- Psidium guajava is the scientific name for guava, which belongs to the Myrtle family.
- Guava trees can reach a height of 10 meters (33 feet) and live for 40 years.
- Guava is a tropical fruit that is mostly grown in the tropics.
- The guava tree is easily identified by its smooth, thin brown bark that peels off to reveal a greenish layer beneath.
• Soil- Sandy loam.
• Cultivation- Well-drained soils are best for guava cultivation.
• pH- 4.5-8.2
• Temperature- 20 to 25°C, If there is a high temperature at the time of fruit development, it can cause fruit drop.
• Susceptibility- They are susceptible to pests.
• Rainfall- 500-1000 mm.
- To allow the root system to develop and become established, water newly planted guava trees every two days for the first week after planting, then once a week for the next few months.
- Grass and weeds should be kept to a minimum in a 0.6 to 1.5 m (2.0-5.0 ft) radius around the trunk.
- A layer of organic mulch, such as bark or wood chips, can be applied around the base of guava trees to help them thrive.
- Allow a 20 to 30 cm (8-10 in) gap between the trunk and the mulch layer; do not mound the mulch around the trunk.
- The type and amount of fertilizer applied to young trees vary depending on the area and soil type.
- Pruning To foster the development of laterals, young trees should be trimmed.
- This is accomplished by chopping existing laterals back to 30 to 60 cm (1 to 2 ft).
- Three to four lateral branches should be let to grow 60 to 90 cm (24-36 in) before the tips are clipped to facilitate further branching during the first year of growth.
- When new shoots grow as a result of this process reach 60 to 90 cm, they should also be pointed (24-36 in).
- Established trees should be pruned to keep their height moderate and to open up the canopy.
- Guavas for processing can be produced from seed, with roughly 70% of seedlings retaining the parent tree's genetic features.
- Sowing seeds Before being transplanted in the field or garden, guava seeds are normally started in nursery beds or pots.
- Planting should only be done with seeds from healthy, strong trees that have the necessary features.
- Seeds should be planted in sandy soil flats and covered to a depth of 6 mm (0.25 in).
- Within 15 to 20 days of seeding, most seeds germinate.
- Seedlings should be transplanted into separate pots when they reach a height of 3.8 cm (1.5 in).
- Seedlings are being transplanted.
- To avoid shade, guava trees should be planted in full sun and spaced 4.5–7.5 m (15–25 ft) apart from other trees and buildings.
- A hole somewhat larger than the existing root ball should be dug, and a layer of compost or rotten manure should be added to the bottom of the planting hole.
- By placing the seedling upright in the planting hole and backfilling the dirt surrounding the plant, the tree should be planted at the same depth as it was in the nursery.
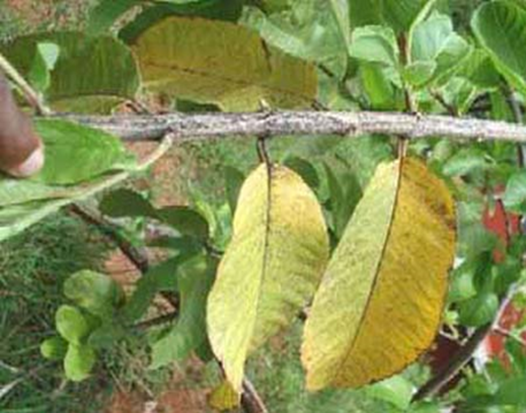
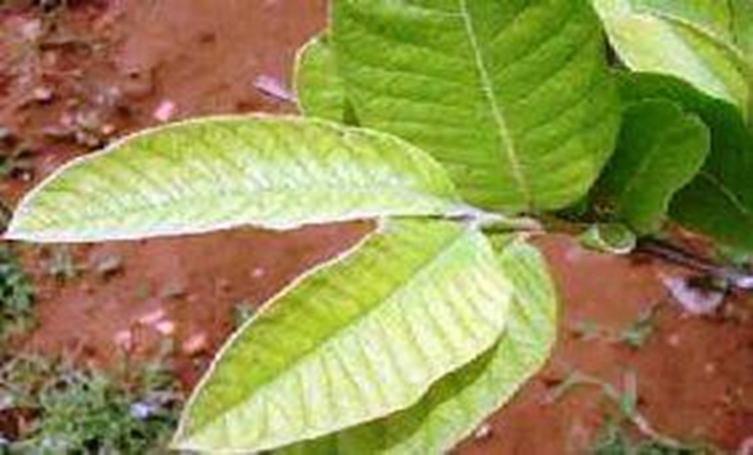
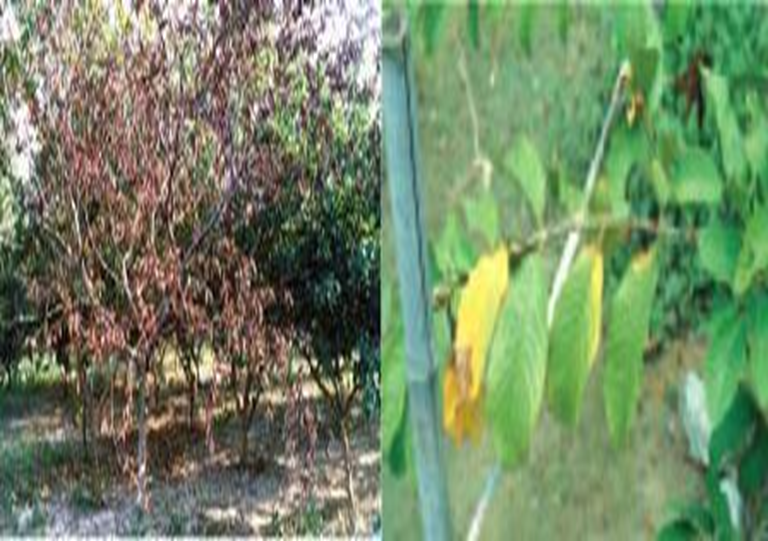
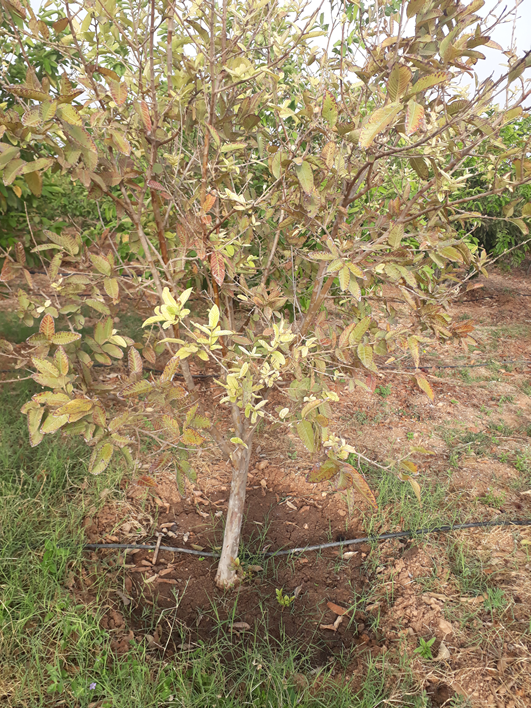
DEFICIENCY OF NITROGEN
TREATMENT :
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use Grow 2 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
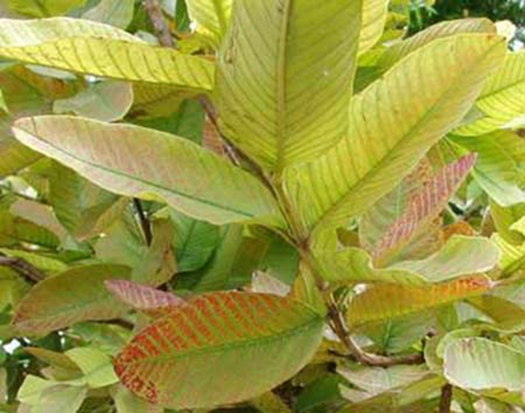
TREATMENT :
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use Grow 2 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
TREATMENT :
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use Grow 2 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
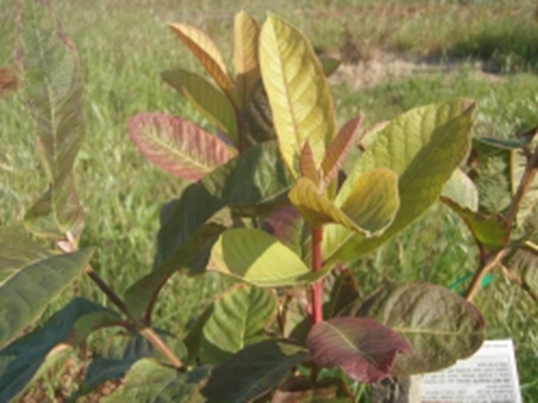
TREATMENT :
|
Use Calcium EDTA 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use BLOOM 2 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (i) CONTACT BASED
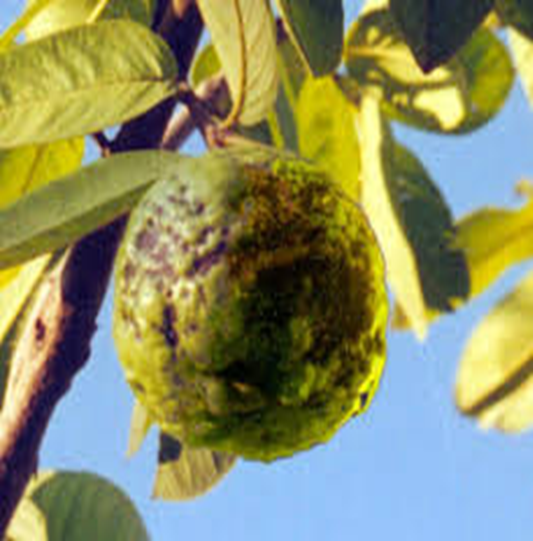
1. ANTHRACNOSE (Glomerulla gossypii)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A.FUNGAL DISEASES: (i) CONTACT BASED
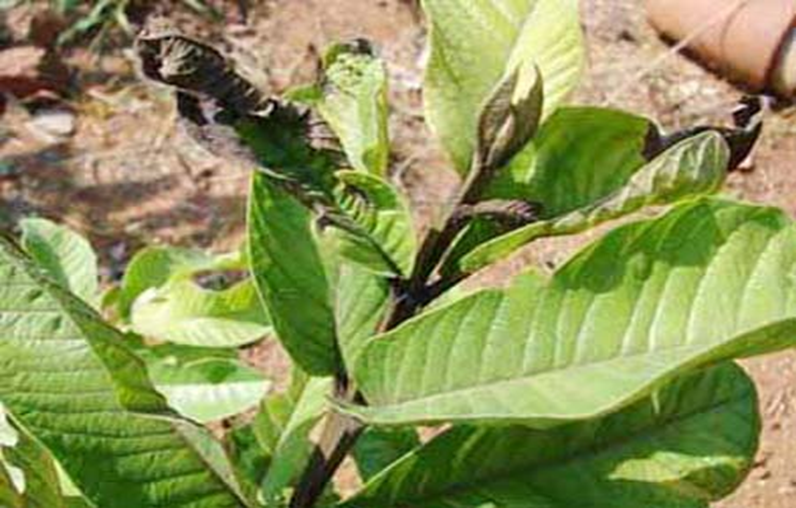
2. LEAF CURLING (Taphrina deformans)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
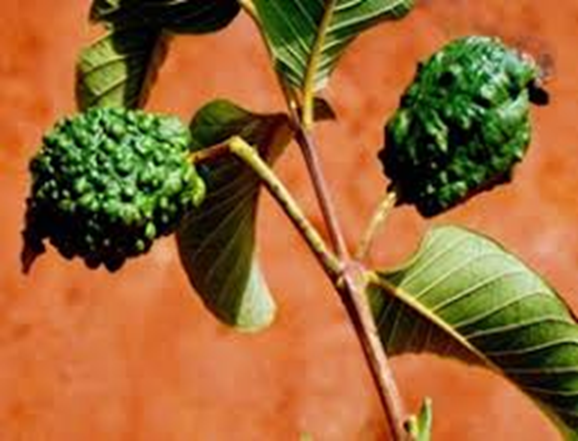
3. FUSARIUM WILT (Fusarium oxysporum)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A.FUNGAL DISEASES: (i) CONTACT BASED
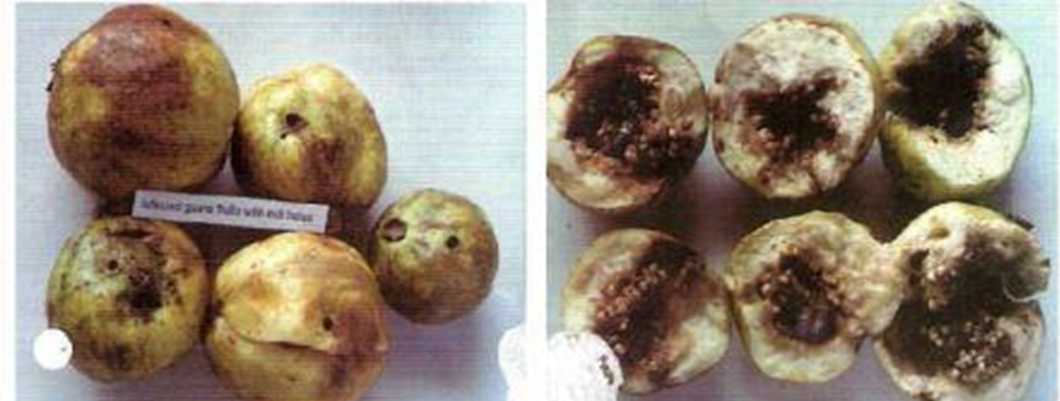
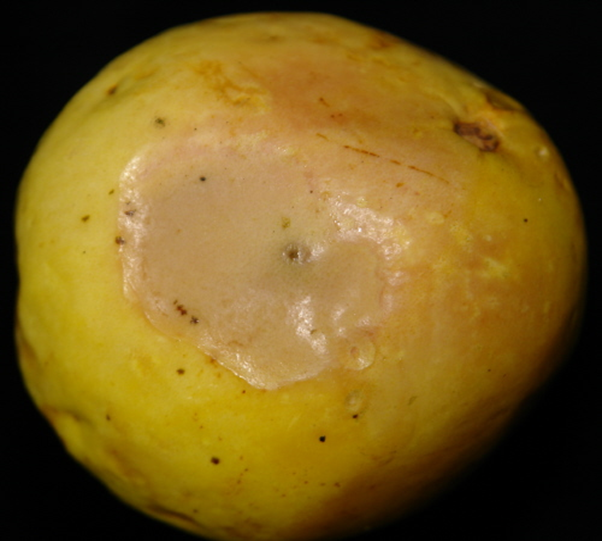
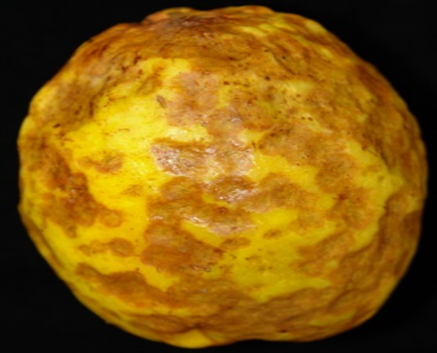
4. ALGAL LEAF AND FRUIT SPOT (Cephaleuros virescens Kuntze)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (ii) SYSTEMIC BASED
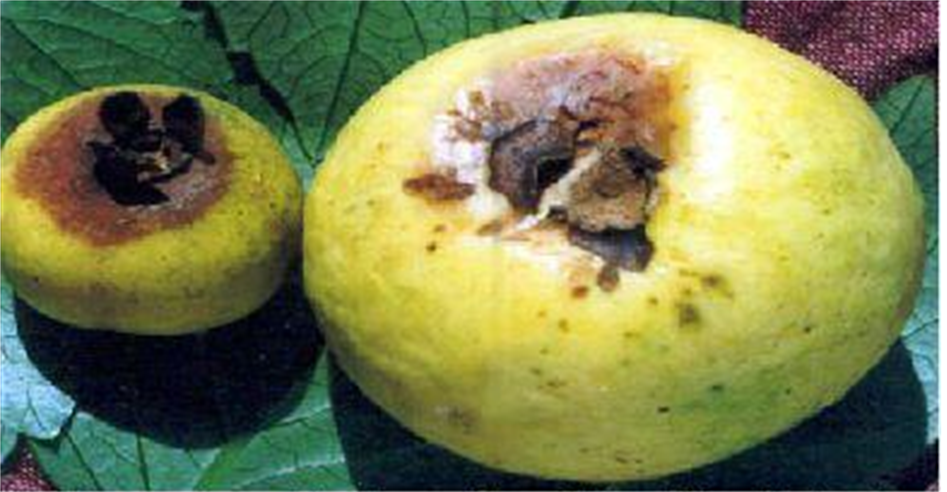
1. FOOT ROT (Nalanthamala psidii)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (ii) SYSTEMIC BASED
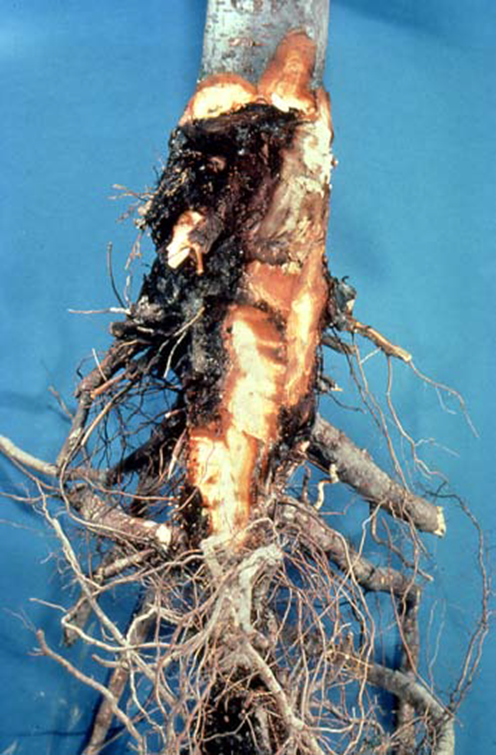
2. ROOT ROT (Armillaria mellea)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (ii) SYSTEMIC-BASED
3. STEM END ROT (Phomopsis)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PEST: (i)CHEWING PESTS
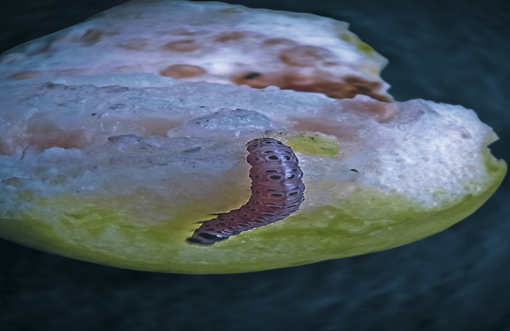
1. RUIT BORER (Leucinodes orbonalis)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PEST:(i) CHEWING PESTS
2. CASTOR CAPSULE BORER (Conogethes punctiferalis)

TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PEST:(i) CHEWING PESTS
3.BARK EATING CATERPILLAR (Indarbela quadrinotata)
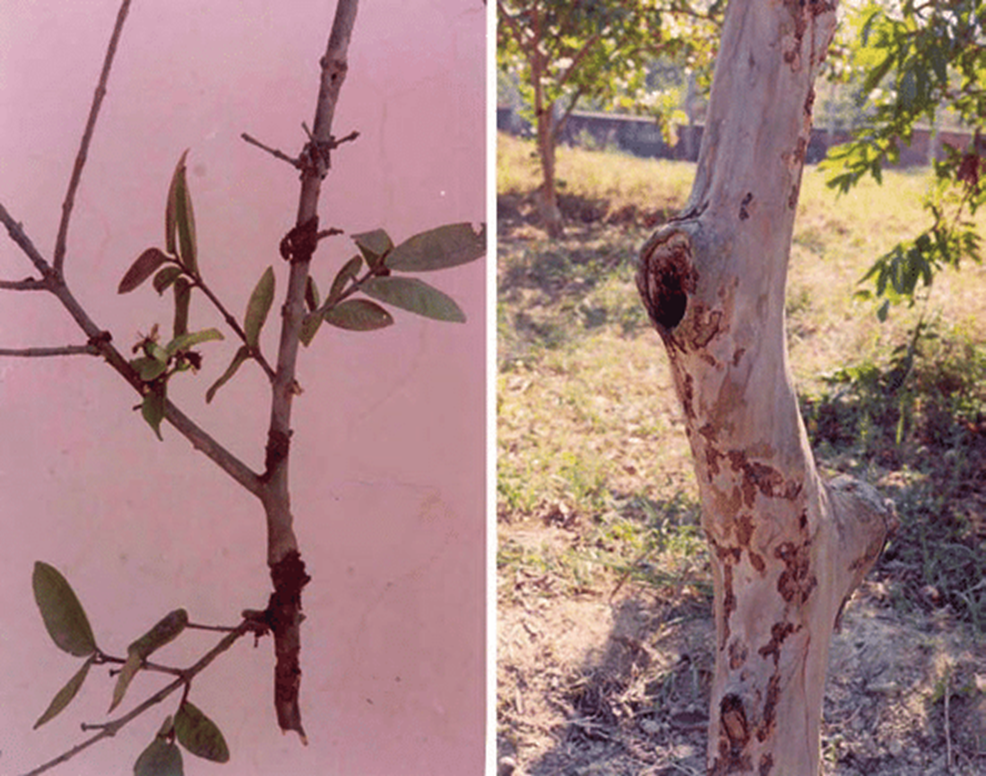

TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PEST:(i) CHEWING PESTS
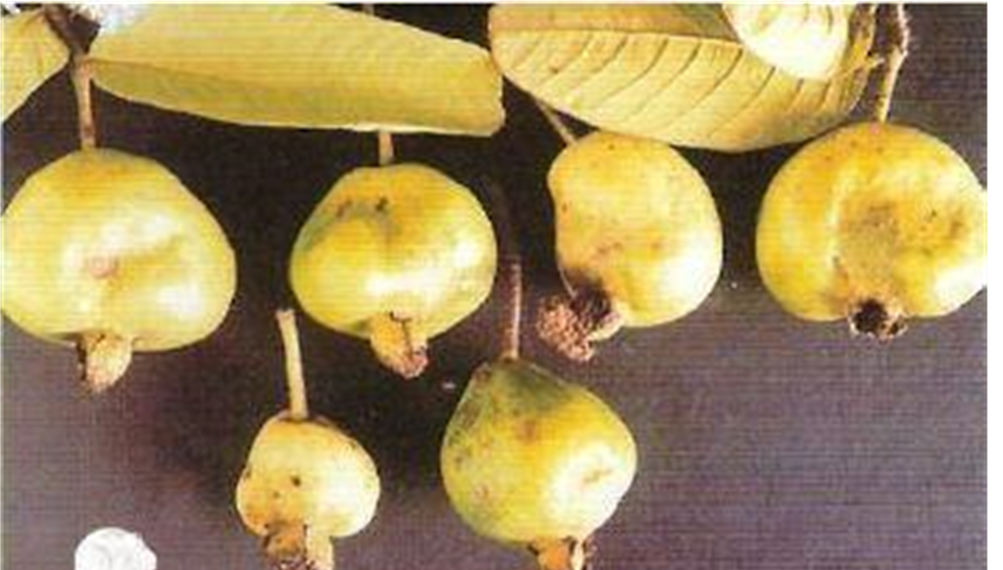
4. FRUITFLY (Drosophila melanogaster)


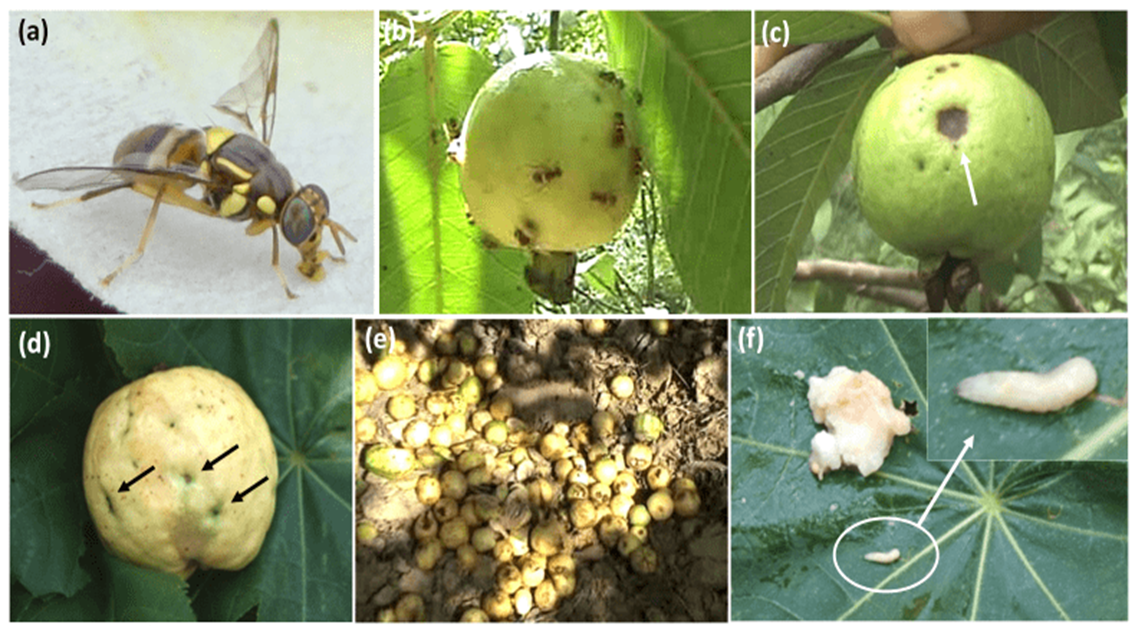
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C.PEST:(ii) SUCKING PESTS
1. MEALYBUG (Pseudococcidae)



TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PEST:(ii) SUCKING PESTS
2. WHITEFLY (Aleyrodidae)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PEST:(ii) SUCKING PESTS
3. THRIP (Thysanoptera)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |