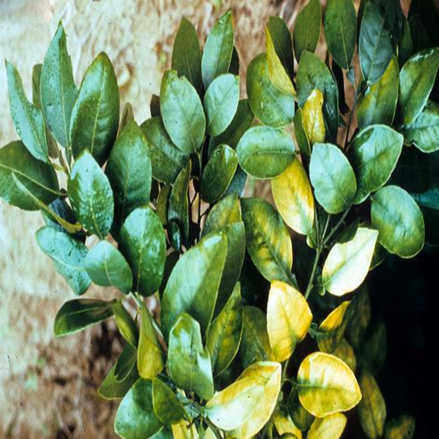
- Citrus belongs to the Rutaceae family.
- India is the world's sixth-largest producer of citrus fruit.
- Andhrapradesh, Maharashtra, Punjab, Madhya Pradesh, Gujrat, Rajasthan, Karnataka, Orissa, Bihar, and Assam are among the states where it is farmed.
- Pectin is abundant in citrus peels.
- Citrus fruit is also known as a plant that loves micronutrients.
- Soils- Light loam well-drained soils are best for lemon cultivation.
- pH- 5.5-7.5. They can also grow in slightly alkaline and acidic soils.
- Climate- Cold weather.
- Temperature- Lemon trees prefer a warmer climate with an acceptable temperature range being between 12-20°C.
- Depending on the season and soil type, citrus should be irrigated every 7 to 28 days.
- Wet the soil to a depth of at least two feet from the tree's trunk to just beyond the drip line.
- Leaf curling is the first indicator of water stress in a citrus tree.
- Drip tubing with attached emitters is one of the best irrigation choices for lemon trees.
- You wrap the tubing around the lemon tree in a cyclical pattern to keep the root ball and surrounding root spread wet.
- Creating a circle basin is another irrigation option.
- This soil ring, placed 2 feet away from the lemon tree's trunk, keeps water contained within the circle for optimal topsoil saturation.
- This basin, however, should not clog the root ball or remain stagnant on the soil's surface; instead, the water should seep down into the soil for healthy and wet soil ecology.
- In the middle of the pot, plant the seed about half an inch deep.
- Using a spray bottle, carefully sprinkle the soil directly above the seed with water.
- Standard-size citrus trees should be spaced 15 to 20 feet apart from their centers, whereas dwarf trees that have reached full size should be spaced 8 to 12 feet apart.
- Citrus trees can be grown vertically or as espaliers in small areas.
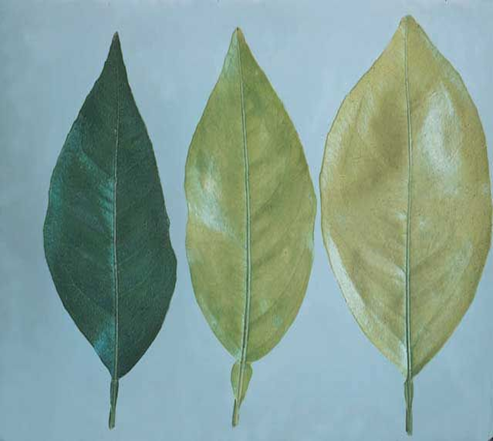
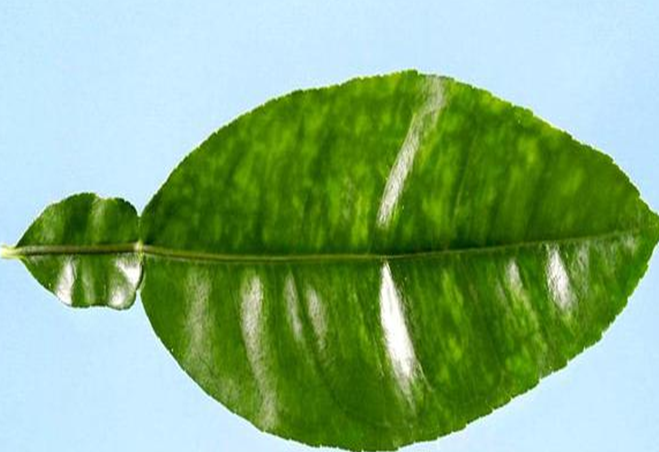
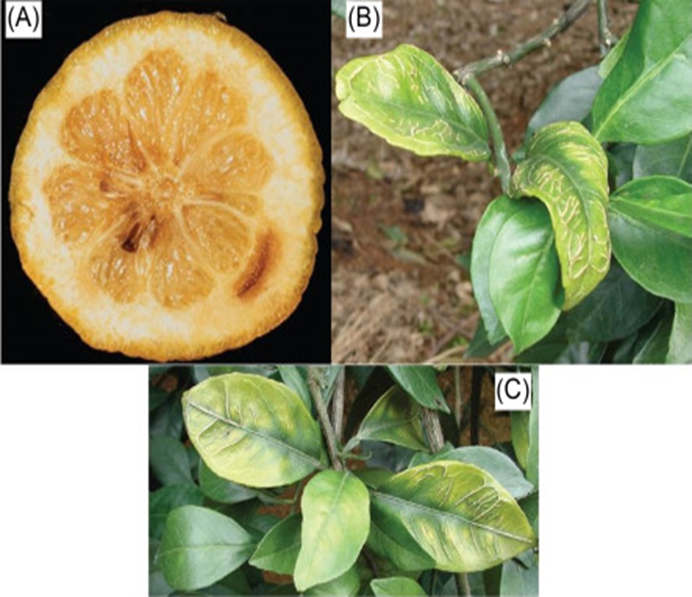
DEFICIENCY OF NITROGEN
TREATMENT :
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use BLOOM 2 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
TREATMENT :
|
Use Calcium EDTA 0.5-01 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5ml per litre of water |
 |
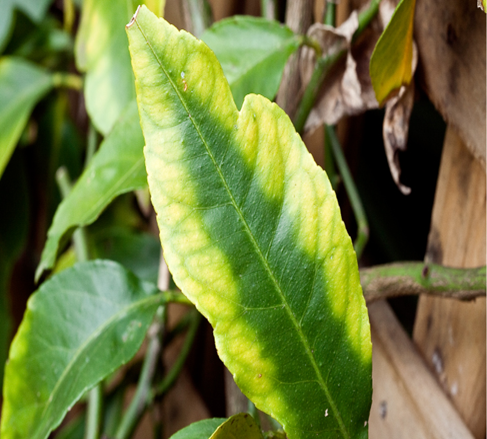
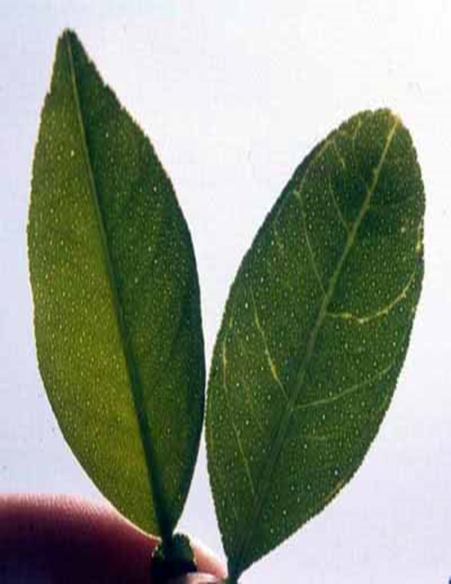
DEFICIENCY OF BORON
TREATMENT :
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use BLOOM 2 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
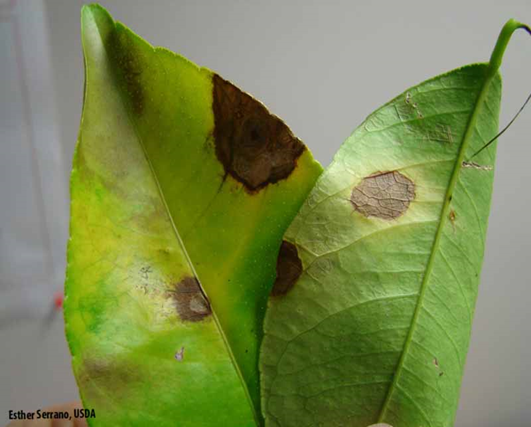
A. FUNGAL DISEASES (i) CONTACT BASED
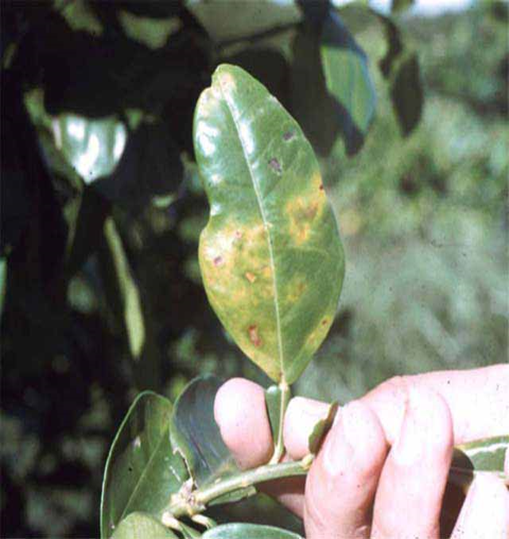
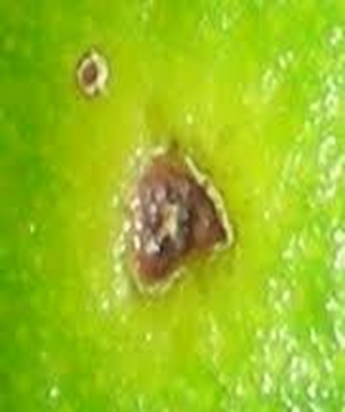
1. ALTERNARIA BROWN SPOT (Alternaria alternate)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES (i) CONTACT BASED
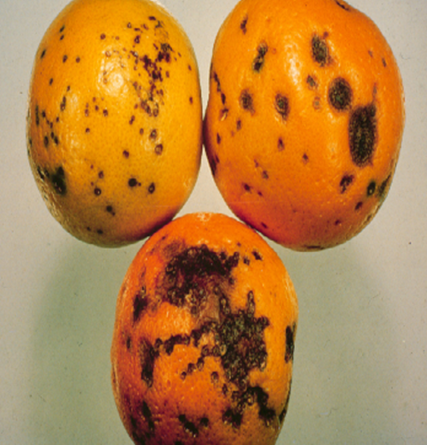
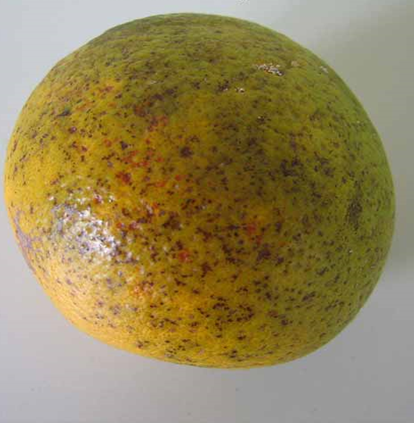
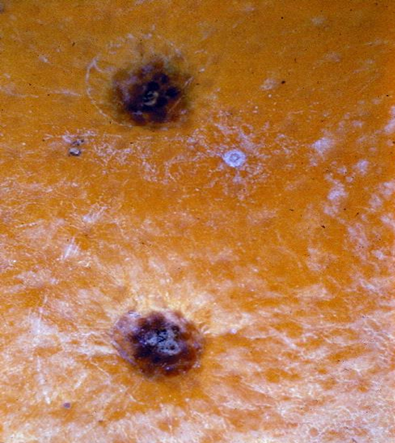
2. BLACK SPOT (Guignardia citricarpa)


TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
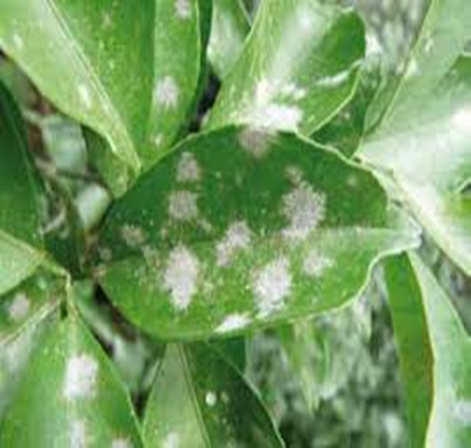
A. FUNGAL DISEASES(i) CONTACT BASES
3. POWDERY MILDEW (Acrosporium tingitaninum)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES (i) CONTACT BASED
4. PINK DISEASE (Erythricium salmonicolor)
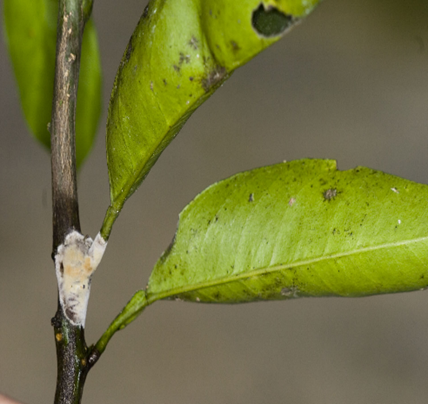
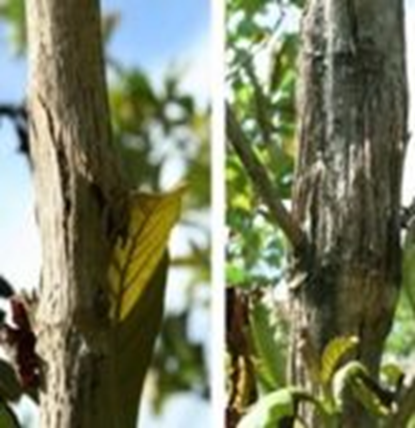
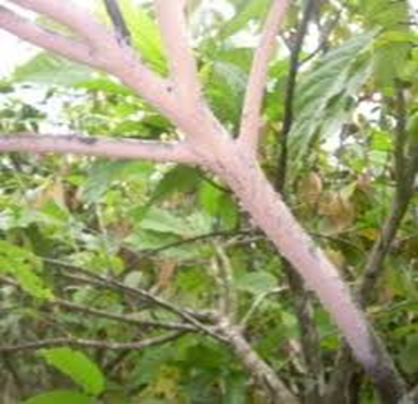



TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES (i) CONTACT BASED
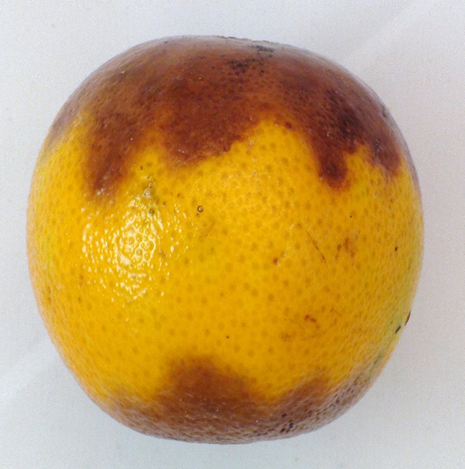
5. GREENING (Liberobactor asiaticum )
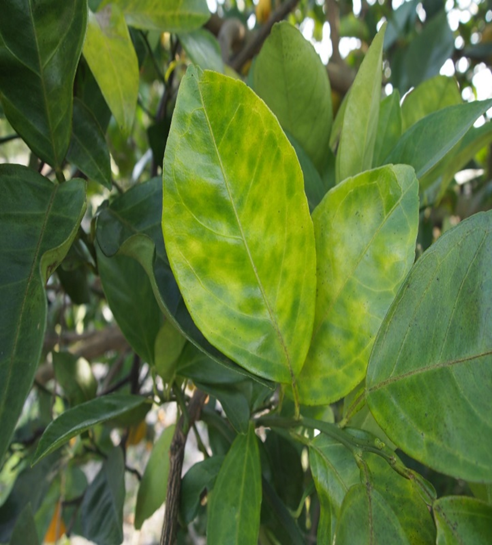
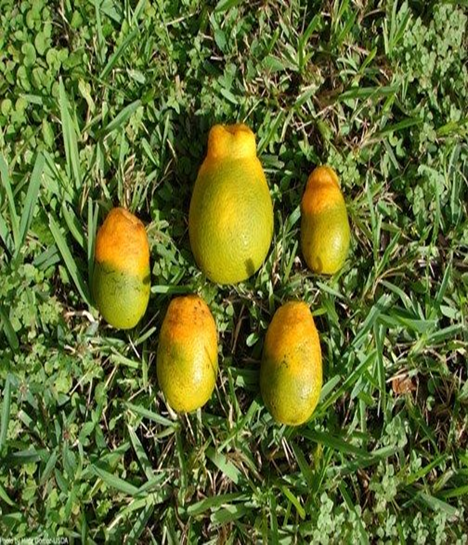
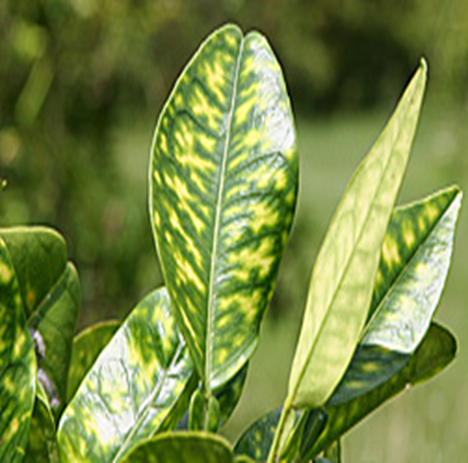



TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
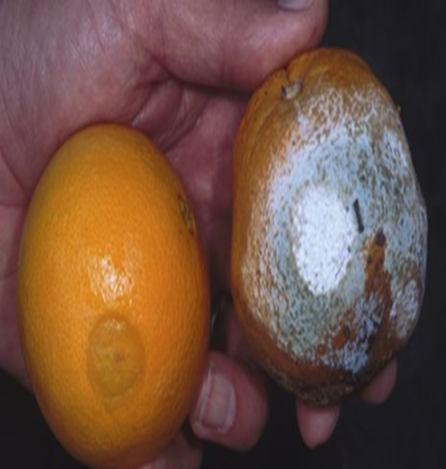
A. FUNGAL DISEASES (ii) SYSTEMIC BASED
1. PHOMOPSIS STEM END ROT(Lasiodiplodia theobromae)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES (ii) SYSTEMIC BASED
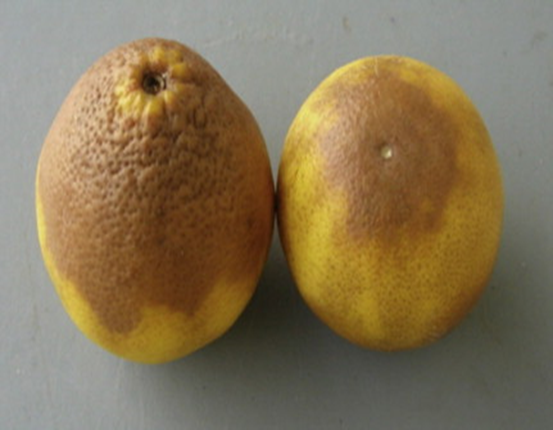
2.DRY ROOT ROT(Nectria haematococca)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES (ii) SYSTEMIC BASED
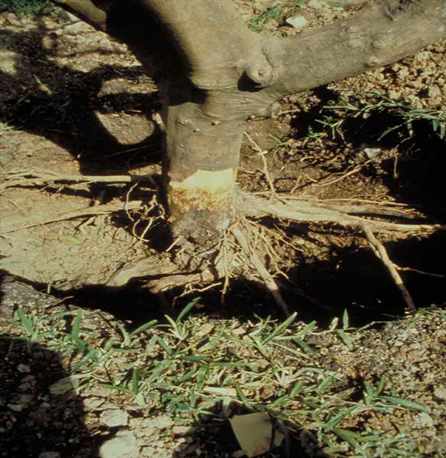
3.PHYTOPHTHORA FOOT ROT(Phytophthora citrophthora)
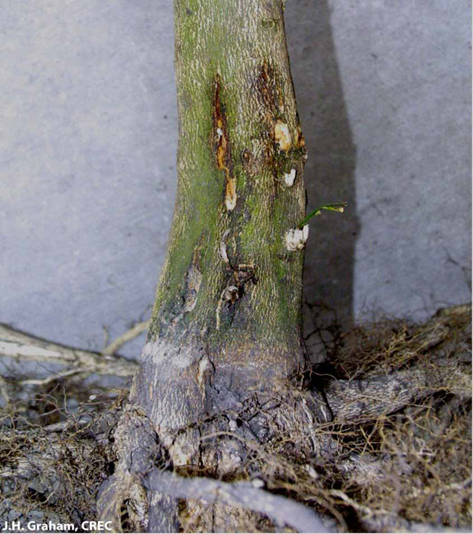
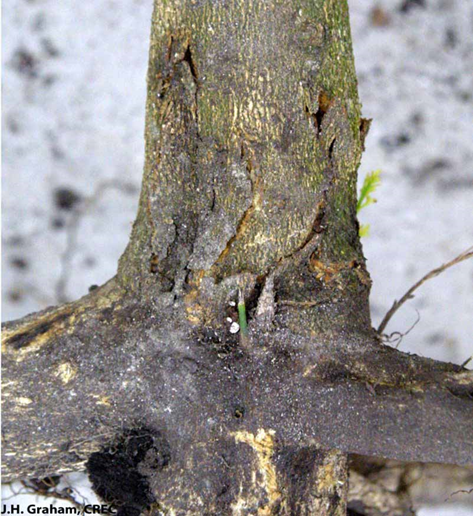
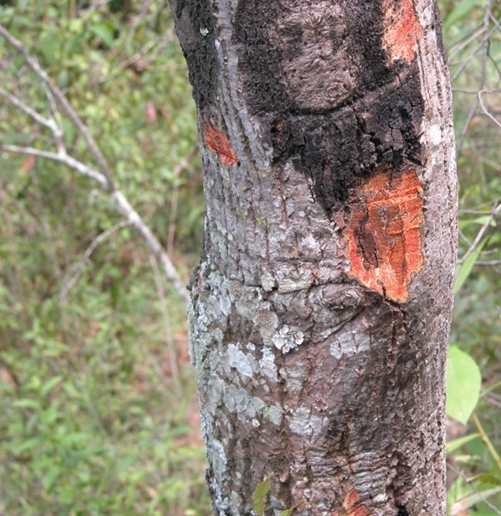



TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES (ii) SYSTEMIC BASED
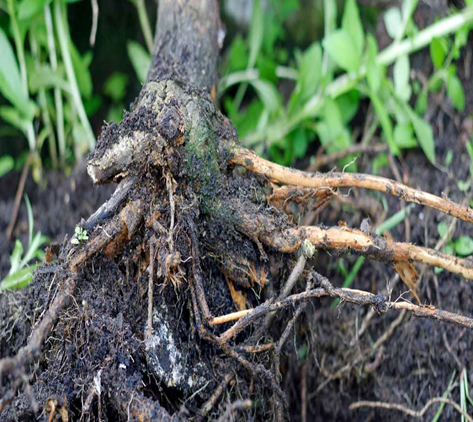
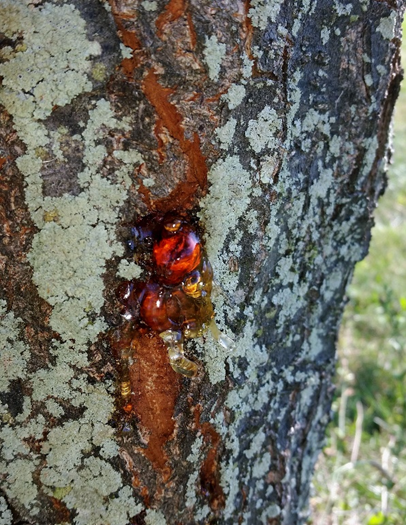
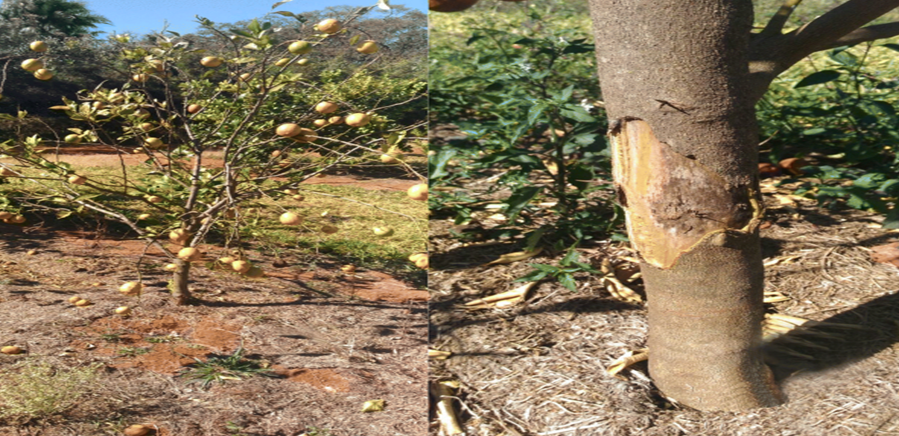
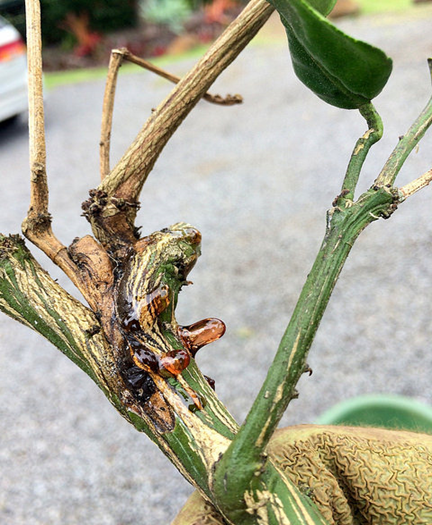
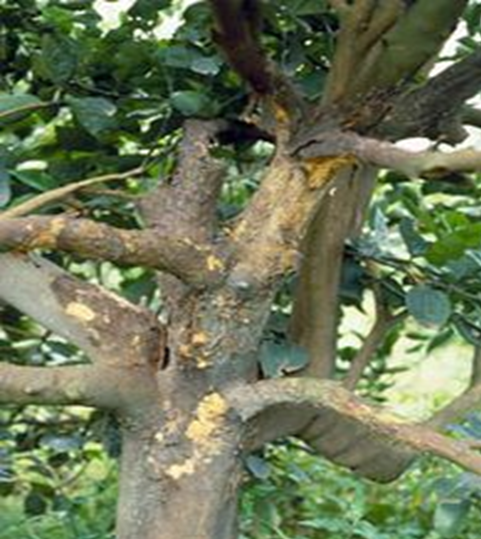
4. GUMMOSIS (Phytophthora parasitica)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5ml per litre of water |
 |
B. VIRAL DISEASES
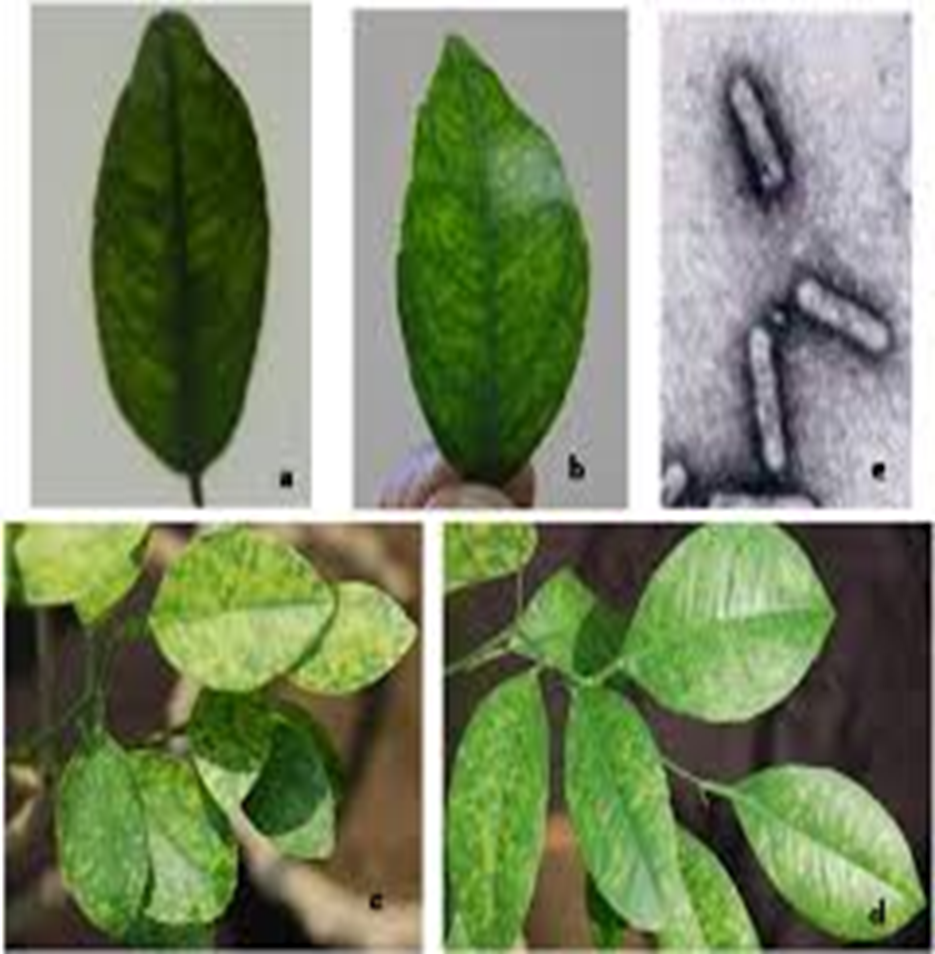
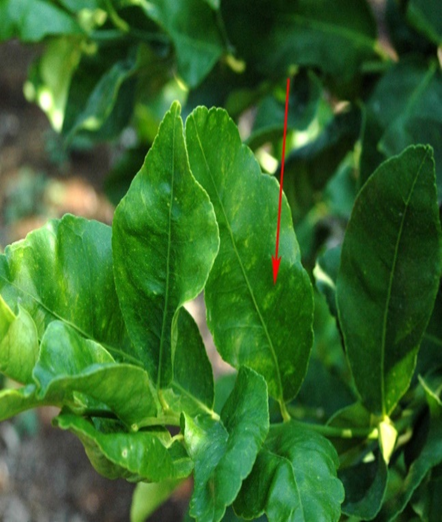
1. CITRUS YELLOW MOSAIC VIRUS
TREATMENT :
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
B. VIRAL DISEASES
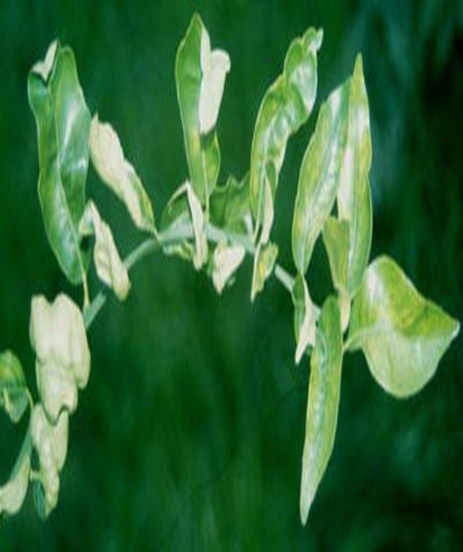
2. CITRUS CHLOROTIC DWARF VIRUS
TREATMENT :
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
B. VIRAL DISEASES
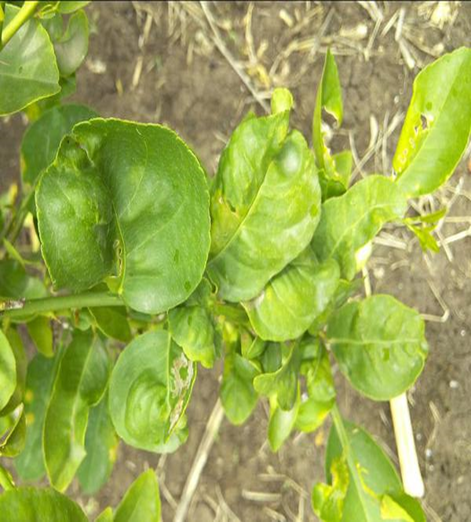
3. CITRUS PSOROSIS VIRUS
TREATMENT :
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
B. VIRAL DISEASES
4.CITRUS TRISTEZA VIRUS
TREATMENT :
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PESTS (i)CHEWING PESTS
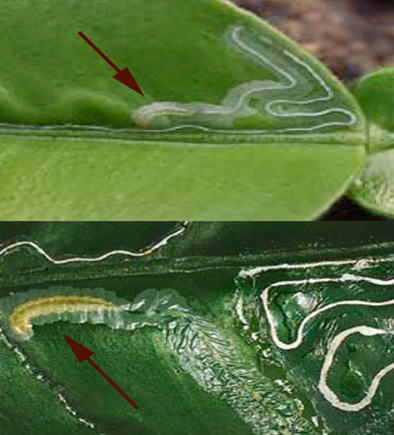
1. CITRUS LEAF MINER (Phyllocnistic citrella)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PESTS (i)CHEWING PESTS
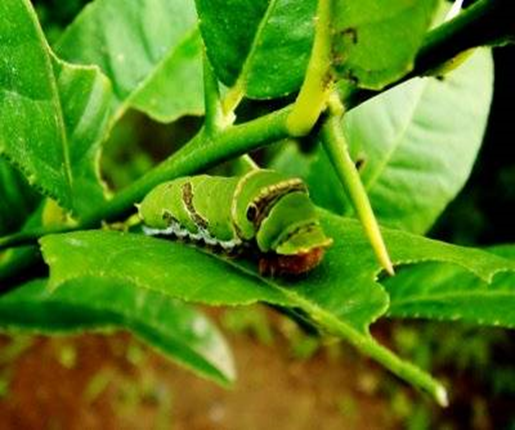
2. CITRUS BUTTERFLY (Papilio demoleus)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PESTS (ii)SUCKING PESTS
1. BLACK APHID (Toxoptera aurantii)
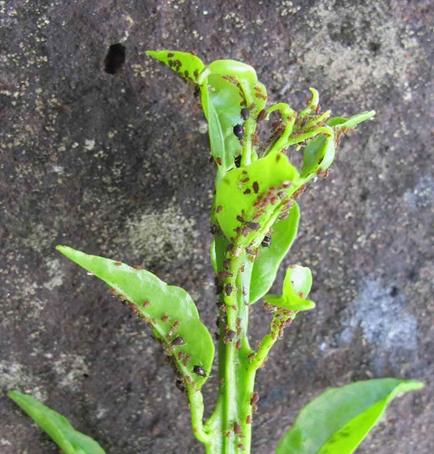
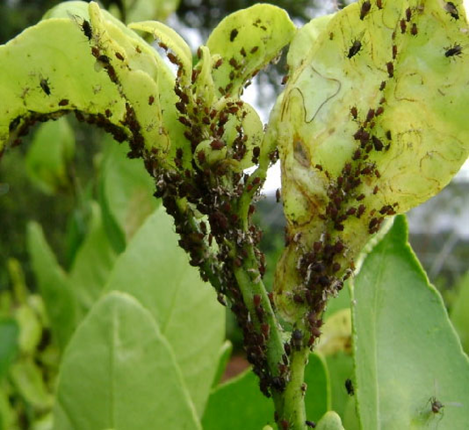



TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PESTS (ii)SUCKING PESTS
2.BROWN APHID (Toxoptera citricida)
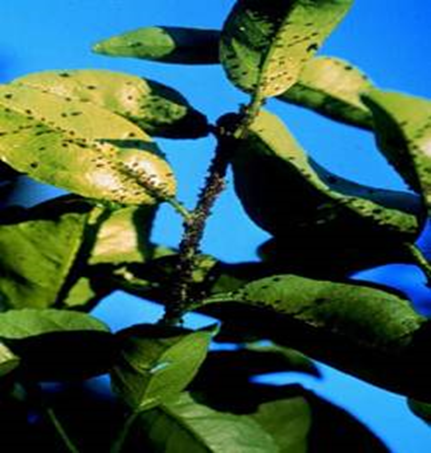
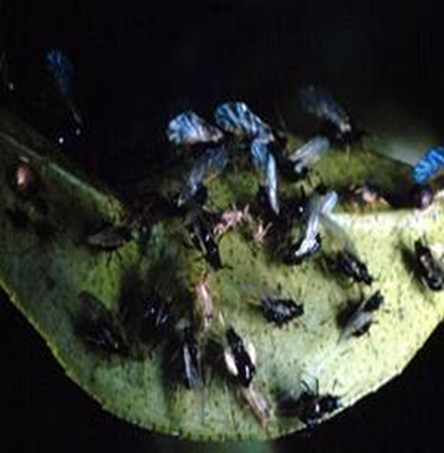



TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PESTS (ii)SUCKING PESTS
3.CITRUS BLACK FLY (Aleurocanthus woglumi )
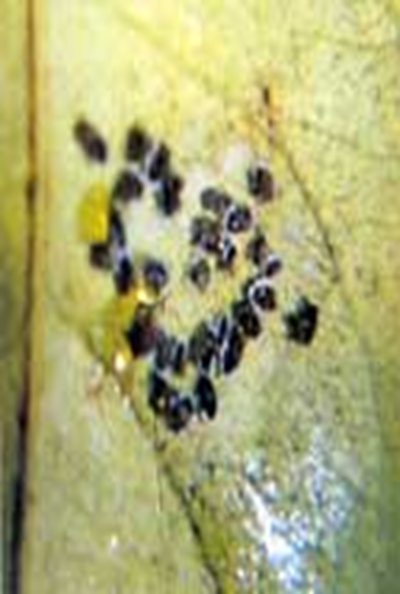



TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PESTS (ii)SUCKING PESTS
4.CITRUS PSYLLID (Diaphorina citri )
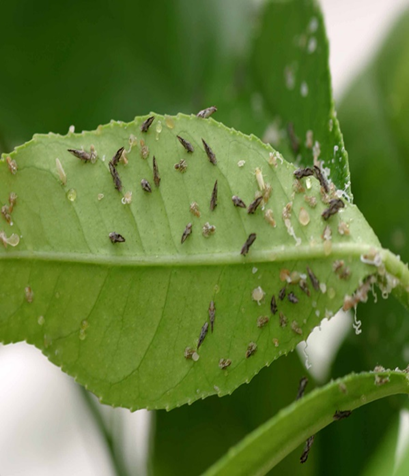
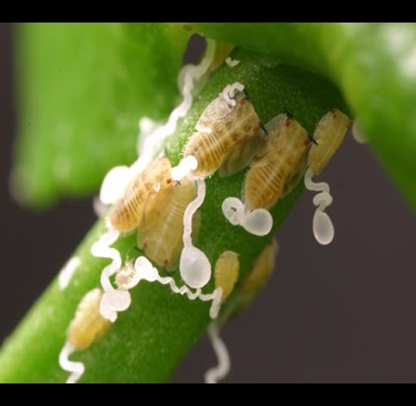
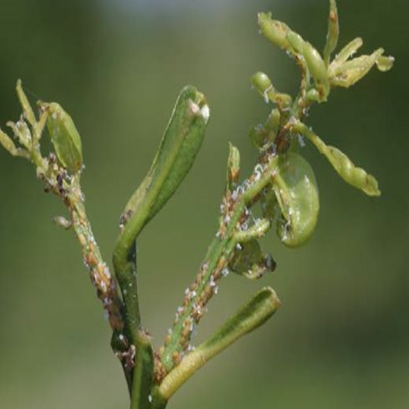



TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PESTS (ii)SUCKING PESTS
5. MEALY BUG (Planoccus citri)
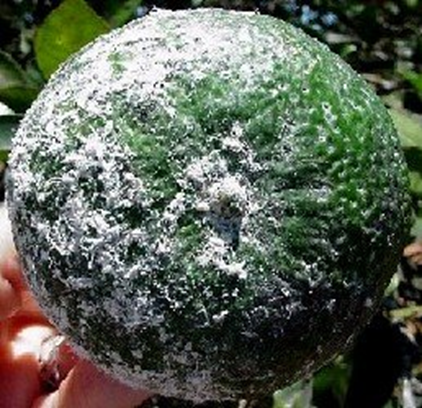
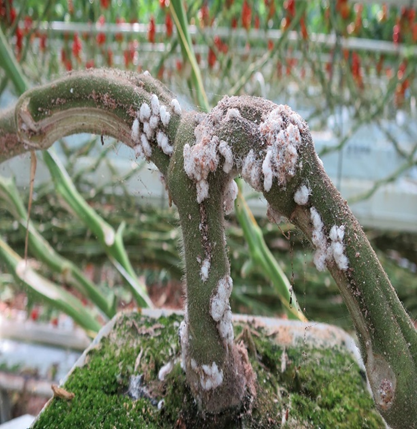



TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PESTS (ii)SUCKING PESTS
6.FRUIT SUCKING MOTH (Otheris maternal)
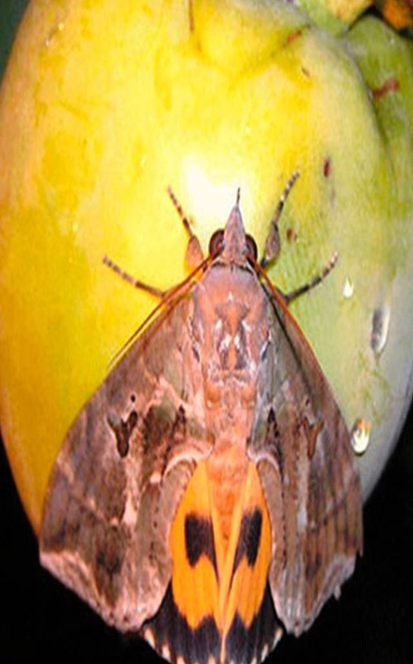



TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PESTS (ii)SUCKING PESTS
7.CITRUS THRIPS(Thrips nilgiriensis)
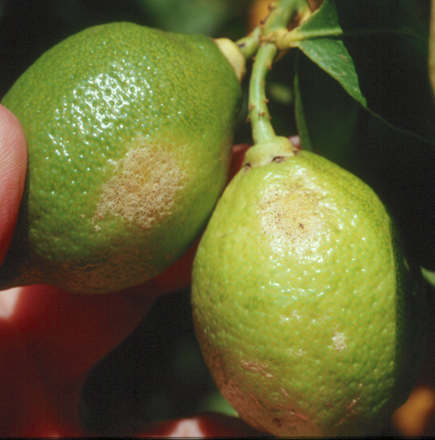
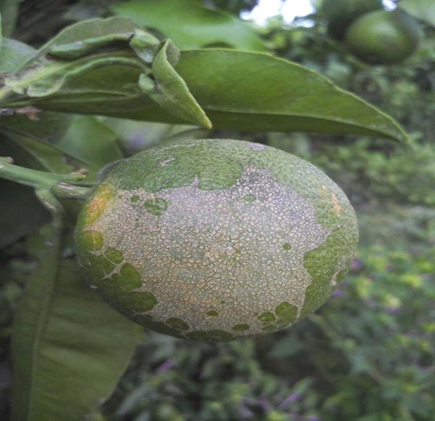



TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PESTS (ii)SUCKING PESTS
8. COTTONY CUSHION SCALE (Icerya purchase)
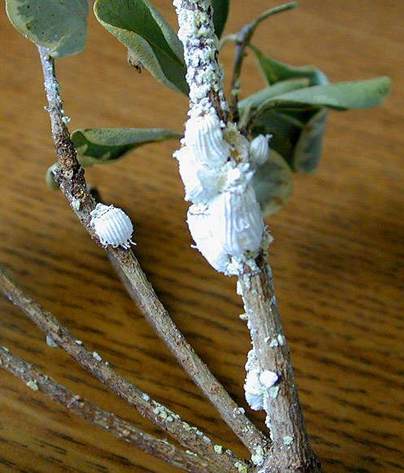
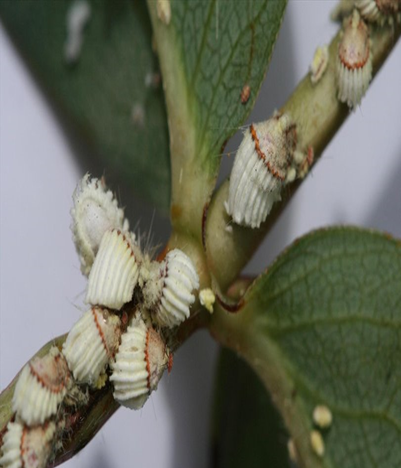



TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |