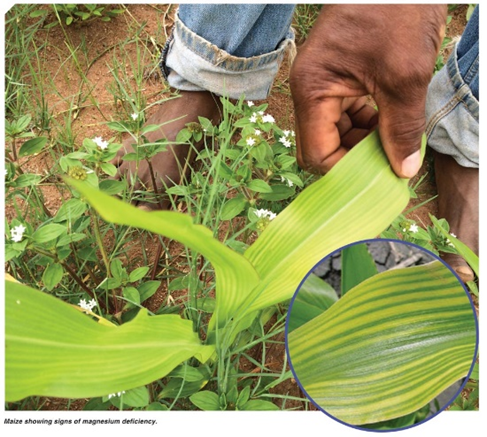
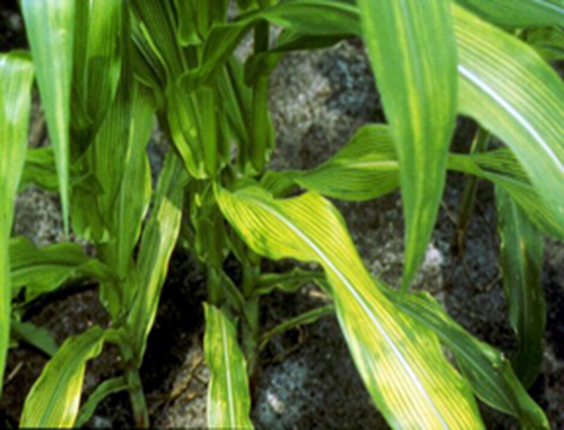
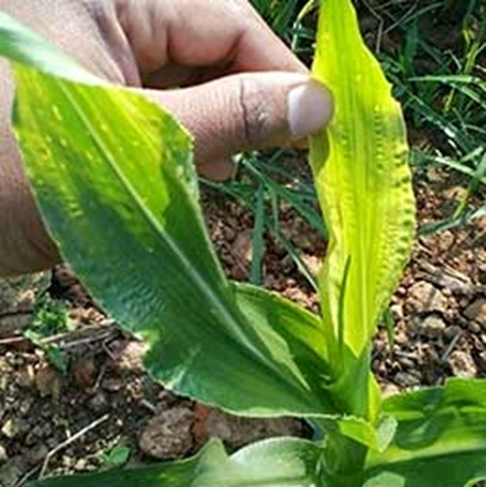
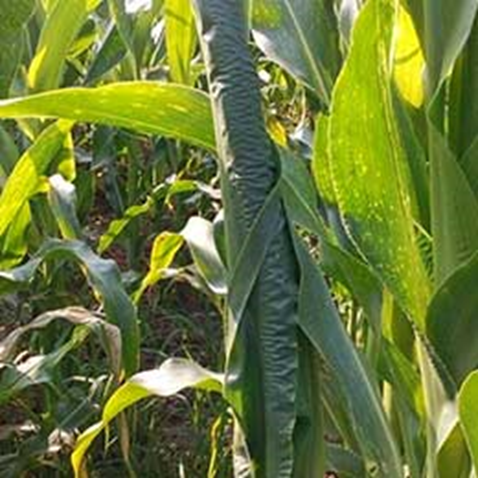
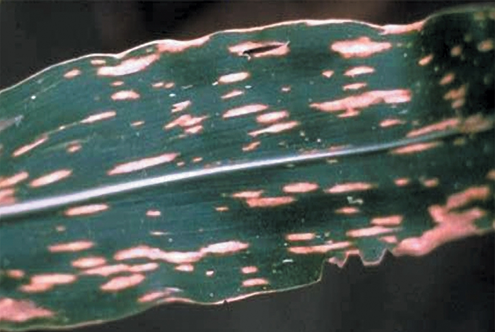
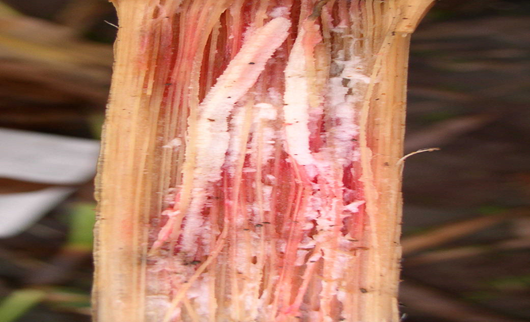
- Zea mays are the scientific name for maize, which belongs to the Poaceae family.
- It is grown throughout the kharif season and cultivated during the rabi season.
- Maize is high in starch, fiber, protein, fat, and other nutrients.
- Soil- Loamy soil to Clay soil, deep and well-drained soils.
- pH- 5.5 to 6.5.
- Temperature- 18°C and 27°C during the day.
14°C during the night.
32°C Critical temperature.
- Rainfall- Annual rainfall between 60 cm to 110 cm.
- Cultivation- Shifting Cultivation
- Susceptibility- Susceptible to frost temperature(0º)
- Maize is planted in rows that are 60-75 cm apart, with plants spaced 20 to 25 cm apart.
- To get the best output, you'll need a population of 60-75 thousand plants per hectare at harvest.
- Drilling or dropping the seed behind the plow is the most common methods for sowing in rows.
- Shifting Cultivation- Maize cultivation is best suited to plain areas.
- Dibbling or drilling should be used to sow maize seed. It varies based on the seeding purpose, maize variety, and farm conditions.
- Seed should not be sown deeper than 5-6 cm in the soil.
1. DEFICIENCY OF NITROGEN
TREATMENT :
|
Use Manganese EDTA 0.5 gm per litre of water |
.png) |
|
Use Grow 2 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5ml per litre of water |
 |
TREATMENT :
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use Grow 2 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
TREATMENT :
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use Grow 2 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
TREATMENT :
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use Calcium EDTA 0.5g per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
TREATMENT :
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use BLOOM 2 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5ml per litre of water |
 |
TREATMENT :
|
Use Zinc EDTA 0.5-01 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5ml per litre of water |
 |
1. FUNGAL DISEASE: CONTACT-BASED FUNGAL DISEASE
1. ANTHRACANOSE(Colletotrichum graminicola)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
1. FUNGAL DISEASE: CONTACT-BASED FUNGAL DISEASE
2. LEAF CURLING (Taphrina deformans)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
1. FUNGAL DISEASE: CONTACT-BASED FUNGAL DISEASE
3. POWDERY MILDEW (Peronosclerospora sorghi)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
1. FUNGAL DISEASE: CONTACT-BASED FUNGAL DISEASE
4. DOWNY MILDEW (Peronosclerospora sorghi)



TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
1. FUNGAL DISEASE: CONTACT-BASED FUNGAL DISEASE
5. SHEATH BLIGHT (Rhizoctonia solani f. sp. sasakii)
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (ii) SYSTEMIC BASED
1. HEAD SMUT (Sphacelotheca reiliana)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (ii) SYSTEMIC BASED
2.ANTHRACANOSE STALK ROT(Colletotrichugraminicola)



TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (ii) SYSTEMIC BASED
3.CHARCOAL ROT (Macrophomina phaseolina)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (ii) SYSTEMIC BASED
4. FUSARIUM STALK ROT (F.verticillioides)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
A. FUNGAL DISEASES: (ii) SYSTEMIC BASED
5.GIBBERELLA STALK ROT(Gib- berella zeae)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
B.VIRUS ATTACK
1. MAIZE CHLOROTIC DWARF VIRUS
TREATMENT :
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
B.VIRUS ATTACK
2. MAIZE LETHAL NECROSIS(MLN)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PEST:(i) CHEWING PESTS
1. SCALE(Coccoidea)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PEST:(i) CHEWING PESTS
2.GRASSHOPPER (Caelifera)



TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5ml per litre of water |
 |
C.PEST:(i) CHEWING PESTS
3. CATERPILLAR (Lepidopteran)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PEST:(i) CHEWING PESTS
4.CUTWORM (Dark sword-grass)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PEST:(i) CHEWING PESTS
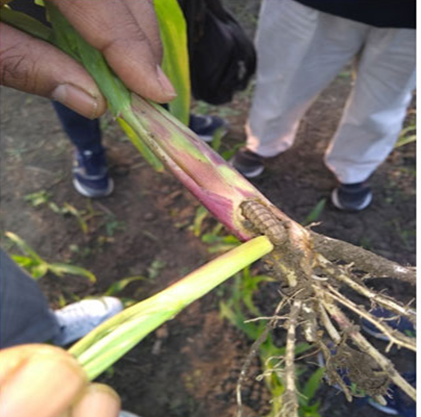
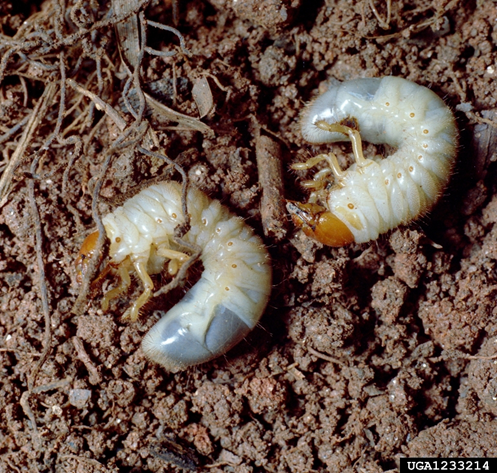
5. WHITE GRUBS
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5ml per litre of water |
 |
C.PEST:(i) CHEWING PESTS
6. ARMYWORM (Spodoptera frugiperda)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5ml per litre of water |
 |
C. PEST:(ii) SUCKING PESTS
1. APHIDS (Myzus persicae)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C.PEST:(ii) SUCKING PESTS
2. WHITEFLY (Bemisia tabaci)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C.PEST:(ii) SUCKING PESTS
3.THRIP (Thysanoptera)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
C.PEST:(ii) SUCKING PESTS
4. MEALYBUG (Pseudococcidae)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |