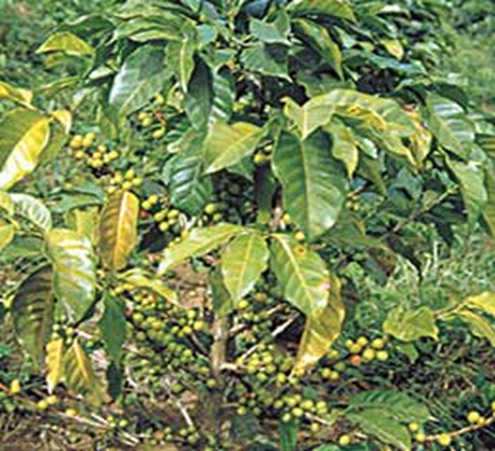
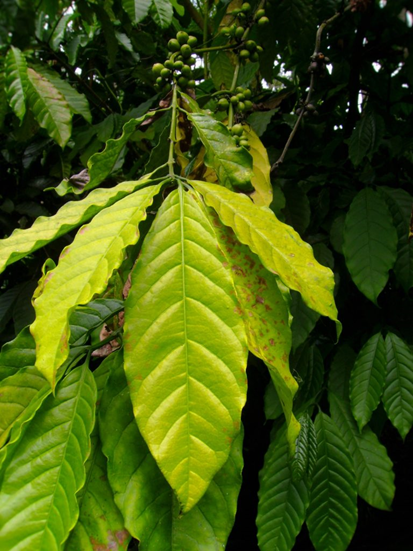
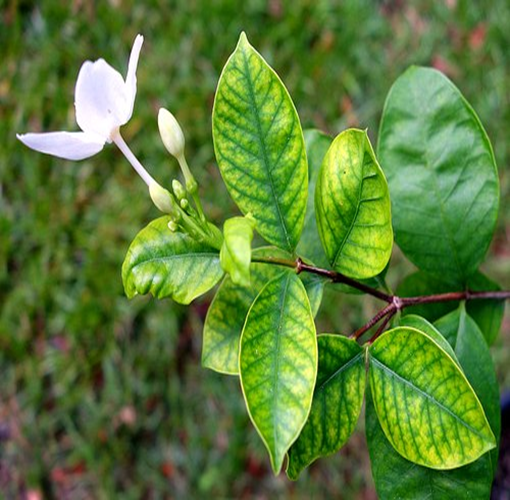
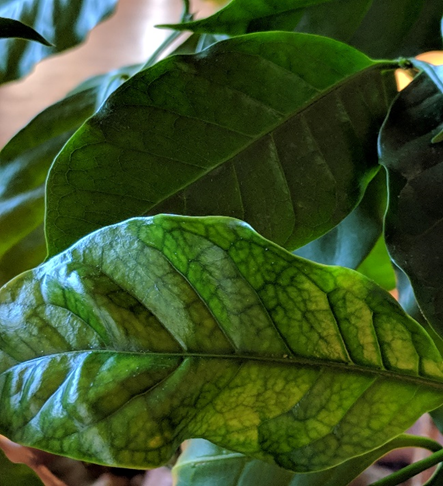
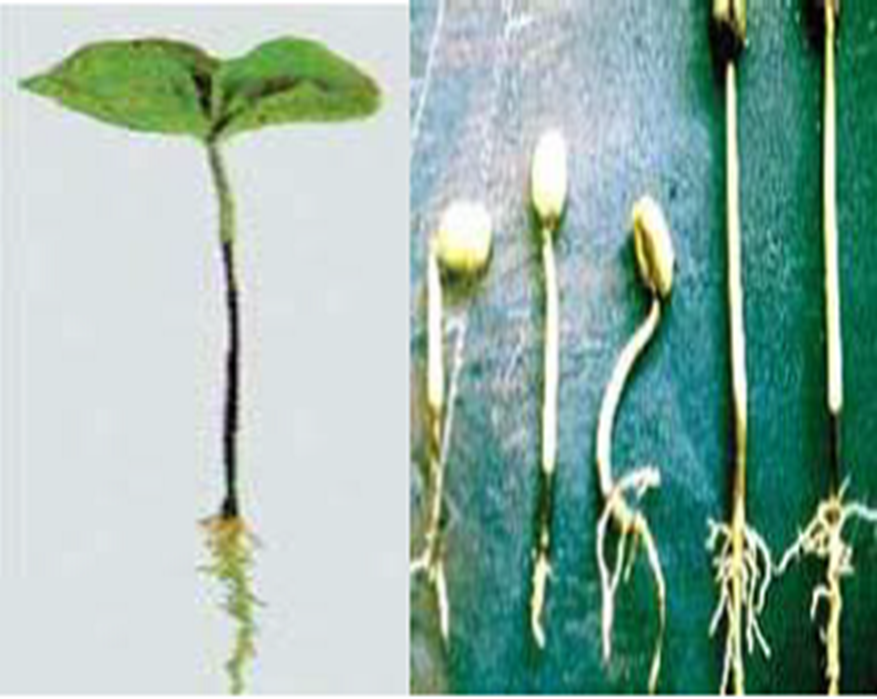
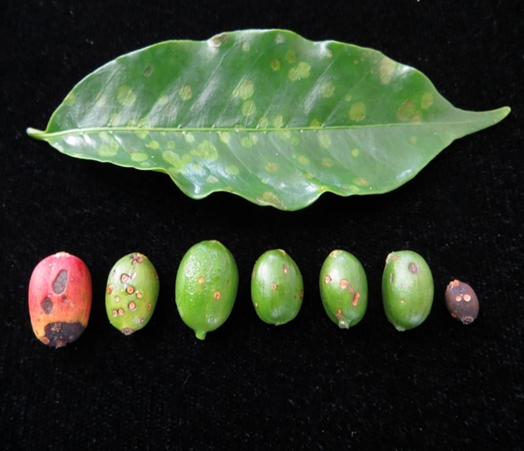
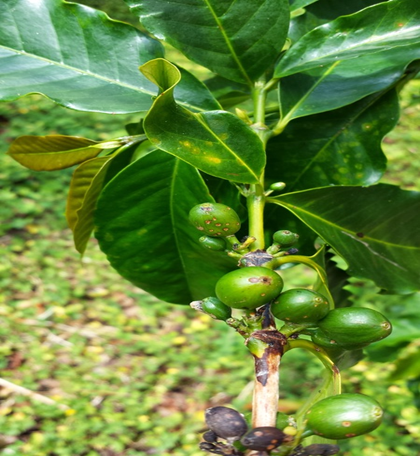
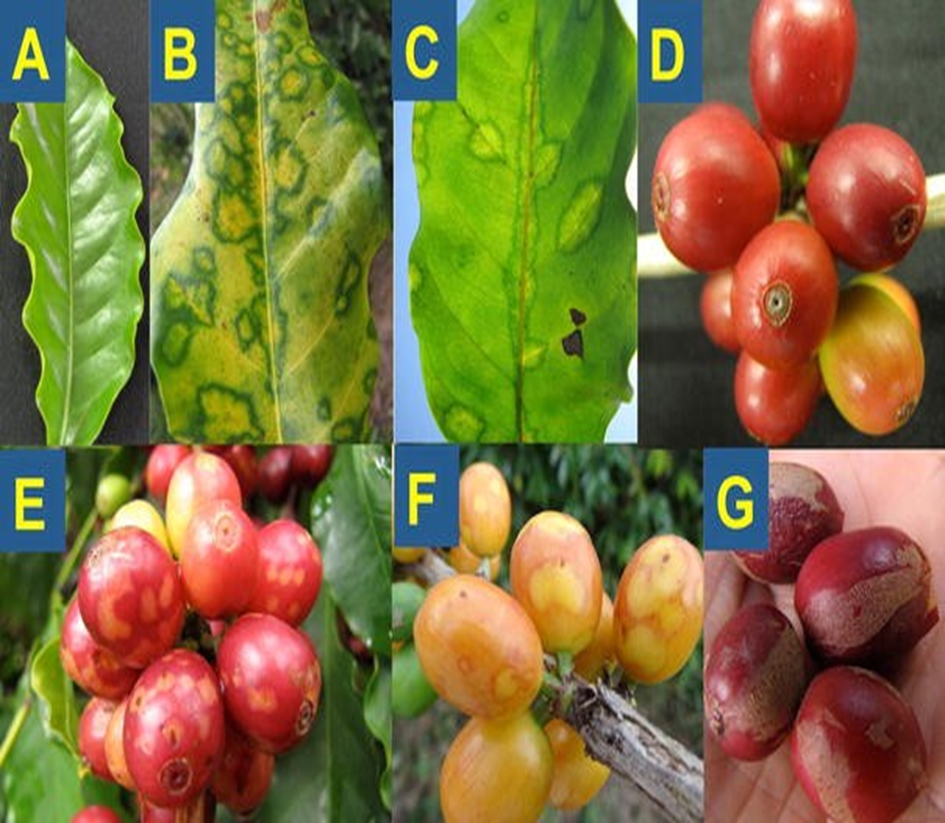
- Coffee is traditionally farmed in Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu in India.
- Coffee production is quickly rising in unconventional areas of Andhra Pradesh and Odisha, as well as in the North-Eastern states.
- Coffee is primarily an export commodity, with 65% to 70% of the crop exported and the remainder eaten domestically.
- Soil- deep sandy loam.
- pH- 4.9–5.6.
- Temperature- 18°C–21°C.
- Rainfall- 100-200 cm annually.
Irrigation depends on the weather, the soils water holding capacity and the development stage of the crop.
For optimal results, you should irrigate your coffee every 1 to 3 days.
It is generally grown as a rainfed crop.
But irrigation with sprinklers during March - April increases blossoming and results in higher yields.
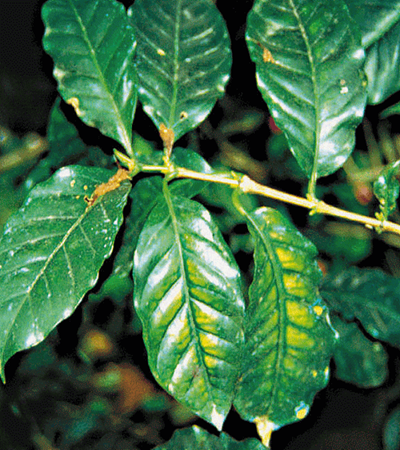
1. DEFICIENCY OF NITROGEN
TREATMENT :
|
Use Ferric EDTA 0.5-01 gm per litre of water |
.png) |
|
Use NITROKING 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5ml per litre of water |
 |
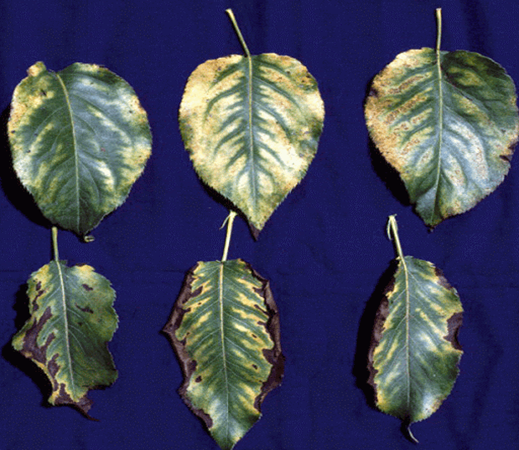
TREATMENT :
|
Use Calcium EDTA 0.5 per litre of water |
 |
|
Use BLOOM 2 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SPALL90 0.5ml per litre of water |
 |
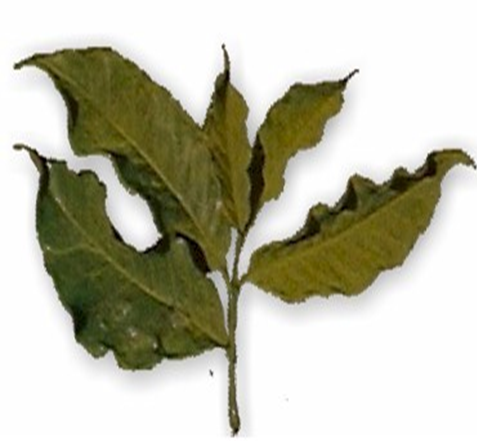
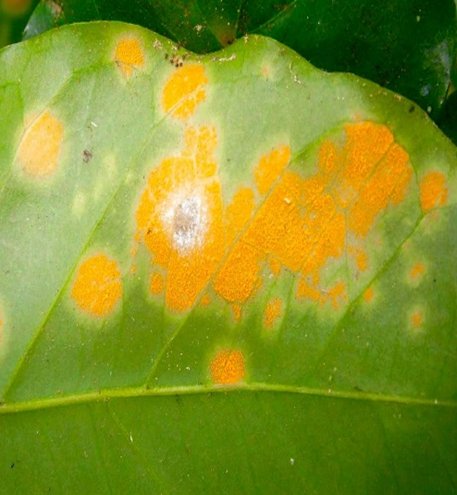
1. FUNGAL DISEASE: CONTACT-BASED FUNGAL DISEASE
1. ANTHRACNOSE (Colletotrichum kahawae)
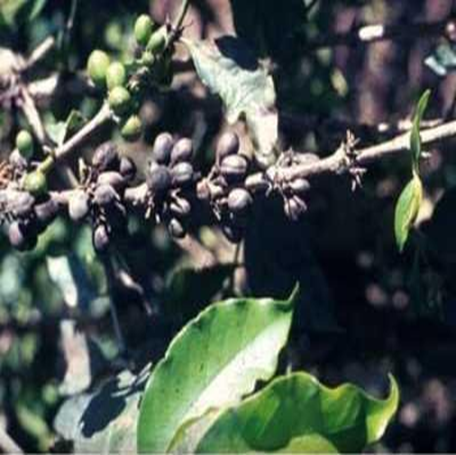
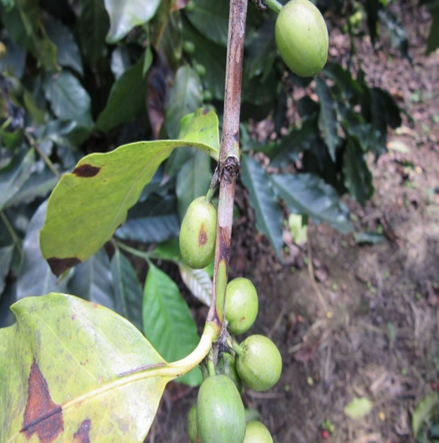
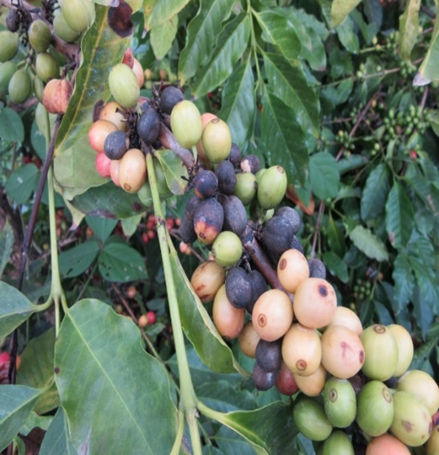



TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
1. FUNGAL DISEASE: CONTACT-BASED FUNGAL DISEASE
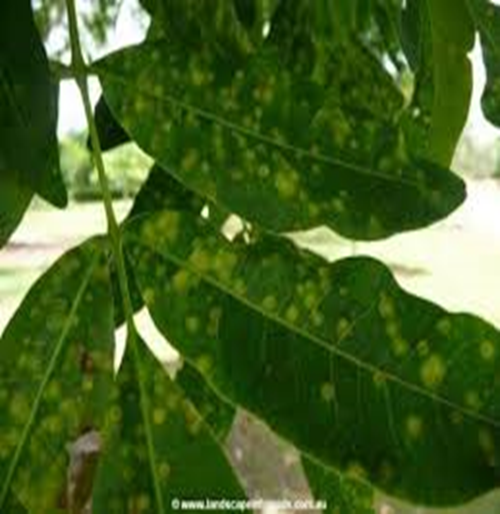
2.BROWN EYE SPOT (Cercospora coffeicola)
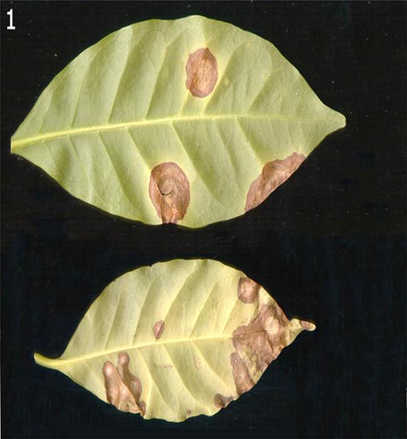



TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
1. FUNGAL DISEASE: CONTACT-BASED FUNGAL DISEASE
TREATMENT :
|
Use PPFC 2-3 gm per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
2. FUNGAL DISEASE: SYSTEMIC-BASED FUNGAL DISEASE
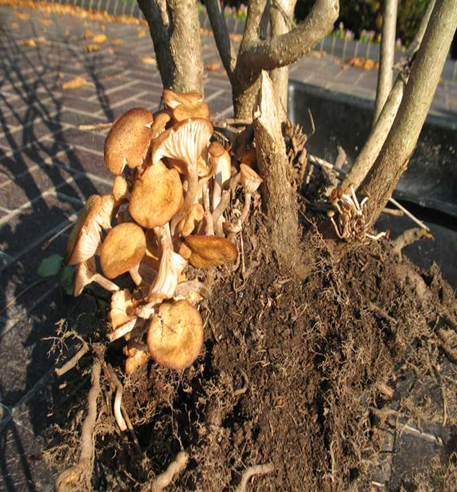
1. ARMILLARIA ROOT ROT (Armillaria mellea)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5ml per litre of water |
 |
2. FUNGAL DISEASE: SYSTEMIC-BASED FUNGAL DISEASE
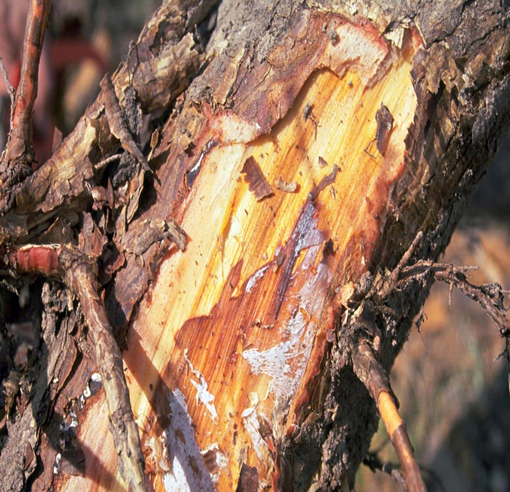
2. BLACK ROT (Corticium salmonicolor)
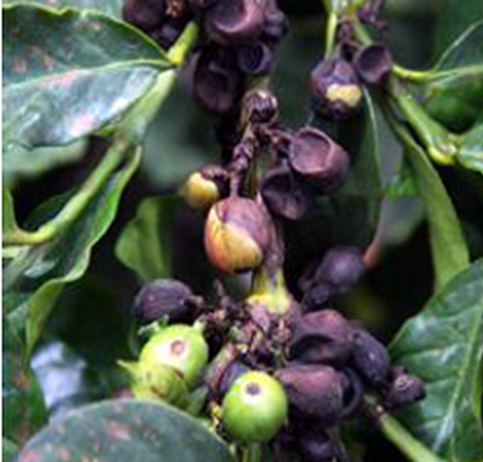
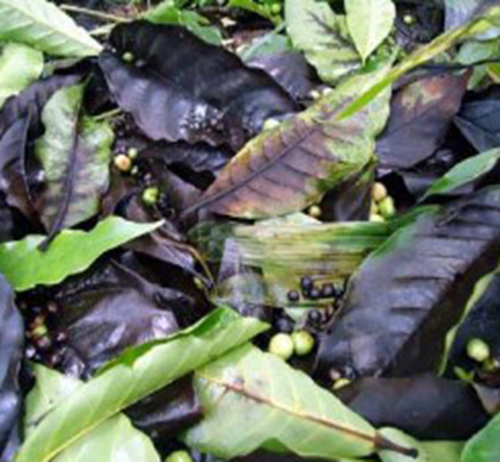
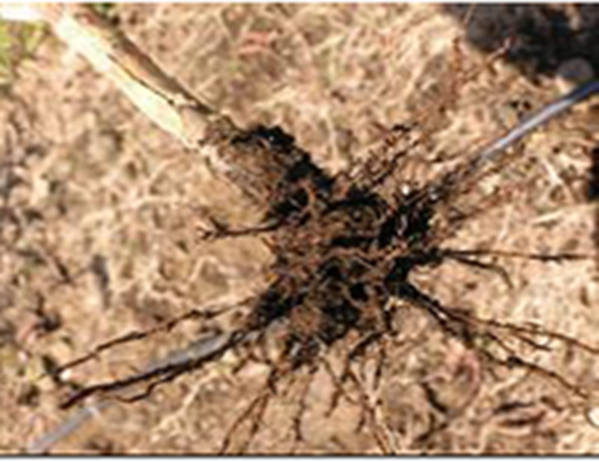



TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5ml per litre of water |
 |
2. FUNGAL DISEASE: SYSTEMIC-BASED FUNGAL DISEASE
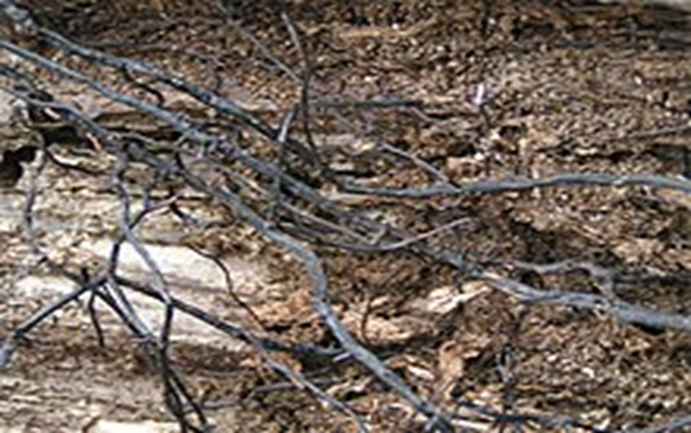
3. COLLAR ROT (Corticium salmonicolor)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Fungohit 2-3ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5ml per litre of water |
 |
B. VIRAL DISEASES:1. BLISTER SPOT
TREATMENT :
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
B. VIRAL DISEASES: 2. COFFEE RING SPOT VIRUS
TREATMENT :
|
Use Virohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use virosol 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
4. PEST : CHEWING PEST
1.WHITE STEM BORER (Xylotrechus quadripes)
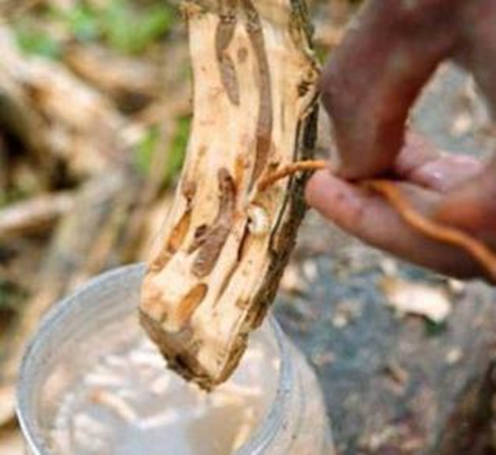
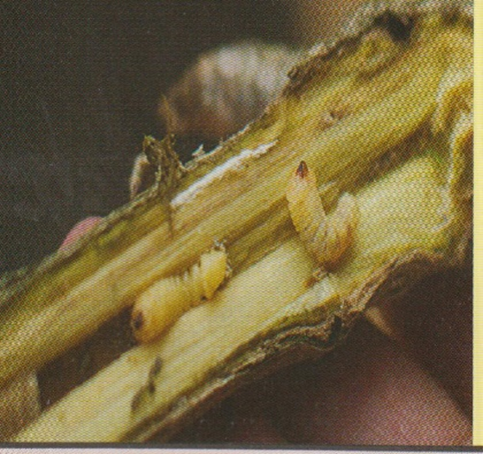



TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
4. PEST : CHEWING PEST
2.COFFEE BERRY BORER(Hypothenemus hampei)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
4. PEST : CHEWING PEST
3. SHOT HOLE BORER (Xylosandrus compactus)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
4. PEST: CHEWING PEST
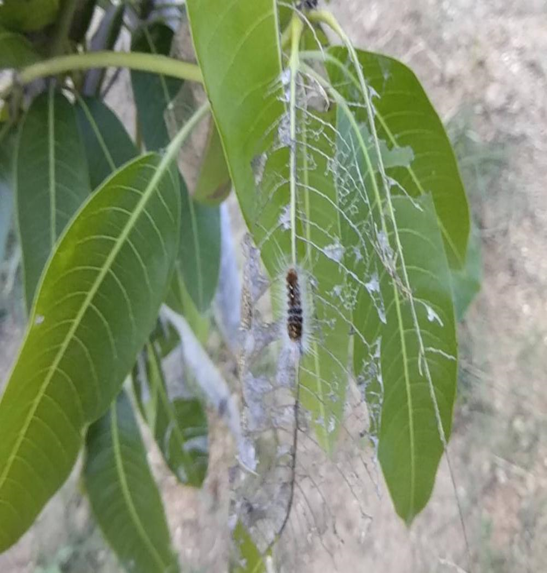
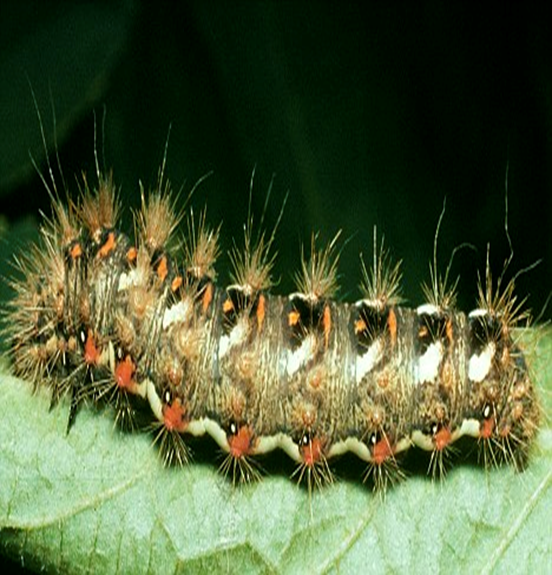
5. HAIRY CATERPILLARS (Eupterote spp.)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
4. PEST: CHEWING PEST
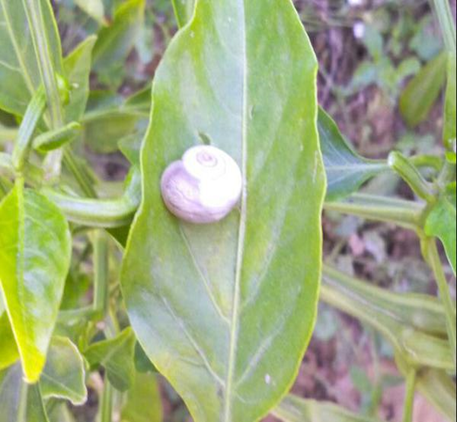
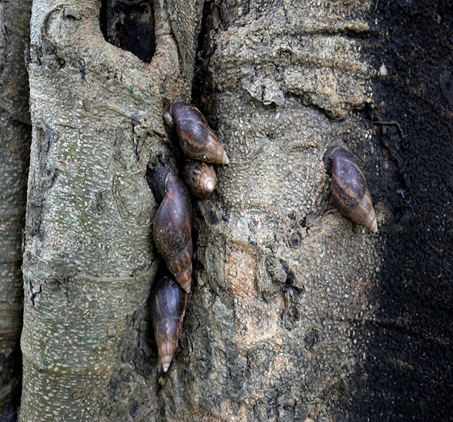
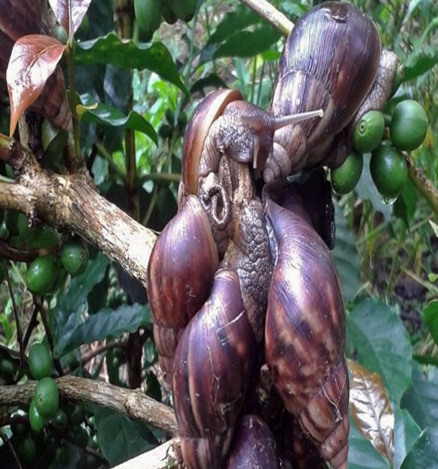
6. SNAIL (Ariophanta solata)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Pestohit 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5 ml per litre of water |
 |
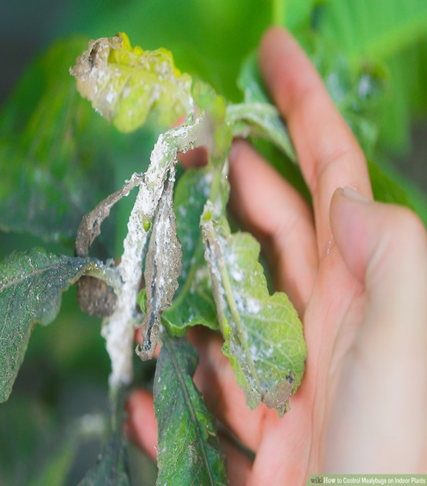
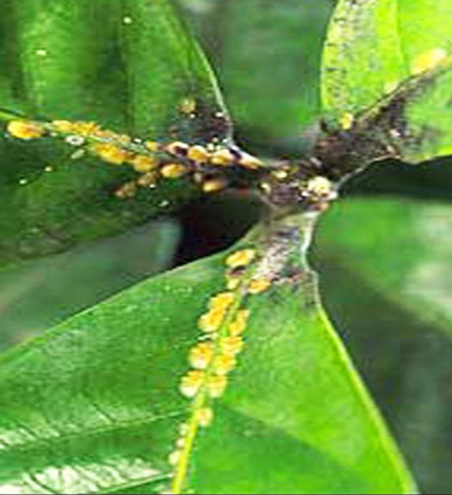
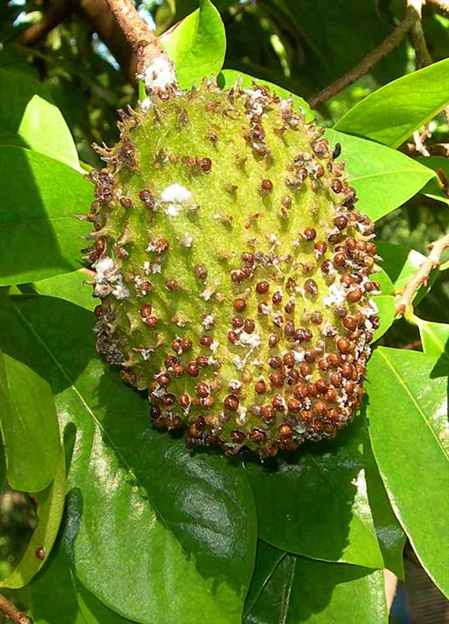
5. PEST: SUCKING PEST
1.MEALY BUGS (Planococcus spp.)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5ml per litre of water |
 |
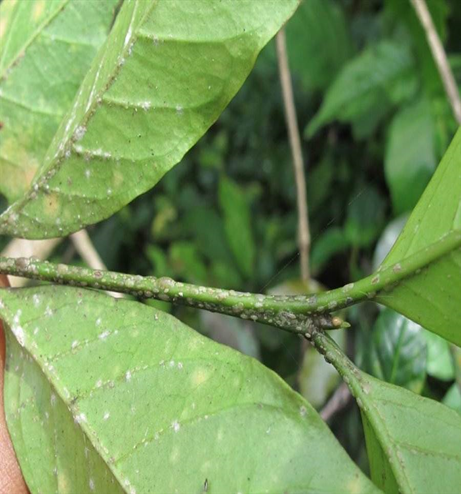
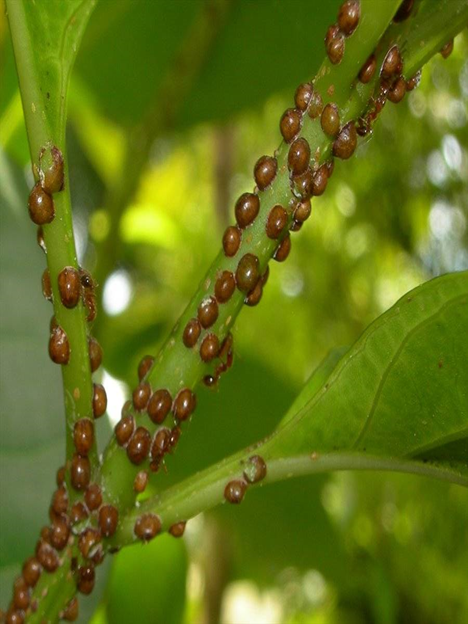
5. PEST: SUCKING PEST
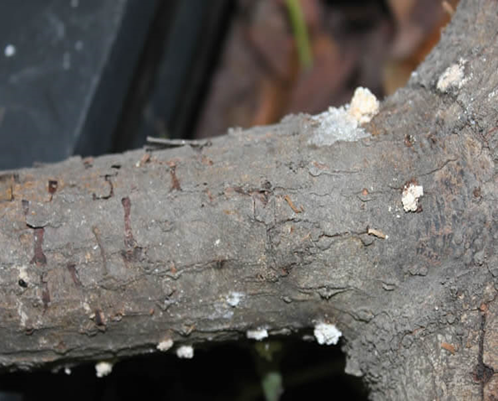
2.GREEN SCALE (Coccus viridis)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5ml per litre of water |
 |
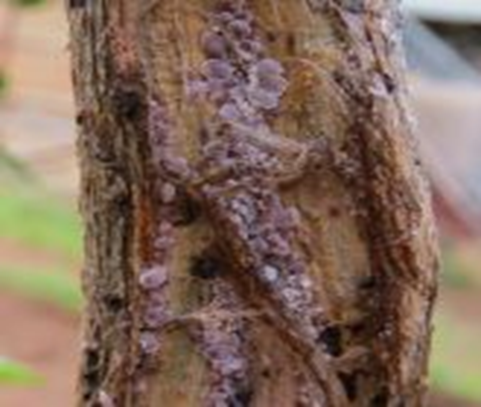
5. PEST: SUCKING PEST
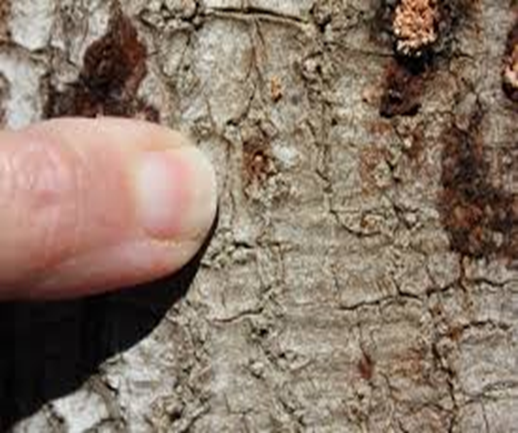
3. BROWN SCALE (Saissetia coffeae)
TREATMENT :
|
Use Orgomite 2-3 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use PPNP 1 ml per litre of water |
 |
|
Use SpAll90 0.5ml per litre of water |
 |