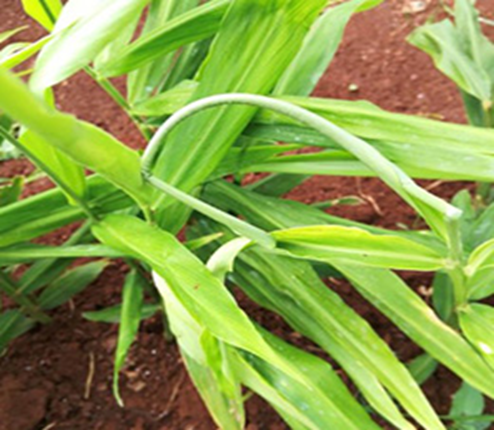
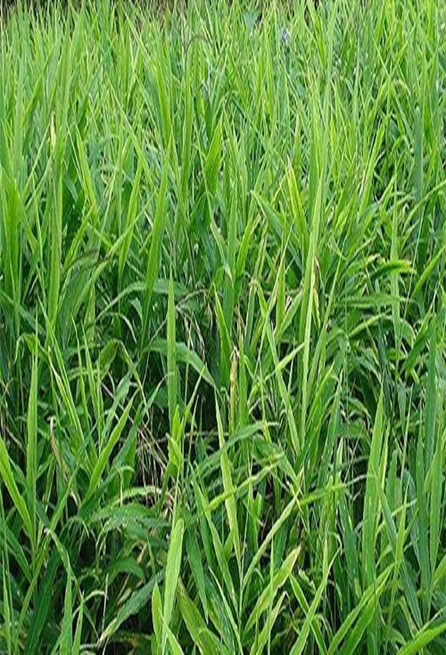
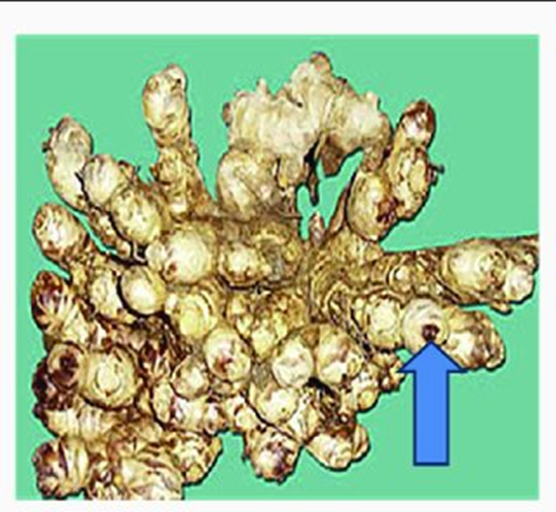
- Ginger belongs to the Zingiberaceae family.
- It is a perennial herbaceous plant that is a major spice crop around the world.
- India is the world's greatest producer and exporter, accounting for more than 70 percent of global production.
• Soil- Ginger will grow optimally in loam soil that is high in organic matter and well-aerated soil.
• pH- 6.0 and 6.5
• Climate- warm and humid weather.
• Temperature- The Plant requires a minimum temperature of 15.5°C.
• Rainfall- 1300-1500 mm of water during its crop cycle.
- After planting, the first light irrigation is applied.
- Irrigations are given every ten days.
- There were a total of 16-18 irrigations.
- One month before harvest, irrigation is turned off and the rhizome clumps are gently extracted with a spade or digging fork.
- Ginger is grown as a rain-fed crop in places with high rainfall (uniform distribution for 5 to 7 months).
- During its crop cycle, ginger requires 1300-1500 mm of water.
- Weeding is done right before fertilizer application and mulching; depending on the severity of weed development, 2-3 hand weedings are required.
- When there is water stagnation, proper drainage routes must be created.
- Earthing up is necessary to prevent rhizome exposure and to provide appropriate soil volume for rhizome development.
- It's done 45 and 90 days following planting, right after weeding and fertilizer application.
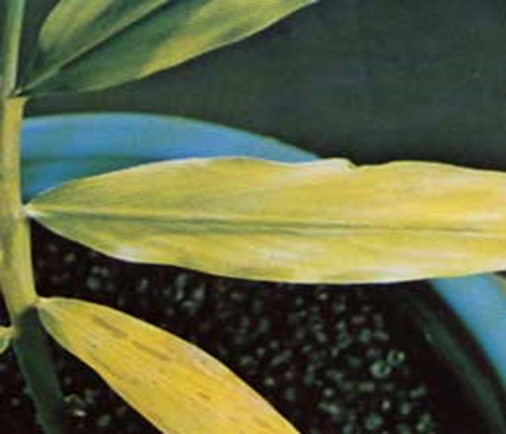
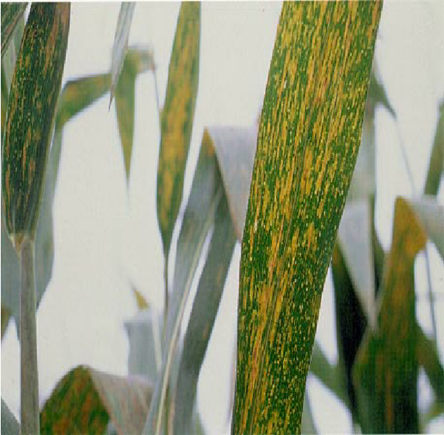
DEFICIENCY OF NITROGEN
´Yellowing that starts at the tip and moves along the centre of older leaves.
TREATMENT :
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
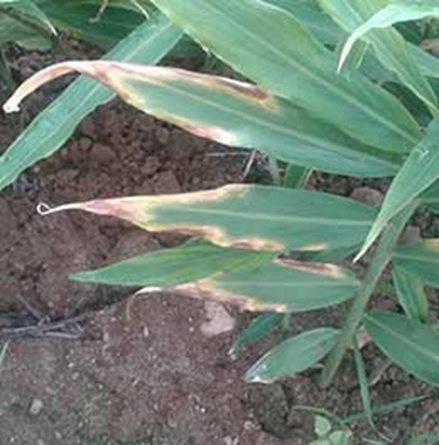
DEFICIENCY OF PHOSPHORUS
´Reduced growth of plant, restricted root development.
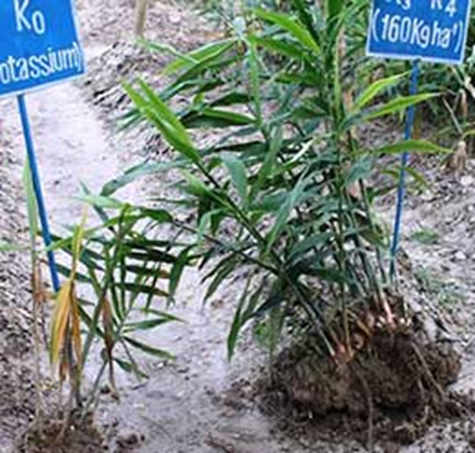
DEFICIENCY OF CALCIUM
TREATMENT :
|
Use Calcium EDTA 0.5 per litre of water |
 |
|
Use BLOOM 2 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
TREATMENT :
|
Use Calcium EDTA 0.5 per litre of water |
 |
|
Use BLOOM 2 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
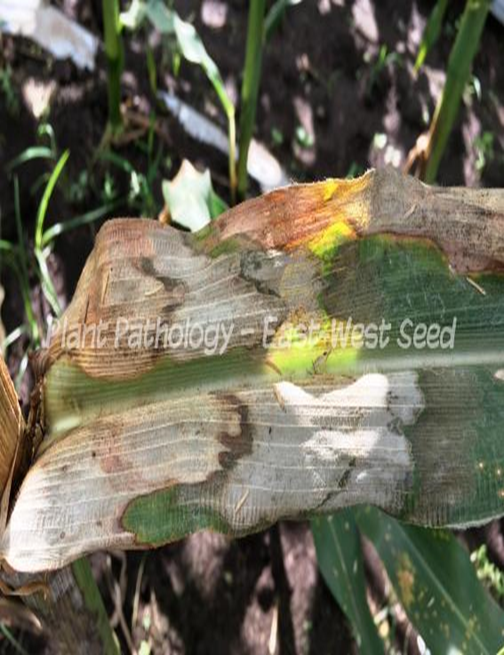
A. FUNGAL DISEASES:(i) CONTACT BASED
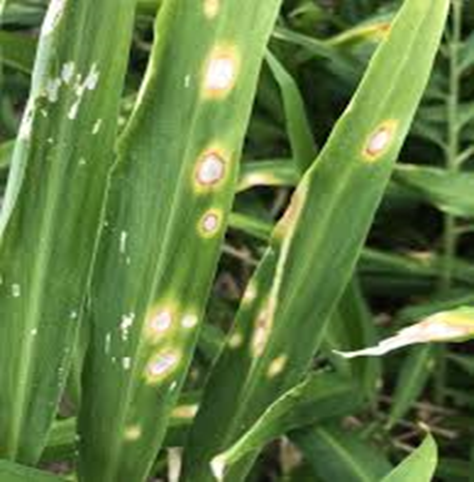
1. LEAF SPOT (Phyllosticta zingiberi)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES:(i) CONTACT BASED
2. SHEATH BLIGHT/LEAF BLIGHT(Rhizoctonia solani)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES:(ii) SYSTEMIC BASED
1.SOFT ROT(Pythium aphanidermatum)
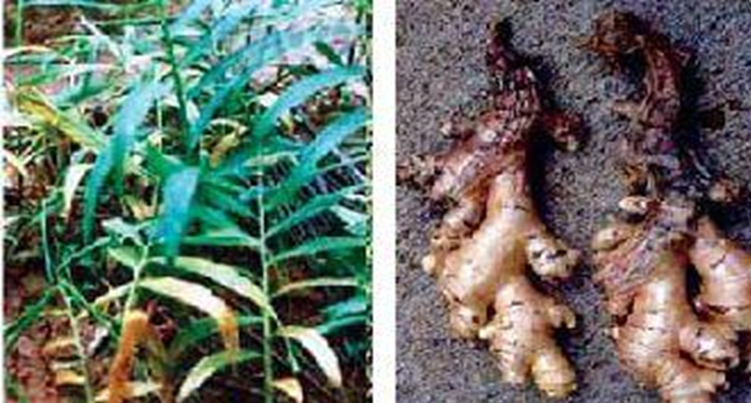
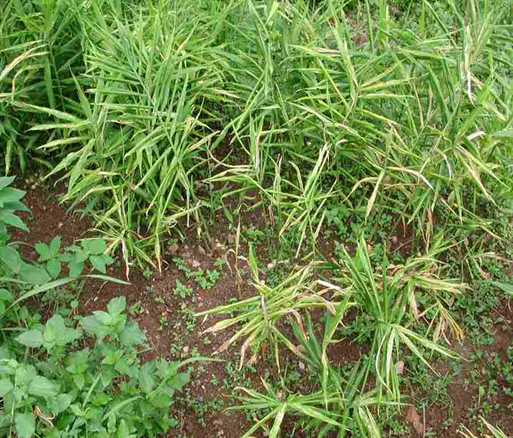



TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES:(ii) SYSTEMIC BASED
2.FUSARIUM YELLOWS (Fusarium oxysporum)
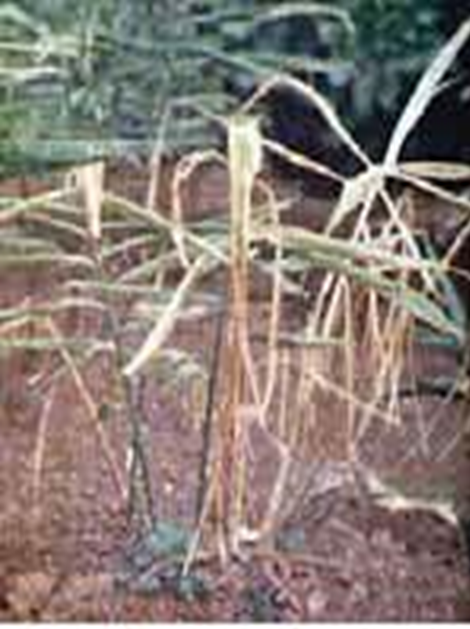
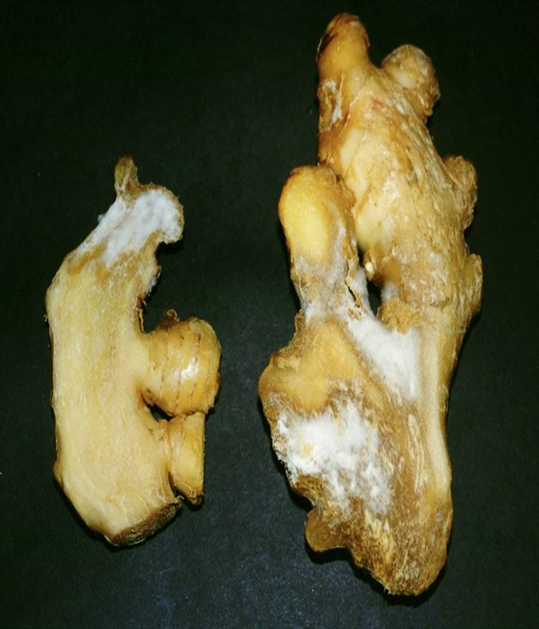

TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES:(ii) SYSTEMIC BASED
3.DRY ROT (Fusarium sp.)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
B. VIRAL DISEASES
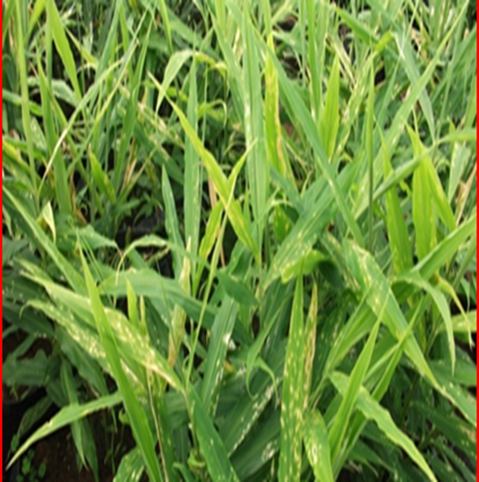
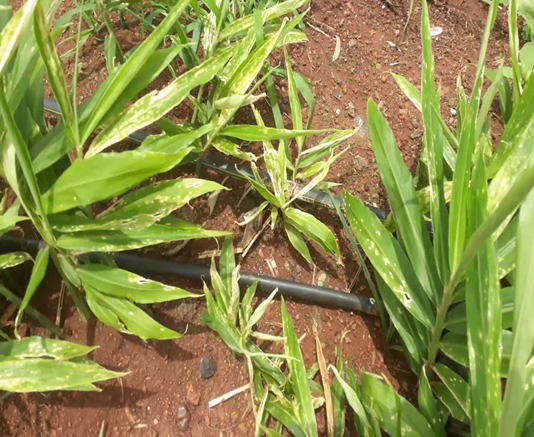
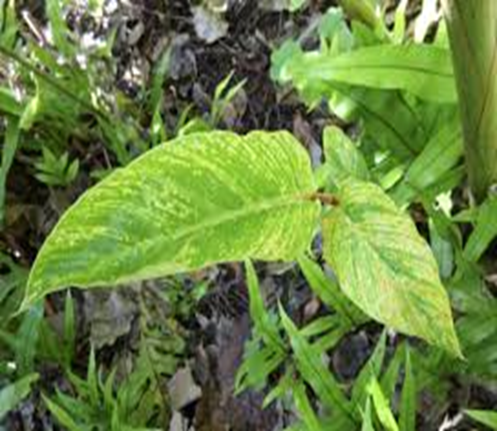
1. GINGER CHLOROTIC FLECK VIRUS
TREATMENT :
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |