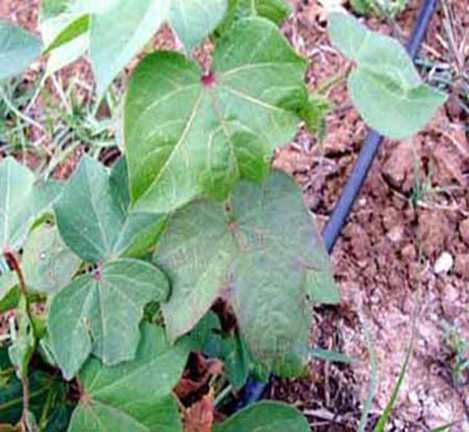
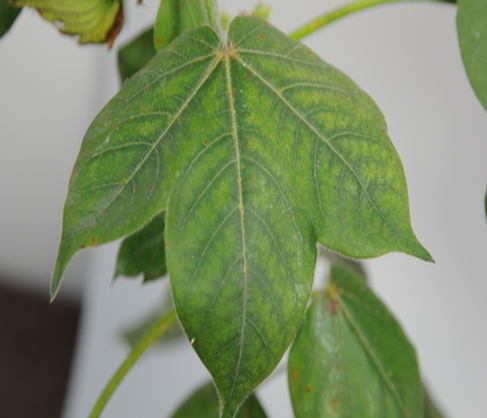
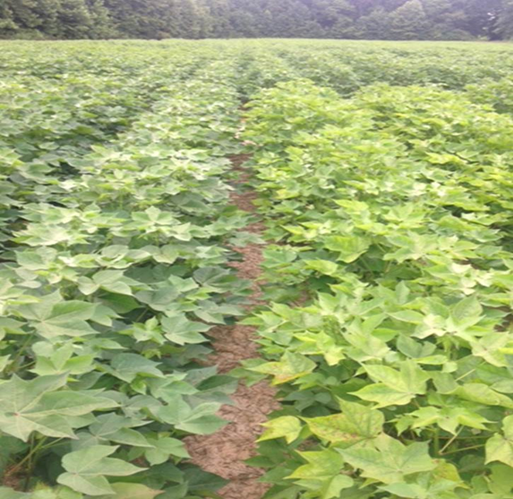
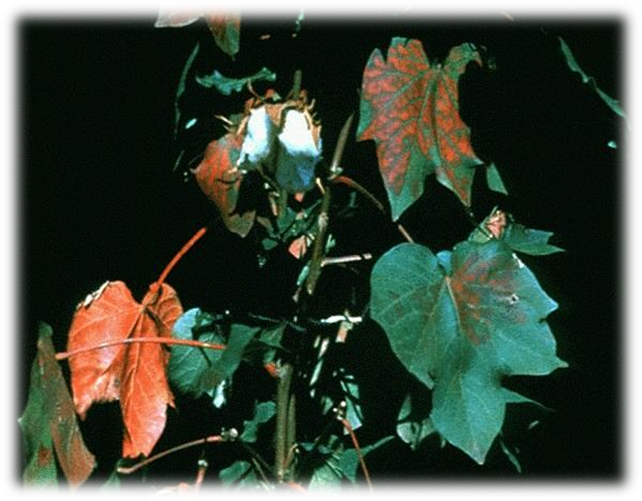
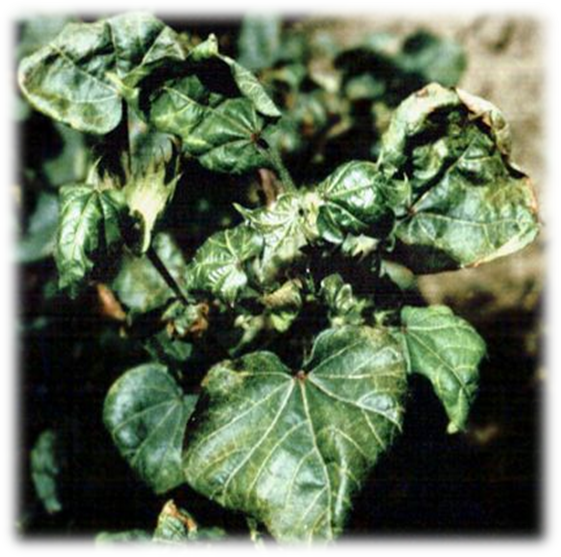
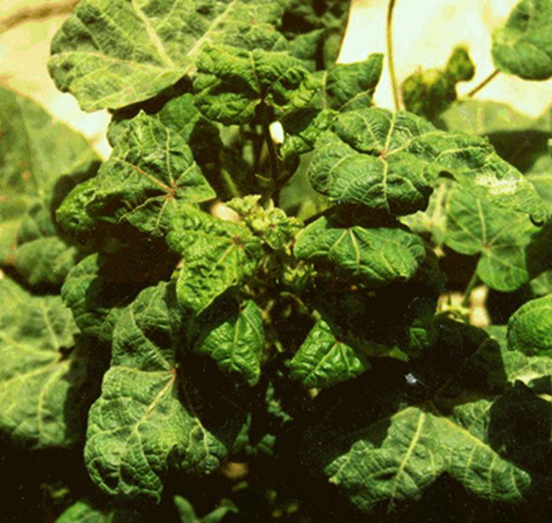
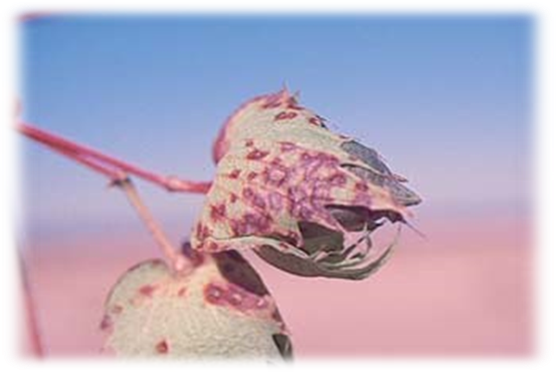
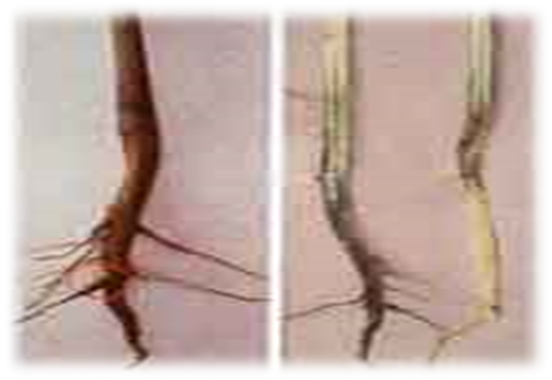
- Cotton is a member of the Malvaceae family, and its scientific name is Gossypium.
- Cotton is a plant that demands a long period of frost-free weather, as well as a lot of heat and light.
- It prefers a hot, humid climate.
- We will not have numerous rainfalls during the maturing (summer) and harvesting days in order to successfully cultivate cotton plants (during autumn).
•Soil- Alluvial, clayey and red sandy loam.
•Temperature- Daily air temperature =15 degrees C (60° F) for germination.
Vegetative growth =21-27 degrees C (70-80°F).
Fruiting period=27-32 degrees C (80-90° F).
•Cultivation- The major soil types suitable for cotton cultivation are alluvial, clayey, and red sandy loam. Cotton is grown both under irrigated and rain-fed conditions.
•pH- 5.8 to 8.0.
•Rainfall- It requires at least 500 mm of mean annual rainfall with uniform distribution.
•Susceptibility- They are susceptible to pests.
- It will take 20-25 cm to produce a square.
- Cotton requires 20-25 cm of water from squaring to first blooming.
- During boll development, the remaining 10-20 cm is necessary.
- Cotton crops require a total of 50-70 cm of water.
- Cotton's growth and output are severely hampered by moisture stress at critical times.
- Moisture stress during boll development will not only limit output but also have a significant impact on fiber quality.
- In comparison to regular watering, when the number of irrigations is reduced, the root development is deeper, allowing moisture to be absorbed from deeper levels.
- During flowering, the crop is vulnerable to moisture stress.
- Cotton cultivation necessitates a long period of frost-free weather and lots of sunlight.
- Frost is a cotton plant's worst enemy, and growth is slowed when temperatures drop below 20 degrees Celsius.
- It can be grown with irrigation in locations with lower rainfall (50-100 cm).
- Punjab, Haryana, Gujarat, and Rajasthan account for over 80% of all cotton-irrigated land.
- High rainfall early in the season and bright, dry weather during the ripening period are both beneficial to a good crop.
- It takes 6-8 months for it to mature.
- Picking is a key period that necessitates a large amount of inexpensive and efficient labor, and it lasts for six months.
- At the time of boll opening and plucking, wet weather and heavy rainfall are damaging, and the plant becomes subject to pests and disease.
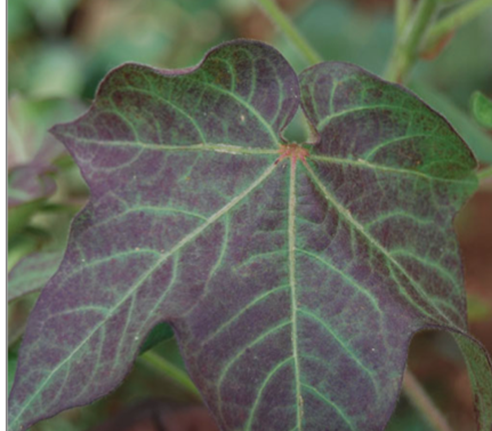
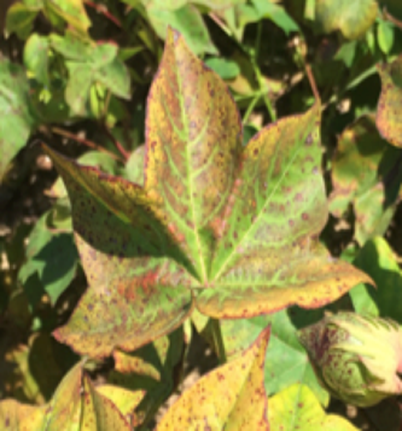
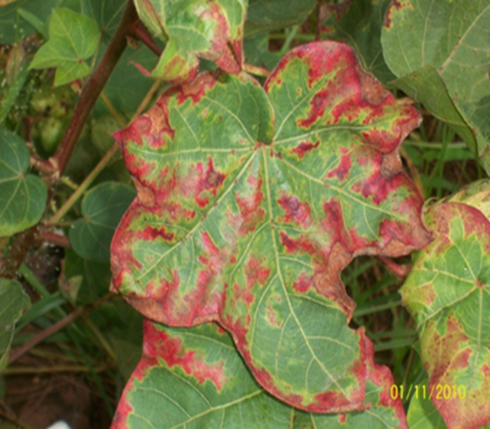
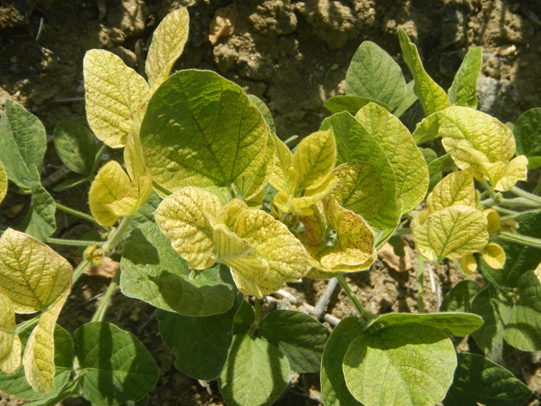
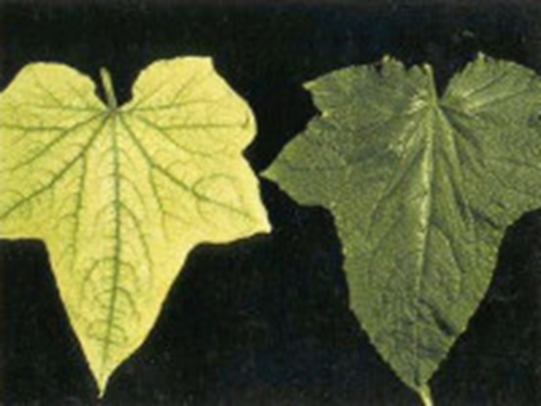
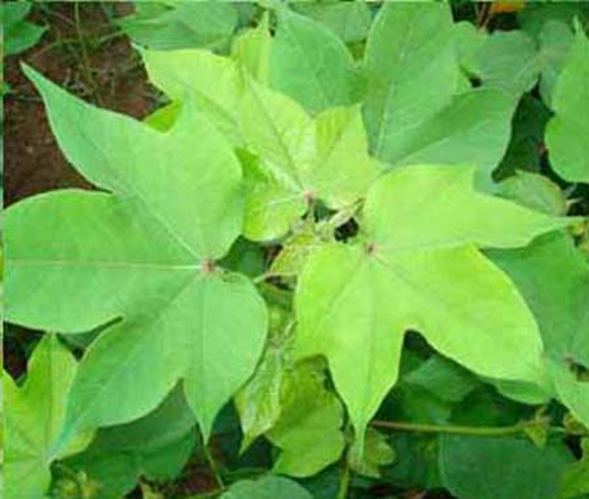
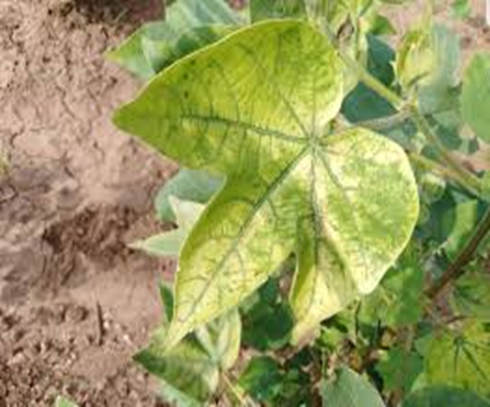
1. DEFICIENCY OF NITROGEN
TREATMENT :
|
Use Manganese EDTA 0.5 gm per litre of water |
.png) |
|
Use Grow 2 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
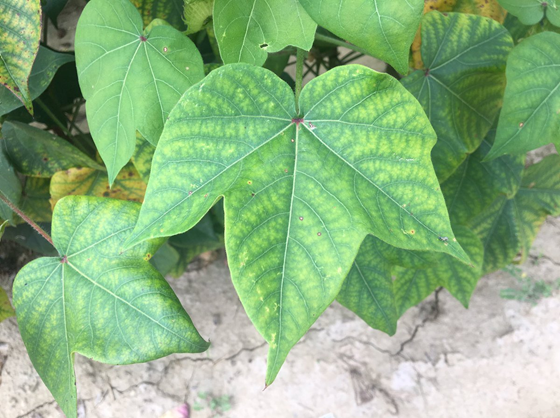
TREATMENT :
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use Grow 2 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
TREATMENT :
|
Use Ferric EDTA 0.5-01 gm per litre of water |
.png) |
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
TREATMENT :
|
Use Zinc EDTA 0.5-01 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A.FUNGAL DISEASES: (i) CONTACT BASED
1. ANTHRACNOSE (Glomerulla gossypii)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (i) CONTACT BASED
2. AREOLATE MILDEW (Ramularia gossypii)



TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A.FUNGAL DISEASES: (i) CONTACT BASED
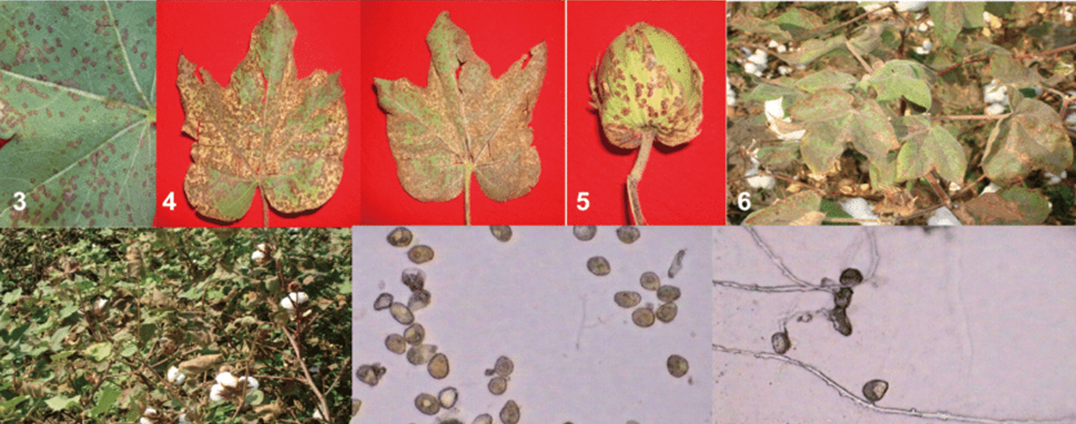
3.FUSARIUM WILT (Fusarium oxysporum)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A.FUNGAL DISEASES: (i) CONTACT BASED
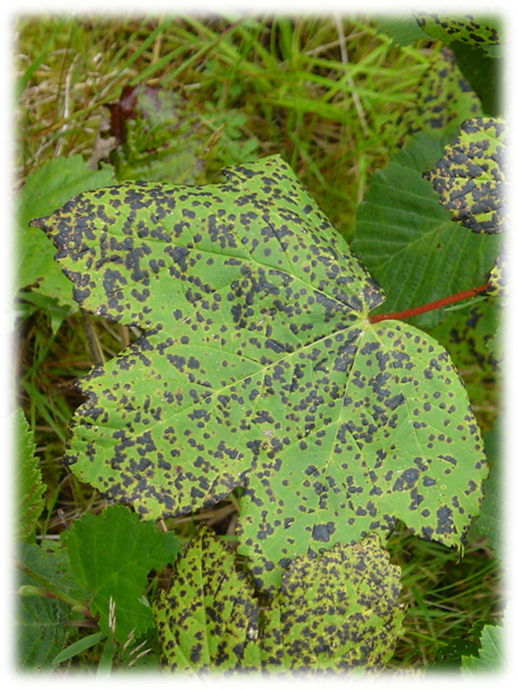
4. LEAF SPOT (Alternaria macrospora)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A.FUNGAL DISEASES: (i) CONTACT BASED
5. POWDERY MILDEW (Leveillula taurica)



TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (i) CONTACT BASED
6. COTTON RUST (Puccinia schedonnardii)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (i) CONTACT BASED
7. VERTICILLIUM WILT (Verticillium dahlia)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
8. GREY MOLD (Botrytis cinerea)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A.FUNGAL DISEASES: (ii) SYSTEMIC BASED
1. BLACK ROOT ROT (Thielaviopsis basicola)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (ii) SYSTEMIC BASED
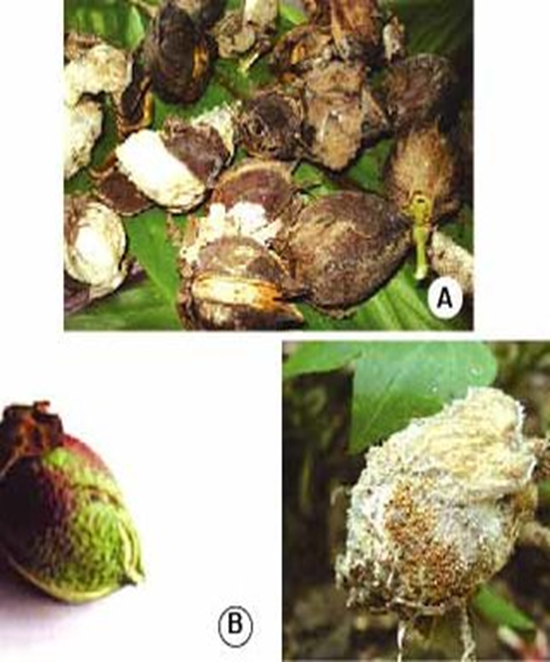
2. BOLL ROT (Colletotrichum gossypii)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (ii) SYSTEMIC BASED
3. CHARCOAL ROT (Macrophomina phaseolina)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (ii) SYSTEMIC BASED
4. STEM CANKER (Phoma exigua)
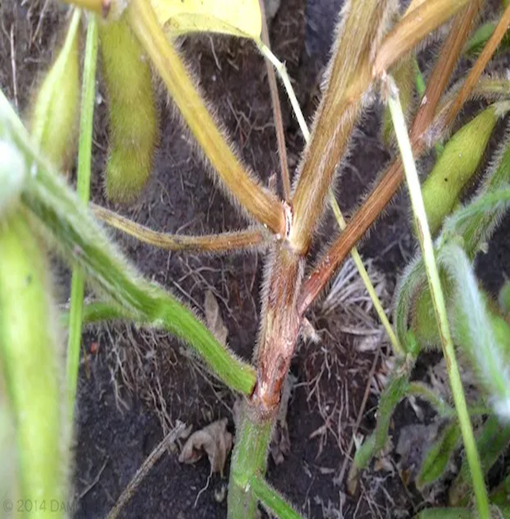
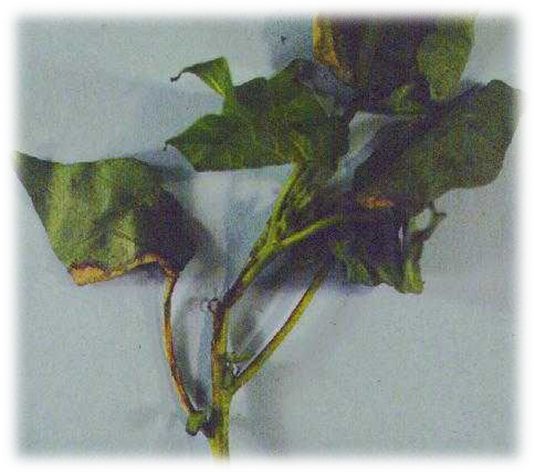
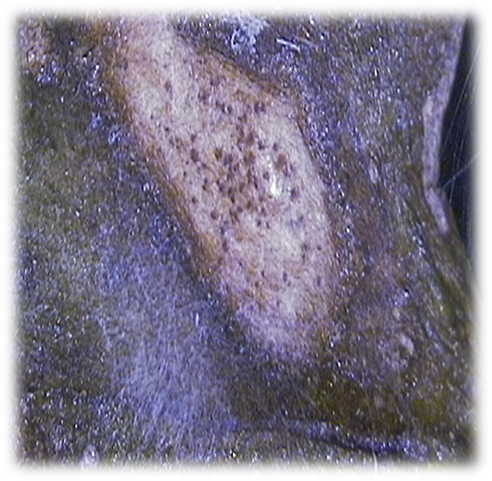


TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (ii) SYSTEMIC BASED
5. DAMPING OFF (Macrophomina phaseoli)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
B. VIRUS ATTACK
1. ANTHOCYANOSIS
TREATMENT :
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
B. VIRUS ATTACK
2. BLUE DISEASE (Phytoplasma)
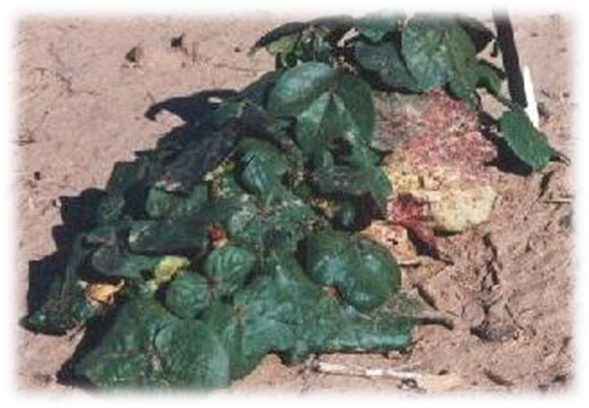
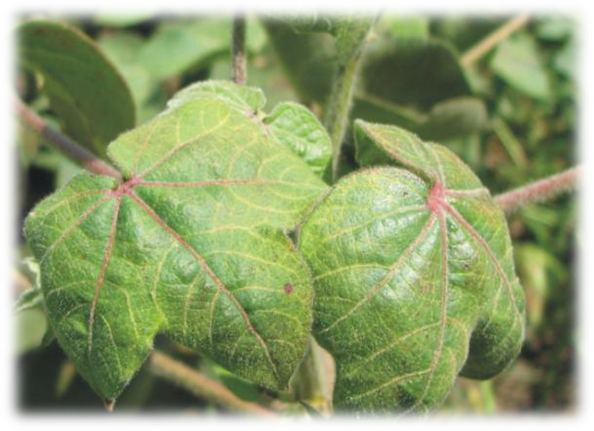



TREATMENT :
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
B. VIRUS ATTACK
3. COTTON LEAF CURL VIRUS



TREATMENT :
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
B. VIRUS ATTACK
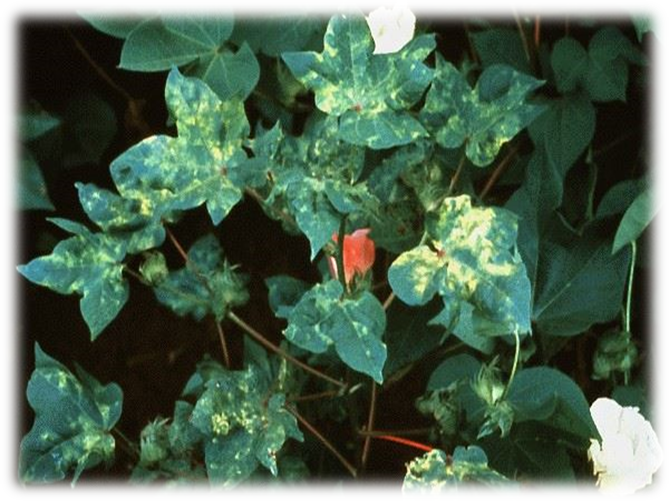
4. COTTON MOSAIC VIRUS
TREATMENT :
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
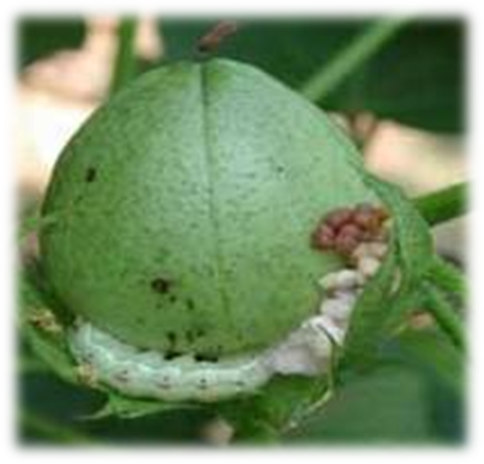
C. PEST:(i) CHEWING PESTS
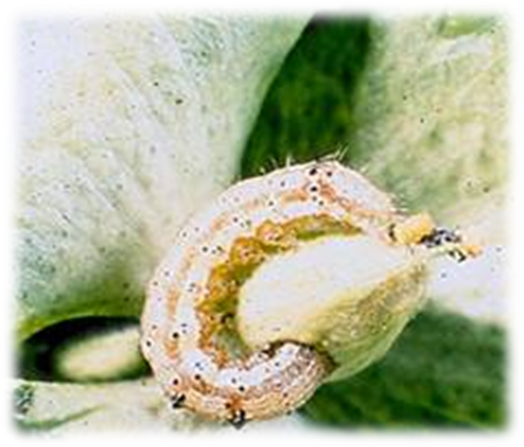
1. FRUIT BORER (Helicoverpa armigera)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PEST:(i) CHEWING PESTS
2. Pink bollworm (Pectinophora gossypiella
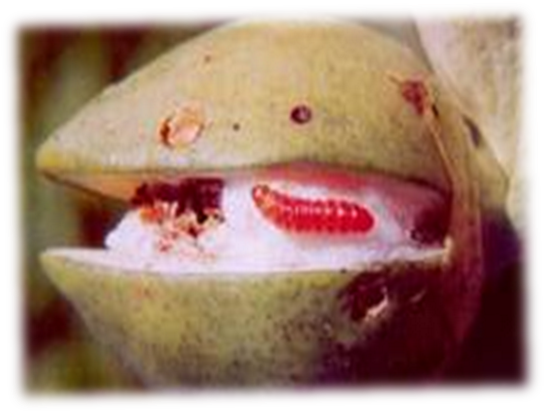
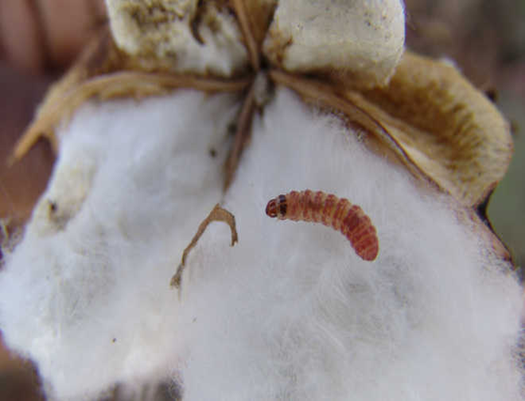
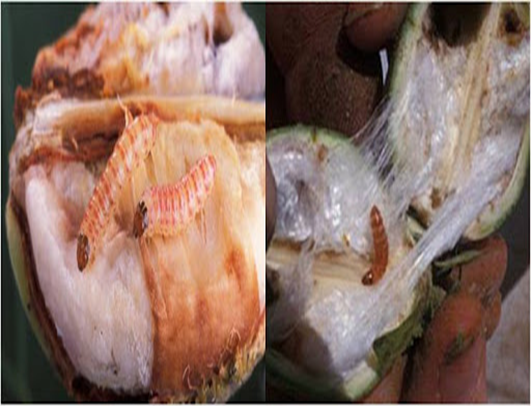



TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PEST:(i) CHEWING PESTS
3. SPOTTED BOLLWORMS (Earias vittella)
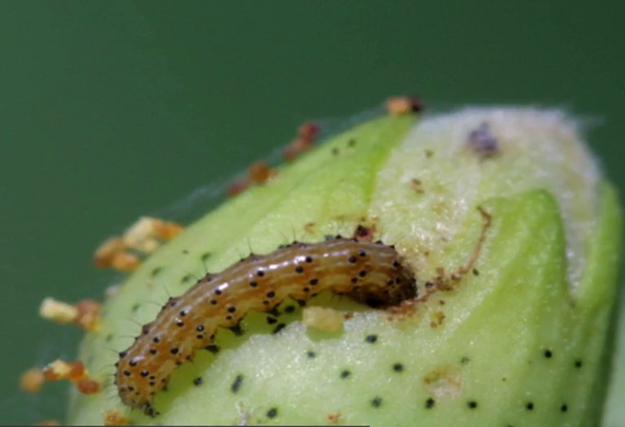
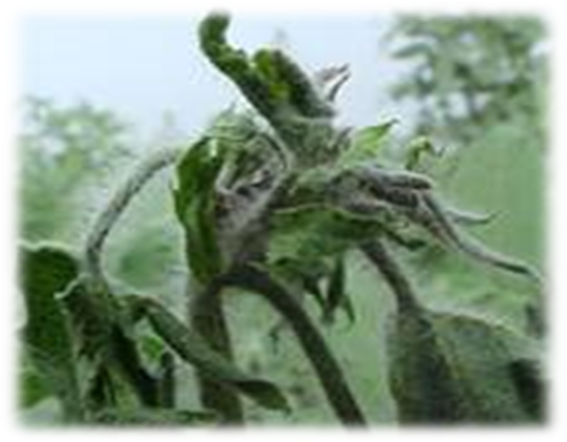
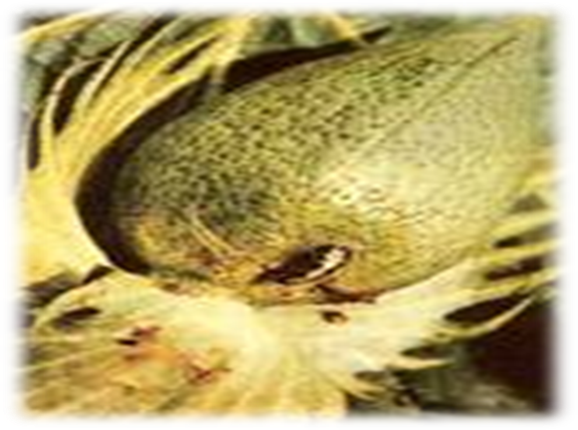



TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C.PEST:(i) CHEWING PESTS
4. Stem Weevil (Pempheres affinis)



TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PEST:(i) CHEWING PESTS
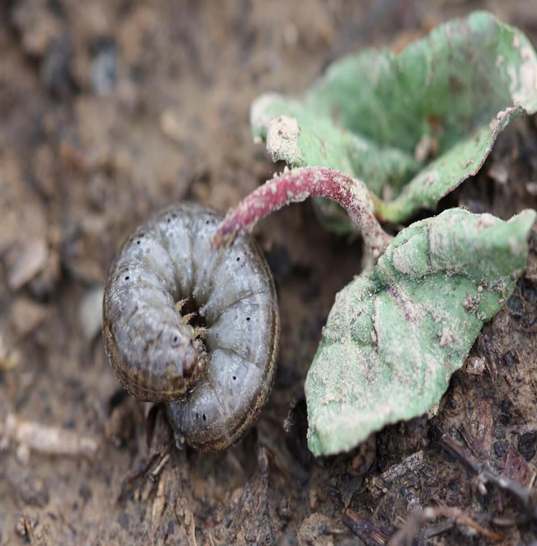
5. STEM BORER (Sphennoptera gossypii)
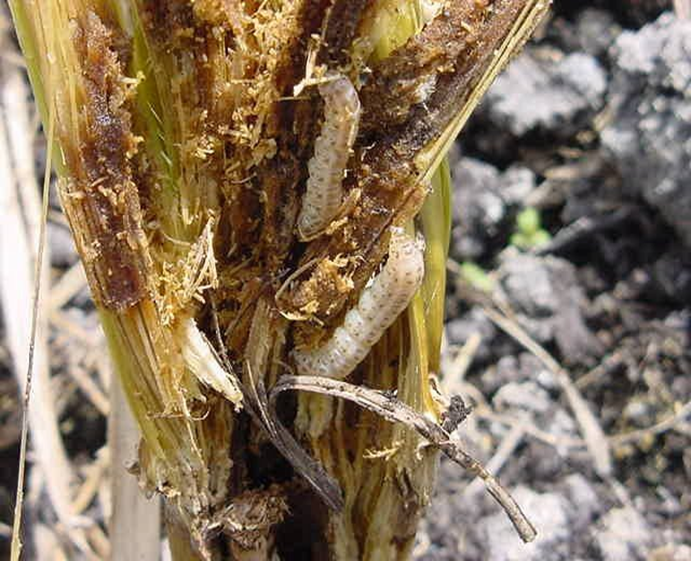
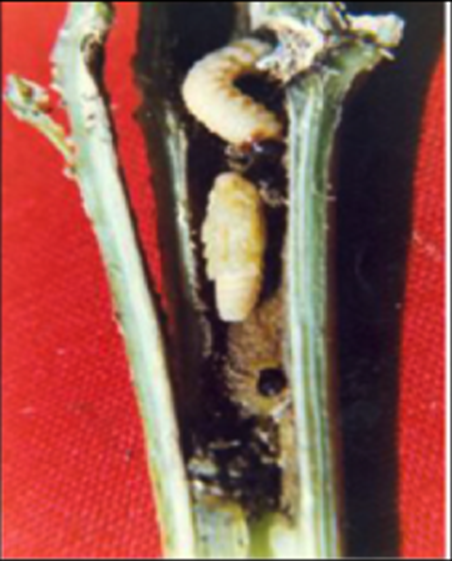

TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PEST:(i) CHEWING PESTS
6. LEAF ROLLER (Sylepta derogate)
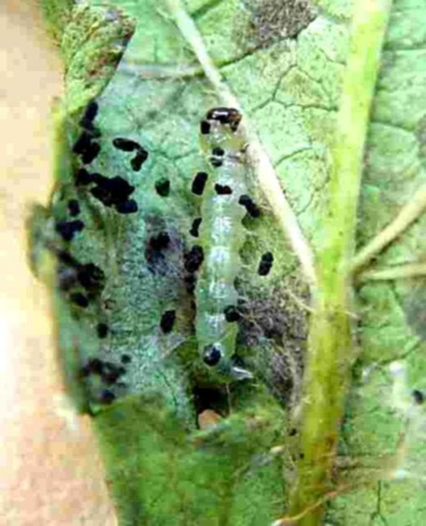
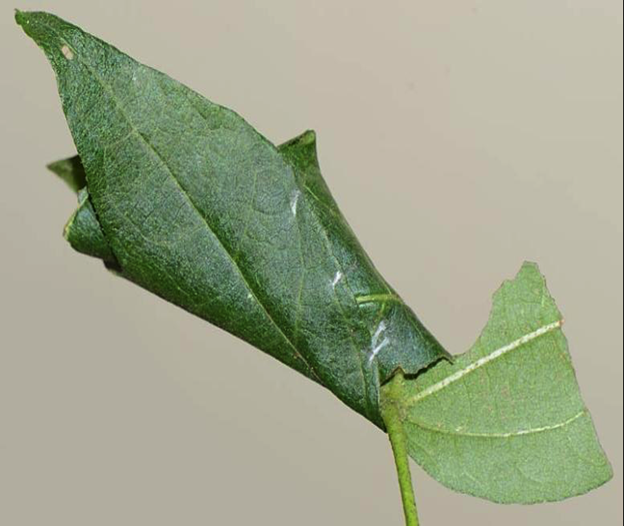



TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PEST:(i) CHEWING PESTS
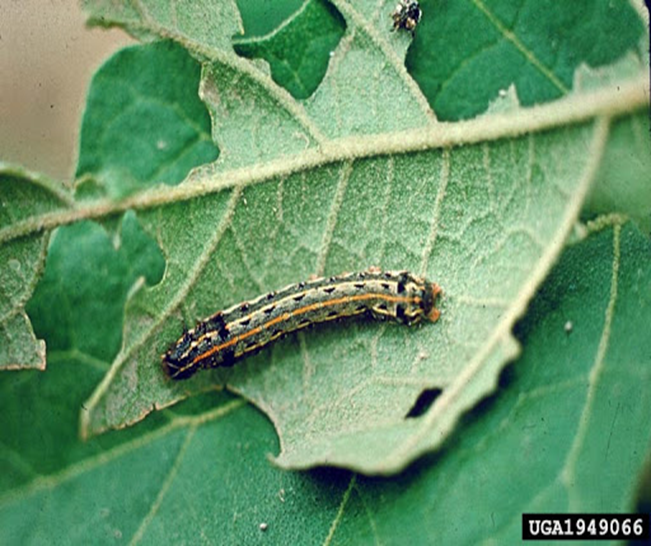
7. Tobacco Cutworm (Spodoptera litura)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PEST:(ii) SUCKING PESTS
1. WHITEFLY (Aleyrodidae)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PEST:(ii) SUCKING PESTS
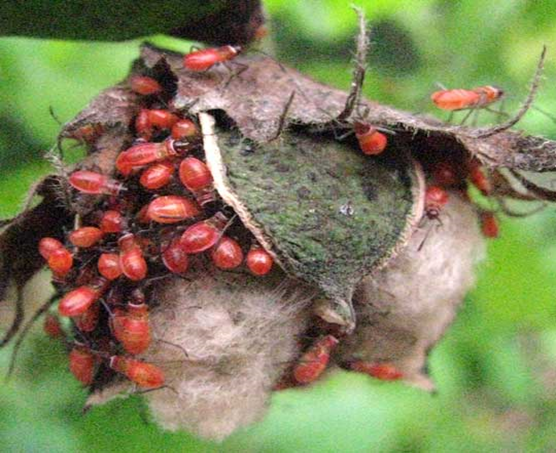
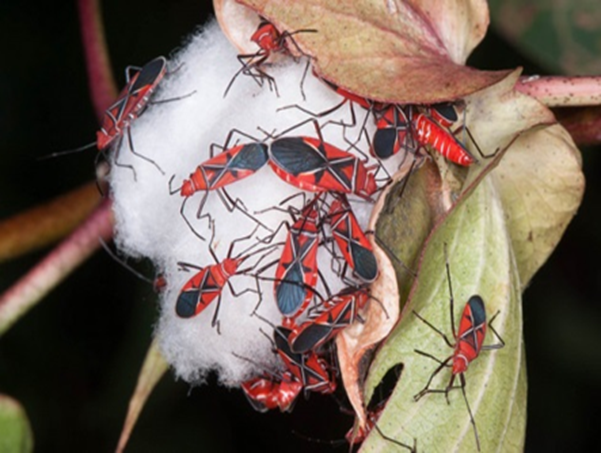
2. RED COTTON BUG (Dysdercus cingulatusi)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PEST:(ii) SUCKING PESTS
4. MEALYBUG (Pseudococcidae)



TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PEST:(ii) SUCKING PESTS
5. COTTON APHID (Aphidoidea)



TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PEST:(ii) SUCKING PESTS
6. THRIP (Thysanoptera)
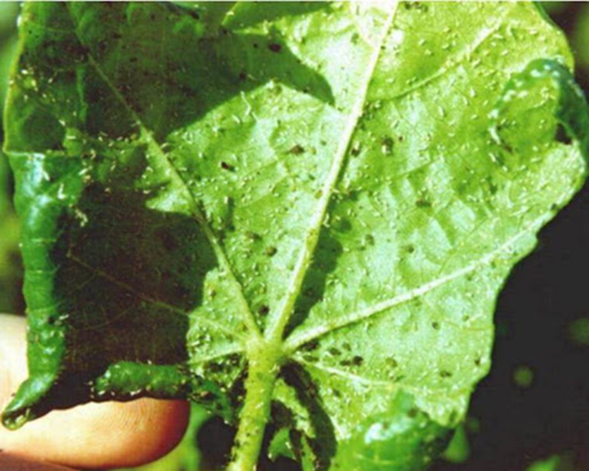
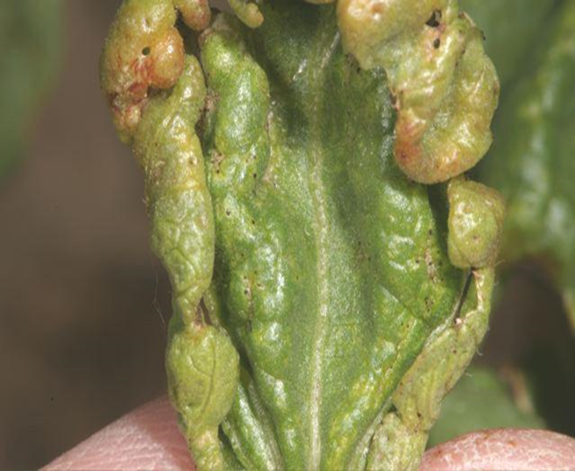



TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |