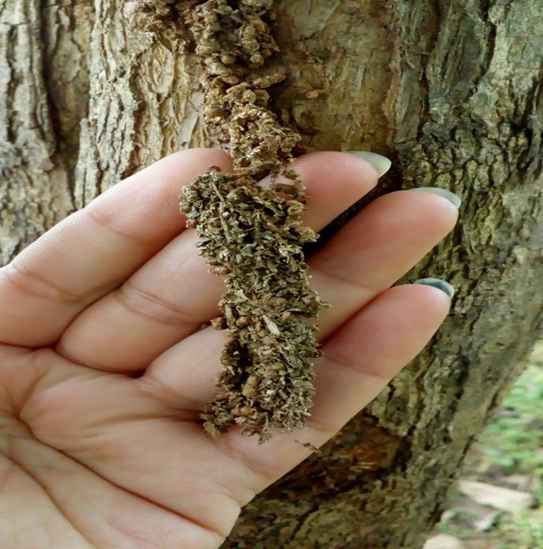
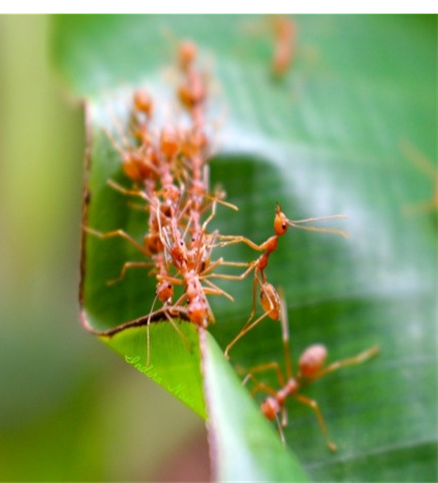
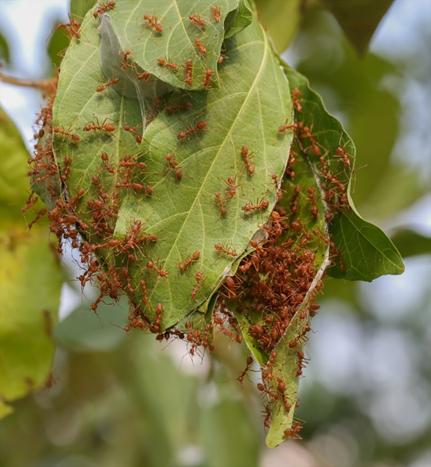
4. RED ANT (Oecophylla smaradina)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PESTS:(ii)SUCKING PESTS
5. MANGO HOPPER (Idioscopus niveoparsus)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5ml per litre of water |
 |